【ES】Best Practices: Anti-Ransomware Testing_V6.0.4
Introduction
Ransomware attacks infect systems and encrypt files and folders to prevent access to important systems and data. Next, threat actors demand ransom for a decryption key that provides access.
Many ransomware attacks succeed because the malware can neutralize backup applications, including the operating systems’ features that copy your files. However, you can still use backup to protect against ransomware.
A backup and recovery strategy, as part of an overall ransomware protection strategy, can help you protect your data and avoid paying ransom using backup solutions outside the reach of attackers. It can help you quickly and efficiently recover business-critical data and resume normal operations.
The backup and recovery can:
- Mitigate advanced ransomware threats.
- Detection based on static and dynamic behaviors, especially advanced attacks, will not be 100% accurate.
- Address early encryption on non-honeypot files.
Value for Customers
- Proactively defending against ransomware does not need to be resolved with decryption tools.
- 100% confidence that Sangfor can protect their assets.
- Improve business efficiency and compliance.
Prerequisites
- Prepare a Windows testing device and install an endpoint secure agent.
- Prepare ransomware samples and injection tools. Please refer to the attachment.
Note:
- The testing process requires running virus samples, so the testing environment and business environment must be isolated to avoid affecting customer business.
- It is recommended to complete the snapshot backup of the test computer in advance and restore it after completing the test.
Best Practices
Ransomware Honeypot
- Disable the Realtime File Protection of the group where the testing machine is located. Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Realtime Protection. In the Realtime File Protection section, clear the Enable realtime file protection checkbox, as shown below.

Note:
Disabling Realtime File Protection only tests the features of the anti-ransomware module. It prevents the test sample from being detected and processed by the Realtime File Protection module as soon as it is decompressed. After completing the test, please select the Enable realtime file protection checkbox to ensure the endpoint is protected.
- Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Anti-Ransomware. In the Ransomware Protection section, select the Enable ransomware honeypot checkbox, as shown below.

- Unzip the Ransomware Honeypot Sample _Password sangfor.zip to the testing PC, and the unzip password is sangfor.
- For this sample, .NET Framework 3.5 is required, which you can turn on in Control Panel > Uninstall a program > Turn Windows features on or off. Select the .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) checkbox, click OK, and reboot your computer if prompted.

- Change the file extension to .exe and run the sample file.
Observe the lower right corner of the testing PC. Endpoint Secure agent detects a ransomware virus and pops up an alert box. (Ensure the Mute notifications function is not enabled and that the normal files of the test computer have not been encrypted.)

Test Result
By running the ransomware virus, the Endpoint Secure agent can detect the ransomware virus and pop up an alert box, and the normal files of the test computer have not been encrypted.
Ransomware Behavior Detection for Process Injection
- Disable the Realtime File Protection of the group where the testing machine is located. Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Realtime Protection. In the Realtime File Protectio section, clear the Enable realtime file protection checkbox, as shown below.

Note:
Disabling Realtime File Protection only tests the features of the anti-ransomware module. It prevents the test sample from being detected and processed by the Realtime File Protection module as soon as it is decompressed. After completing the test, please select the Enable realtime file protection checkbox to ensure the endpoint is protected.
- Unzip the Ransomware Behavior Detection for Process Injection_Password sangfor.zip to the testing PC, and the unzip password is sangfor. Change the file extension to .exe.

- Add the ransomware sample to the trusted files list to bypass the Endpoint Secure static detection capabilities and ransomware honeypot capabilities, which will affect subsequent ransomware behavior detection results, as shown below.

- Use the injection tool (inject_xor.exe) to encrypt the sample (usually, it is impossible to detect it statically after the encryption), as shown below.

- Use the injection tool (inject_exec.exe) to inject the sample into explorer.exe, as shown below.
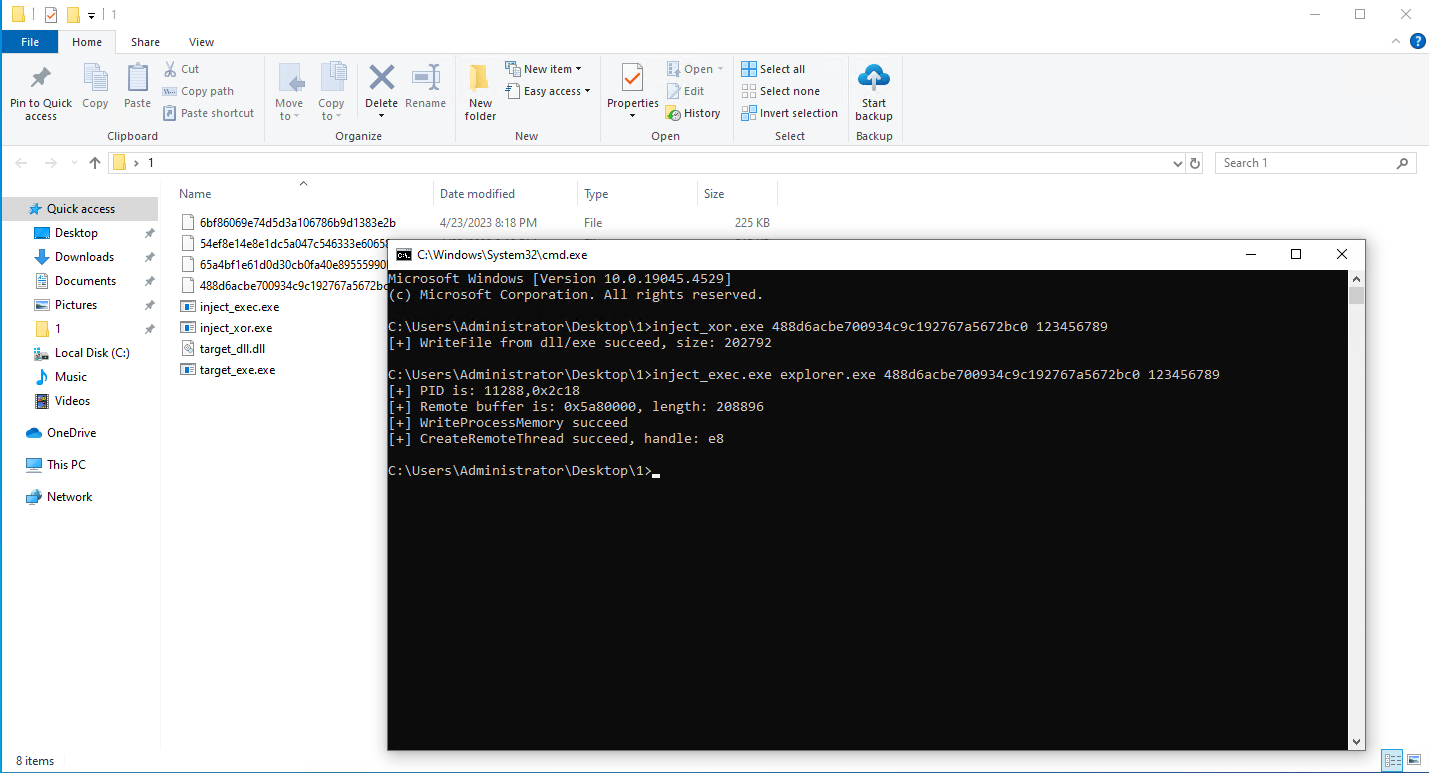
- After successfully injected, the explorer automatically restarts and pulls up the ransomware sample for encryption. The Endpoint Secure ransomware behavior detection capability detects and immediately stops the encryption activity, as shown in the figure below.

Test Result
Endpoint Secure ransomware behavior detection capability can detect new attack methods, such as ransomware virus encryption obfuscation and whitelist process injection. When a ransomware virus is injected into a whitelist process, and the whitelist process pulls up the ransomware, the Endpoint Secure ransomware behavior detection capability detects the encryption behavior of the ransomware virus in real time and blocks it. The alert window in the lower right corner of the endpoint will prompt, as shown below.

Ransomware Backup Files
- Disable the Realtime File Protection of the group where the testing machine is located. Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Realtime Protection. In the Realtime File Protection section, clear the Enable realtime file protection checkbox, as shown below.

Note:
Disabling Realtime File Protection only tests the features of the anti-ransomware module. It prevents the test sample from being detected and processed by the Realtime File Protection module as soon as it is decompressed. After completing the test, please select the Enable realtime file protection checkbox to ensure the endpoint is protected.
- Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Anti-Ransomware. In the Ransomware Protection section, select the Enable ransomware backup checkbox, then select Remove and quarantine the encrypted files and Enable password authentication for "encrypted file restoration", as shown in the figure below.

- Extract the Ransomware Backup Files Sample_Password sangfor.zip to the desktop of the testing PC, and the unzip password is sangfor. Change the file extension to .exe and add it to the trusted files list to prevent real-time file monitoring and ransomware honeypot, which will affect the ransomware backup testing effect, as shown below.

- For this sample, .NET Framework 3.5 is required, which you can turn on in Control Panel > Uninstall a program > Turn Windows features on or off. Select the .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) checkbox, click OK, and reboot your computer if prompted.

-
To highlight the effect of the ransomware sample, please create dozens of text files and combine them with the sample file. When you run the virus sample file, it will first infect the documents in this folder.
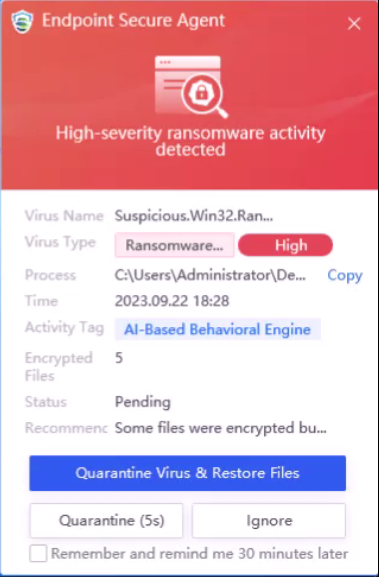
-
Double-click to run the ransomware virus. The ransomware behavior is detected and intercepted. At this time, some existing files are encrypted (the original files have been backed up), as shown below.
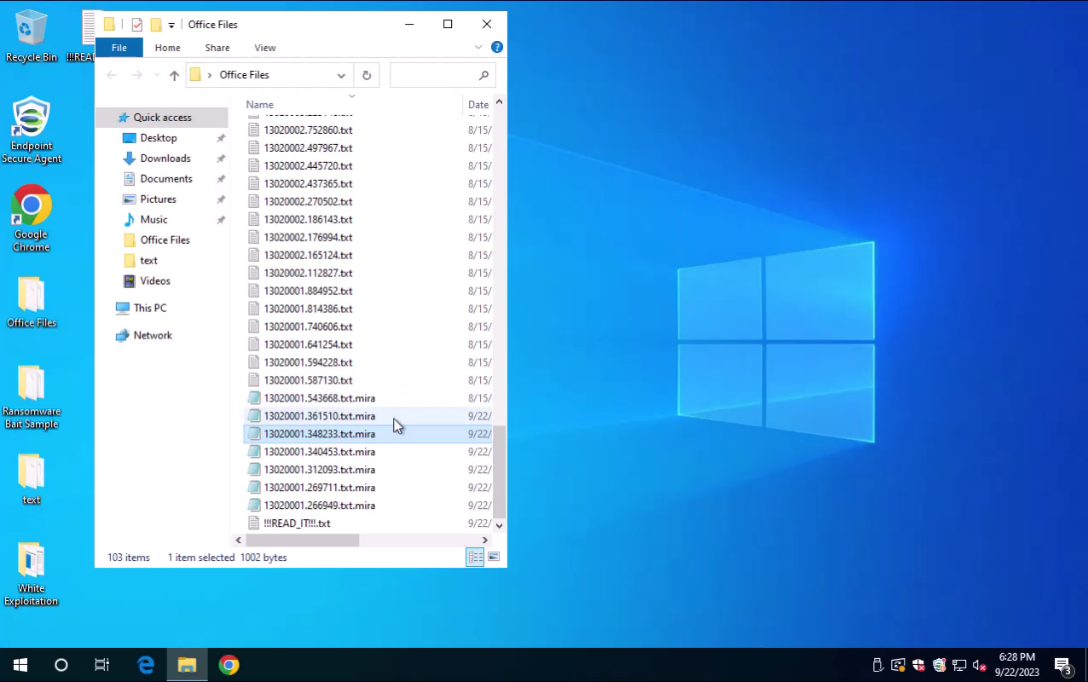
-
You can see that some files are already infected.
Test Result
Some encrypted files can be recovered through Ransomware Backup, as shown below.



Note:
The principle is that through continuous detection, Endpoint Secure will automatically back up files and block ransomware infection within 3 seconds once a ransomware trigger is detected. Since it backs up files in real-time and blocks ransomware, dozens to hundreds of files may still be infected instead of doing a complete backup in advance.
Ransomware Snapshot Backup
- The Snapshot-Based Ransomware Recovery function is hidden by default. Go to System > System > General to enable the Snapshot-Based Ransomware Recovery function.

- Disable the Realtime File Protection of the group where the testing machine is located. Navigate to Policies > General Policies > Realtime Protection. In the Realtime File Protection section, clear the Enable realtime file protection checkbox, as shown below.

Note:
Disabling Realtime File Protection only tests the features of the anti-ransomware module. It prevents the test sample from being detected and processed by the Realtime File Protection module as soon as it is decompressed. After completing the test, please select the Enable realtime file protection checkbox to ensure the endpoint is protected.
- Configure the Anti-Ransomware function in the group where the testing server is located. On the web console, navigate to Policies > General Policies > Anti-Ransomware, and select the Enable snapshot-based ransomware recovery checkbox.

- Extract the Ransomware Snapshot Backup Sample_Password sangfor.zip to the desktop of the testing PC, and the unzip password is sangfor. Change the file extension to .exe and add it to the trusted files list to prevent real-time file monitoring and ransomware honeypot, which will affect the ransomware backup testing effect, as shown below.

- For this sample, .NET Framework 3.5 is required, which you can turn on in Control Panel > Uninstall a program > Turn Windows features on or off. Select the .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) checkbox, click OK, and reboot your computer if prompted.

- Because snapshots are created daily at 12:00 p.m., you need to adjust the testing Windows Server System Time to before 12:00 p.m, for example, 11:55 a.m., each time before running the test.
- Log in for about 15 minutes and check the snapshot generation status. The figure below shows that the snapshot has been generated. Please do not click OK. This is just to verify that the snapshot has been produced.


- Double-click to run the ransomware virus, you can see that the ransomware virus has encrypted some files.


Test Result
Click Restore All Files to restore the snapshot with one click and observe whether the snapshot restoration is successful.

Precautions
- The snapshot function only supports Windows Server, except for Windows Server 2003 systems.
- The snapshot is backed up at 12:00 p.m. daily and takes about 10 minutes.
- Snapshots typically take up no more than 10% of disk space.
Configuration After Testing
- Disabling Realtime File Protection only tests the features of the anti-ransomware module. It prevents the test sample from being detected and processed by the Realtime File Protection module as soon as it is decompressed. After completing the test, please select the Enable realtime file protection checkbox to ensure the endpoint is protected.