【HCI】CLI Command Line Operation Guide_V6.8.0
Overview
CLI Product Introduction
CLI commands command line tools mainly undertake the operation and maintenance for Sangfor HCI. You can manage virtual machines, disks, and device operations without logging into the WebUI console, just by using the CLI command line.
Supporting components
| Product Name | Version |
|---|---|
| HCI-CLI | SangforcliInstall |
Installation Guide
Installation
HCI Upgrade
Background Information:
Steps:
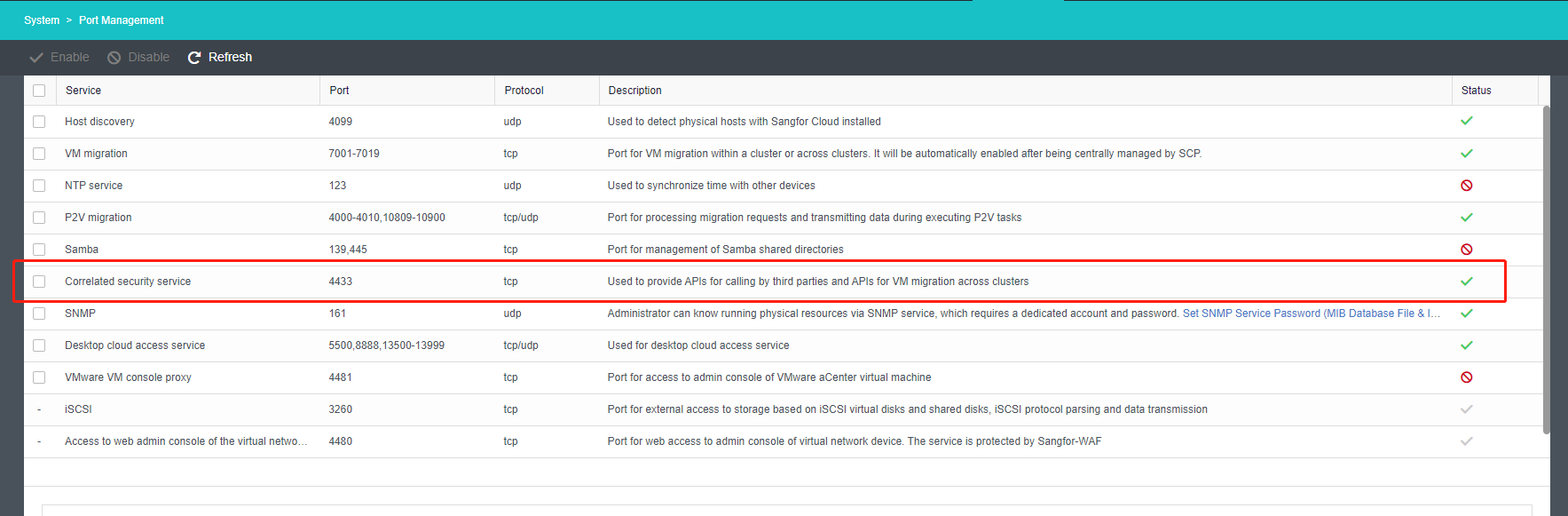
- Navigate to System, click Port Management.
- Enable port 4433.
Install and launch CLI
Background Information:
Install the CLI feature component package for PowerShell on Windows.
Operating System Compatibility List Runtime Environment:
Windows 7, Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Run Environment:
.net framework 4.x version and above.
https://dotnet.microsoft.com/en-us/download/dotnet-framework
Steps:
- Double-click SangforcliInstall.exe and follow the instruction to install.
Note:
Do not install in the system directory.
Command Usage Instructions
Pre-requisite:
The supporting components and the CLI command-line tool have been successfully installed and started.
Description:
If you have any questions about a certain command, you can execute the following command to get help information for that command.
- Get-Help + command: Get help.
- Get-Help + command + -Detailed: Get detailed help information (recommended)
- Get-Help + command + -Full : Get more detailed help information.
- Command + -Debug: Debug on request URL and send body information.
- Regarding user script edit, you can directly write PS scripts in the current directory and run them after starting the CLI.
- Please refer to Powershell for other feature details.
If you want to know the specific field information of a certain type, you can execute the following commands to obtain the detailed information of the type. (take BackupDatastore as example)
-
Input command: $object=New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupDatastore
-
Input: $object to view the detailed fields of BackupDatastore.
Example of Managing HCI using Command Line Tools
Login/Logout
Login HCI
Name:
Connect-HciServer
Syntax:
Connect-HciServer -Server <String> -Username <String> -Password <String>
Port <Int32>] [-Protocol <String>] [-Secret <String>
Description:
Login HCI server.
Parameters:
-Server <String>
The IP address or DNS name of the server to connect to.(The server address is the address where the API gateway is deployed)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? False
-Username <String>
Specify the username for authentication with the server.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? False
-Password <String>
Specify the password for authentication with the server.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? False
-Port <Int32>
Specify a port on the server for connection.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Protocol <String>
The Internet protocol specified for connection.It can be http or https.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Secret <String>
Specify the secret key for authentication with the server.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Login HCI server
PS > Connect-HciServer -Server 192.168.0.1 -username admin -Password xxx -Port 4433 -Protocol https -Secret xxxxxx
Logout
Name:
Disconnect-HciServer
Syntax:
Disconnect-HciServer [-Username <String>
Description:
Logout HCI server.
Parameters:
-Username <String>
User name.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
PS>Disconnect-HciServer -Username admin
======================================================
* * The command line tool has been logged out * *
======================================================
PS>
Virtual Machine Management
Query virtual machine
Name:
Get-VM
Syntax:
Get-VM [-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>] [-Name <String[]>] [-IsDeleted] [-TemplateId <String>] [-Application <String>] [-GraphicSchedule <String>
Get-VM [-Id <String[]>
Get-VM [-Keyword <String>
Get-VM [-OSOption <IOSOption>
Get-VM [-Type <String[]>
Description:
The cmdlet retrieves VM systems on the HCI server, and returns a set of VMs based on the filter criteria. The parameter Name supports fuzzy query (test.*) and exact query (test). The returned results show the running VMs first, and then show VMs in the lexicographical order of VM names.
Parameters:
-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>
-
Virtual datastore
-
Currently, only one virtual datastore can be queried.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
Specify the list of VM IDs to be searched.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Specify the list of VM names
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Keyword <String>
Currently, only one VM name/IP can be found by fuzzy query.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-OSOption <IOSOption>
Specify the operating system of the new VM.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Type <String[]>
Specify the VM type to be searched. VM types include VM (ordinary VM), TEMPLATE (VM template), and PLACEHOLDER (placeholder VM).
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDeleted [<SwitchParameter>
VM deleted? A VM that has not been deleted is returned by default.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TemplateId <String>
VM template ID. This field indicates which VM template the filtered VM is derived from, including from the VDI template and HCI template. The VDI template will also be returned, because there is a template field whose value is its own vmid.
To construct, see NOTES section for TEMPLATE properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Application <String>
VM application scenario type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GraphicSchedule <String>
3D VM power-on scheduling mode
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all virtual machines.
PS > Get-VM
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query virtual machine on a sepcifc storage
PS > $datastore = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $datastore.Id = "xxx"
PS > Get-VM -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM running on the specified datastore using pipeline
PS > Get-Datastore -Id "xxx" | Get-VM
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machine by name
PS > Get-VM -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machine by ID
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001"
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machine by keywords
#Notes keywords as virtual machine IP address.
PS > Get-VM -Keyword "192.168.0.1"
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Query virtual machines by OS kernel type
PS > $osoption = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.OSOption
PS > $osoption.KernelName = "linux"
PS > $osoption.DistributionName = "ubuntu"
PS > $osoption.Arch = "amd64"
PS > Get-VM -OSOption $osoption
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machine by virtual machine type
PS > Get-VM -Type "TEMPLATE"
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machine by virtual machine template
PS > $tpl = Get-Template
PS > Get-VM -TemplateId $tpl[1].Id
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machines by application scenario type
PS > Get-VM -Application COMPUTE_SCENARIO
————————– EXAMPLE 11 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of virtual machines by 3D VM power-on automation level
PS > Get-VM -GraphicSchedule DENSITY
————————– EXAMPLE 12 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of deleted VMs
PS > Get-VM -IsDeleted
————————– EXAMPLE 13 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the storage through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.Datastore
Query the snapshot through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.Snapshot
Query the node through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.VMHost
Query the share disk through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.Sharedisk
Query the storage policy through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.StoragePolicy
Query the operation logs through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.Log
Query the alert logs through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.AlarmLog
Query backup through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.Backup
Query the backup policy through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.BackupPolicy
Query the physical edge through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
Ps > $vm.VdSwitch
Query the virtual swtich through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.DistributeSwitch
Query the port group through the VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM
PS > $vm.VdPortGroup
Query Virtual Machines’ Backup
Name:
Get-VMBackup
Syntax:
Get-VMBackup -VMId <String> [-FileType <String>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource>] Get-VMBackup -Id <String>
Description:
Query the virtual machines backup list.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
ID of the VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FileType <String>
Filter by backup file type: BACKUP (backup), BACKUPCOPY (backup copy), and ARCHIVE (archive)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Datastore
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
VM backup ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all backup files of a VM
PS > Get-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM backup files by ID
PS > Get-VMBackup -Id "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM backup files on the specified storage
PS > $datastore = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $datastore.Id = "xxx"
PS > Get-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001" -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM backup files on the specified storage through the pipe
PS > Get-Datastore -Id "xxx" | Get-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001"
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM backup files by file type
PS > Get-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001" -FileType "BACKUP"
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VM objects through the VM backup file
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.VMId = "0000000000001"
PS > $vmbackup.VM
Qeury VM Group
Name:
Get-VMGroup
Syntax:
Get-VMGroup [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Descrition:
Query the list of VM groups.
Query a single VM group.
Parameters:
-Name <String[]>
List of group names
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM groups by name
PS > Get-VMGroup -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM groups by ID
PS > Get-VMGroup -Id "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs under the group through the VM group
PS > $vmgroup = Get-VMGroup
PS > $vmgroup.VM
Query VM Disk Mount Information
Name:
Get-VMDisk
Syntax:
Get-VMDisk -VM <IVirtualMachine> [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMDisk -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the mount information list of virtual disks, physical disks, and shared disks mounted to a VM.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Mount information ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM disk mount information.
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Get-VMDisk -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM disk mount information through the pipe.
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Get-VMDisk
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM disk mount information by ID
PS > Get-VMDisk -Id "xxx"
Query The List Of All The VMs IP Addresses
Name:
Get-VMIPD
Syntax:
Get-VMIP [-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Description:
Query the list of all the VMs IP addresses.
Parameters:
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
IP enabled?
Returns all IP addresses by default
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of all VMs IP addresses.
PS > Get-VMIP
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of enabled VM IP addresses.
PS > Get-VMIP -IsEnabled 1
Query VM NIC Information
Name:
Get-VMNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
-
Get-VMNetworkAdapter [-VM
<IVirtualMachine[]> -
Get-VMNetworkAdapter -Id
<String>
Description:
- Query the information of all NICs under the VM.
- Query the information of a single NIC by ID.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
Virtual NIC ID.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine[]>
VM, required parameter: VM ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all NIC information of a VM.
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Get-VMNetworkAdapter -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all NIC information of a VM through the pipe.
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Get-VMNetworkAdapter
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM NIC information by ID.
PS > Get-VMNetworkAdapter -Id "0000000000001:eth0"
Query The New NIC MAC Address
Name:
Get-VMNetworkAdapterMacAddress
Syntax:
Get-VMNetworkAdapterMacAddress
Description:
Query the new NIC MAC address, which can be used to fill in the physical address of the device when creating a network device.
Parameters:
N/A
Output Paramater:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query a new NIC MAC address.
PS > Get-VMNetworkAdapterMacAddress
Query VM Template
Name:
Get-Template
Syntax:
Get-Template [-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>] [-Name <String[]>
Get-Template [-Id <String[]>
Description:
The cmdlet retrieves VM systems on the HCI server, and returns a set of VM templates based on the filter criteria. The parameter Name supports fuzzy query *(test.) and exact query (test)**.
Parameters:
-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>
Only one virtual datastore can be queried.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Specify VM template name.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
Specify the list of VM template IDs to be searched.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all VM templates.
PS > Get-Template
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM templates on the specified storage.
PS > $datastore = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $datastore.Id = "xxx"
PS > Get-Template -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM templates on the specified storage through the pipe.
PS > Get-Datastore -Id "xxx" | Get-Template
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM templates by name.
PS > Get-Template -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM templates by ID.
PS > Get-Template -Id "0000000000001"
Query Available Operating Systems
Name:
Get-VMGuestOsoption
Syntax:
Get-VMGuestOsoption
Description:
Query available operating systems.
Parameters:
N/A
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all available operating systems.
PS > Get-VMGuestOsoption
Query The Installation Information Of vmTools
Name:
Get-Tools
Syntax:
Get-Tools [-Id <String[]>
Description:
Query the installation information of vmTools.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
The list of VM IDs.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the installation information of vmTools for all VMs.
PS > Get-Tools
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of vmTools installation information by ID.
PS > Get-Tools -Id "0000000000001"
Update VM
Name:
Set-VM
Syntax:
Set-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-Name <String>] [-Cpu <ICpu>] [-OSOption <IOSOption>] [-Memory <IMemory>] [-IsImportant] [-Notes <String>] [-RunAsync] [-IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled] [-IsDualScreenEnabled] [-Uuid <IVmuuidInfo>] [-GroupId <String>] [-Application <String>] [-Video <IVMVideo>
[-RestoreMode <String>] [-Gpu <IVmgpu>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>] [-IsHaEnabled] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
Cloned VM.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Cpu <ICpu>
CPU
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-OSOption <IOSOption>
OS type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Memory <IMemory>
Memory
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsImportant [<SwitchParameter>
Critical VMs enabled?
It is recommended to mark critical services with high requirements on continuity and performance as critical VMs, such as core databases.
When a VM is marked as critical, the system performs intelligent resource guarantee for the VM:
-
Memory guarantee: When the memory reclaiming mechanism is disabled, memory usage is prioritized to improve service performance.
-
Storage guarantee: Data rebuilding is performed first when a fault occurs; data of other VMs is transferred first when data is balanced; it is recommended to select a high-performance storage policy to ensure the best performance.
-
Continuity guarantee: When the physical host fails, it will be started first to shorten the service interruption time; when the physical host has no sufficient resources, other VMs will be scheduled first to release resources for critical VMs so as to ensure stable and normal service operation.
-
You are recommended to mark only a few critical VMs, because marking too many critical VMs may affect the performance optimization effect.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
2.
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Nested virtualization enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDualScreenEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Dual screen enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Uuid <IVmuuidInfo>
UUID
To construct, see NOTES section for UUID properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GroupId <String>
ID of the group where the VM is located.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Application <String>
VM application scenario type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Video <IVMVideo>
VM graphics card
To construct, see NOTES section for VIDEO properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RestoreMode <String>
Recovery mode
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Gpu <IVmgpu>
Physical graphics card of 3D VM GPU
To construct, see NOTES section for GPU properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policy
To construct, see NOTES section for STORAGEPOLICY properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsHaEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
High availability enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
\#Notes Create VM CPU object
PS > $cpu = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Cpu
PS > $cpu.Cores = 1
PS > $cpu.Sockets = 1
PS > $cpu.Cpuid = 1
PS > $cpu.FrequencyMHz = 100
PS > $cpu.IsExclusiveEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.IsInvtscEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.Type = "HOST"
\#Notes Create an object of the VM OS kernel type
PS > $osoption = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.OSOption
PS > $osoption.KernelName = "linux"
PS > $osoption.DistributionName = "ubuntu"
PS > $osoption.Arch = "amd64"
\#Notes Create VM memory object
PS > $memory = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Memory
PS > $memory.SizeGb = 1
PS > $memory.IsBalloonEnabled = $true
PS > $memory.IsHugePageEnabled = $true
\#Notes Obtain VM group
PS > $group = Get-VMGroup -Name cjm
\#Notes Create VM GPU object
PS > $gpu = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Vmgpu
PS > $gpu.Has3DFastPath = $true
PS > $gpu.Schedule = "DENSITY"
\#Notes Create VM UUID object
PS > $uuid = new-object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VmuuidInfo
PS > $uuid.OnlyToQemu = $true
PS > $uuid.Uuid = "260449b9-e3b1-4f5a-a61a-25e934c54eec"
PS > $uuid.Enable = $true
\#Notes Create VM video object
PS > $video = new-object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMVideo
PS > $video.DeviceId = "12345"
PS > $video.QxlRevision = "12344"
PS > $video.Type = "STD"
\#Notes Create storage policy object
PS > $storagePolicy = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > Set-VM -VM $vm -Name "test-name" -Cpu $cpu -OSOption $osoption -Memory $memory -IsImportant -Notes "test-notes" -IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled -IsDualScreenEnabled -GroupId $group.Id -Gpu $gpu -Uuid $uuid -Application "COMPUTE_SCENARIO" -RestoreMode "DISABLED" -Video $video -StoragePolicy
$storagePolicy[0] -IsHaEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Set-VM -VM $vm -Name "test-name" -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Set-VM -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear VM description
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Set-VM -VM $vm -Notes $null
Edit VM NIC
Name:
Set-VMNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
Set-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter> [-Type <String>] [-NetworkId <String>] [-MacAddress <String>] [-IsConnected] [-Ipv4 <IIPAddress>] [-Ipv6 <IIPAddress>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit VM NIC.
Parameters:
-VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter>
NIC
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Type <String>
NIC adapter types: E1000, RTL8139, and VIRTIO
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkId <String>
Connected VM network ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MacAddress <String>
MAC address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsConnected [<SwitchParameter>
Network cable connected?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv4 <IIPAddress>
IPv4 information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv6 <IIPAddress>
IPv6 information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit VM NIC (synchronous call)
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.Id = "0000000000001:eth0"
#Notes Create IP address object
PS > $ipv4 = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IPAddress
PS > $ipv4.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $ipv4.PrefixLength = 24
PS > $ipv6 = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IPAddress
PS > $ipv6.Address = "2001::f000"
PS > $ipv6.PrefixLength = 64
#Notes Obtain an available MAC address
PS > $mac = Get-VMNetworkAdapterMacAddress
PS > Set-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadapter -Type "E1000" -MacAddress $mac.Address -Ipv4 $ipv4 -Ipv6 $ipv6 -IsConnected
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit VM NIC (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.Id = "0000000000001:eth0"
PS > Set-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadapter -Type "E1000" -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit VM NIC through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VMNetworkAdapter -Id "0000000000001:eth0" | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -Type "E1000"
Update VM Backup
Name:
Set-VMBackup
Syntax:
Set-VMBackup -VMBackup <IVMBackup> [-Isprotected] [-Description <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM Backup.
Parameters:
-VMBackup <IVMBackup>
Backup
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Isprotected [<SwitchParameter>
Backup lock enabled?
Instructions for use:
1.Protected backups will not be cleaned up automatically.
2.Protected backups also cannot be deleted.
3.After the protection is canceled, backup files whose backup retention period expires will be automatically cleared.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Description <String>
description
Instructions for use:
- The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Paramter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM backup (synchronous call)
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Set-VMBackup -VMBackup $vmbackup -Isprotected -Description "test-notes"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM backup (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Set-VMBackup -VMBackup $vmbackup -Description "test-notes" -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM backup through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VMBackup -Id "xxx" | Set-VMBackup -Isprotected -Description "test-notes"
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear VM backup description
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Set-VMBackup -VMBackup $vmbackup -Description $null
Edit VM Group
Name:
Set-VMGroup
Syntax:
Set-VMGroup -VMGroup <IVMGroup> [-Name <String>
Description:
Edit VM group.
Parameters:
-VMGroup <IVMGroup>
Search by Group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Group name
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
-
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Paramter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit VM group (synchronous call)
PS > $vmgroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMGroup
PS > $vmgroup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Set-VMGroup -VMGroup $vmgroup -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmgroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMGroup
PS > $vmgroup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Set-VMGroup -VMGroup $vmgroup -Name "test-name" -RunAsync
Create Virtual Machine
Name:
New-VM
Syntax:
New-VM [-NetworkId <String[]>] [-Name] <String> [[-VMHost] <IVMHost>] [[-Notes] <String>] [[-StoragePolicy] <IStoragePolicy>] [[-GroupId] <String>] [[-OSOption] <IOSOption>] [[-Memory] <IMemory>] [[-Cpu] <ICpu>] [[-Datastore] <IStorageResource>] [-RunAsync] [-Source <String>
<String>] [-IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled] [-IsDualScreenEnabled] [-IsHaEnabled] [<CommonParameters>
New-VM [-Snapshot] <ISnapshot> -Name <String> [-VMHost <IVMHost>] [-Notes <String>] [-GroupId <String>] [-Count <Int64>] [-ShouldStartAfterClone] [-ShouldConnectNiCs] [-VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter[]>] [-CloneType <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] -VMId <String> [-TargetVMId <String[]>
[-RunAsync] [-NameSuffix <String>] [<CommonParameters>
New-VM [-VMBackup] <IVMBackup> [-Name] <String> [-GroupId <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-StoragePolicyId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-VM [-VM] <IVirtualMachine> [-Name <String>] [-VMHost <IVMHost>] [-Notes <String>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>] [-GroupId <String>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource>] [[-Count] <Int64>] [-ShouldStartAfterClone] [-TargetId <String[]>
<IVMNetworkAdapter[]>] [-CloneType <String>] [-RunAsync] [-Source <String>] [-NameSuffix <String>] [-JoinDomainInfo <IJoinDomain>] [-Application <String>] [-ResetSidAfterClone] [-IsHaEnabled] [<CommonParameters>
New-VM [-Template] <ITemplate> [-Name <String>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>] [-GroupId <String>] [-Memory <IMemory>] [-Cpu <ICpu>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource>] [-Count <Int64>] [-VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter[]>] [-VMHostId <String>] [-DiskGb <Int64[]>
[-JoinDomainInfo <IJoinDomain>] [-ResetSidAfterDerive] [-IsHaEnabled] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Creation VM.
Parameters:
-NetworkId <String[]>
List of network IDs
Network ID format: peerDeviceID: peerVlanGroupID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? 1
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMBackup <IVMBackup>
Backup ID
Required? true
Position? 1
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
Cloned VM
Required? true
Position? 1
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Template <ITemplate>
Template
Required? true
Position? 1
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
-
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? 1
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHost <IVMHost>
The node where the VM is running
Required? false
Position? 2
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
-
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? 3
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policy
Required? false
Position? 4
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GroupId <String>
Group Id
Required? false
Position? 5
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-OSOption <IOSOption>
OS type
Required? false
Position? 6
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Memory <IMemory>
Memory
Required? false
Position? 7
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Cpu <ICpu>
CPU
Required? false
Position? 8
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
The storage where the VM is located
Required? false
Position? 9
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Count <Int64>
Quantity
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldStartAfterClone [<SwitchParameter>
Powered on automatically after the clone?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetId <String[]>
New VM ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldConnectNiCs [<SwitchParameter>
All NICs disconnected?
To prevent the IP address conflict between the cloned VM and the original VM, the default is false.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter[]>
VM NIC settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CloneType <String>
Clone types: FULL (full clone), LINK (linked clone), and FAST (fast clone)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String>
ID of the node where the VM deployed from the template is located
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DiskGb <Int64[]>
Private disk size
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreId <String>
Storage ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicyId <String>
Recovered storage policy ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String>
ID of the cloned VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetVMId <String[]>
New VM Id
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Source <String>
VM creation source type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NameSuffix <String>
The suffix specified when cloning multiple VMs. If not specified, the suffix is 0001,0002 by default.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-JoinDomainInfo <IJoinDomain>
Automatically add domain parameters after cloning
To construct, see NOTES section for JOINDOMAININFO properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Application <String>
VM application scenario type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ResetSidAfterClone [<SwitchParameter>
SID reset after cloning?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Nested virtualization enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDualScreenEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Dual screen enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ResetSidAfterDerive [<SwitchParameter>
Reset SID after derivation
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsHaEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
High availability enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM by default (synchronous call)
#Notes Obtain VM node
PS > $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Name "192.168.0.1"
#Notes Obtain storage policy
PS > $storagepolicy = Get-StoragePolicy -Name "Default policy of 2 replicas"
#Notes Create an object of the OS kernel type
PS > $osoption = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.OSOption
PS > $osoption.KernelName = "linux"
PS > $osoption.DistributionName = "ubuntu"
PS > $osoption.Arch = "amd64"
#Notes Create VM memory object
PS > $memory = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Memory
PS > $memory.SizeGb = 1
PS > $memory.IsBalloonEnabled = $true
PS > $memory.IsHugePageEnabled = $true
#Notes Create VM CPU object
PS > $cpu = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Cpu
PS > $cpu.Cores = 1
PS > $cpu.Sockets = 1
PS > $cpu.Cpuid = 1
PS > $cpu.FrequencyMHz = 100
PS > $cpu.IsExclusiveEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.IsInvtscEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.Type = "HOST"
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
PS > New-VM -Name "test-name" -VMHost $vmhost -Notes "test-notes" -StoragePolicy $storagepolicy -GroupId "xxx" -OSOption $osoption -Memory $memory -Cpu $cpu -Datastore $datastore -NetworkId xxxxxxxx -IsNestedVirtualizationEnabled -IsDualScreenEnabled -Source NORMAL -Applicat
COMPUTE_SCENARIO -IsHaEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone VM from the snapshot (synchronous call)
#Notes Take VM snapshot
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > $snapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vm
#Notes Obtain VM node
PS > $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Name "192.168.0.1"
#Notes Create VM NIC object
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.DeviceId = "net0"
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
PS > New-VM -Snapshot $snapshot -Name "test-name" -VMHost $vmhost -Notes "test-notes" -GroupId "xxx" -Count 2 -ShouldStartAfterClone -ShouldConnectNiCs -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadapter -CloneType "FULL" -Datastore $datastore.Id -VMId "0000000000001" -TargetVMId "000000000
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone VM from the VM backup (synchronous call)
#Notes Obtain VM backup
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > $vmbackup = Get-VMBackup -VM $vm
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
#Notes Obtain storage policy
PS > $storagepolicy = Get-StoragePolicy -Name "Default policy of 2 replicas"
PS > New-VM -VMBackup $vmbackup -Name "test-name" -GroupId "xxx" -DatastoreId $datastore.Id -StoragePolicyId $storagepolicy.Id
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone VM (synchronous call)
#Notes Create cloned VM object
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
#Notes Obtain VM node
PS > $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Name "192.168.0.1"
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
#Notes Create VM NIC object
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.DeviceId = "net0"
#Notes Create the parameter JoinDomainInfo
PS > $jd = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.JoinDomain
PS > $jd.User = "admin"
PS > $jd.Name = "test"
PS > $jd.Password = "test"
#Notes Create storage policy object
PS > $storagePolicy = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > New-VM -VM $vm -Name "test-name" -VMHost $vmhost -Notes "test-notes" -GroupId "xxx" -Datastore $datastore -Count 2 -ShouldStartAfterClone -TargetId "0000000000002" -ShouldConnectNiCs -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadapter -CloneType "FULL" -NameSuffix 000 -Source CREATE_BY
DESK_SCENARIO -JoinDomainInfo $jd -ResetSidAfterClone -StoragePolicy $storagePolicy[0] -IsHaEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Deploy VM from the template (synchronous call)
#Notes Obtain VM template
PS > $template = Get-Template -Id "0000000000001"
#Notes Create VM memory object
PS > $memory = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Memory
PS > $memory.SizeGb = 1
PS > $memory.IsBalloonEnabled = $true
PS > $memory.IsHugePageEnabled = $true
#Notes Create VM CPU object
PS > $cpu = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Cpu
PS > $cpu.Cores = 1
PS > $cpu.Sockets = 1
PS > $cpu.Cpuid = 1
PS > $cpu.FrequencyMHz = 100
PS > $cpu.IsExclusiveEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.IsInvtscEnabled = $true
PS > $cpu.Type = "HOST"
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
#Notes Create VM NIC object
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.DeviceId = "net0"
#Notes Obtain VM node
PS > $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Name "192.168.0.1"
#Notes Create VM JoinDomain object
PS>$dd = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.JoinDomain
PS>$dd.User = "user"
PS>$dd.Name = "test"
PS>$dd.Password = "test"
#Notes Create storage policy object
PS > $storagePolicy = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > New-VM -Template $template -Name "test-name" -GroupId "xxx" -Memory $memory -Cpu $cpu -Datastore $datastore -Count 1 -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadapter -VMHostId $vmhost.Id -DiskGb 1 -ResetSidAfterDerive -JoinDomainInfo $dd -StoragePolicy $storagePolicy[0] -IsHaEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM by default (asynchronous call)
PS > New-VM -Name "test-name" -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a VM on a specific storage through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-Datastore -Id "xxx" | New-VM -Name "test-name"
Create Virtual Machine Backup
Name:
New-VMBackup
Syntax:
New-VMBackup -VMId <String> -BackupDatastoreId <String> [-Description <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM backup
Instruction for use:
- If the Guest OS is shut down or restarted during backup, the backup task of the VM will be terminated.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
ID of the VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BackupDatastoreId <String>
Backup storage ID
Instructions for use:
- It is recommended that the destination backup repository be different from the original location, so that the device can be recovered normally after the storage of the original location fails.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Description <String>
description
Instructions for use:
- The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM backup (synchronous call)
PS > New-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001" -BackupDatastoreId "xxx" -Description "test-notes"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM backup (asynchronous call)
PS > New-VMBackup -VMId "0000000000001" -BackupDatastoreId "xxx" -RunAync
Create Virtual Machine Group
Name:
New-VMGroup
Syntax:
New-VMGroup -Name <String> [-ParentId <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM group
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Group name
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
-
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ParentId <String>
Parent group ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM group (synchronous call)
PS > New-VMGroup -Name "test-name" -ParentId "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > New-VMGroup -Name "test-name" -ParentId "xxx" -RunAsync
Create Virtual Machine NIC
Name:
New-VMNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
New-VMNetworkAdapter -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-Type <String>] [-NetworkId <String>] [-MacAddress <String>] [-IsConnected] [-Ipv4 <IIPAddress>] [-Ipv6 <IIPAddress>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM NIC.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Type <String>
NIC adapter types: E1000, RTL8139, and VIRTIO
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkId <String>
Connected VM network ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MacAddress <String>
MAC address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsConnected [<SwitchParameter>
Network cable connected?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv4 <IIPAddress>
IPv4 information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv6 <IIPAddress>
IPv6 information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM NIC (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
#Notes Obtain available MAC addresses
PS > $mac = Get-VMNetworkAdapterMacAddress
#Notes Create IP address object
PS > $ipv4 = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IPAddress
PS > $ipv4.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $ipv4.PrefixLength = 24
PS > $ipv6 = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IPAddress
PS > $ipv6.Address = "2001::f000"
PS > $ipv6.PrefixLength = 64
PS > New-VMNetworkAdapter -VM $vm -Type "E1000" -MacAddress $mac.Address -IsConnected -Ipv4 $ipv4 -Ipv6 $ipv6
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM NIC (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > New-VMNetworkAdapter -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM NIC through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | New-VMNetworkAdapter
Delete Virtual Machine
Name:
Remove-VM
Syntax:
Remove-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-DeletePermanently] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM
Note:
-
By default, a deleted VM is saved in the recycle bin but not actually deleted, and can be recovered from the recycle bin later.
-
VMs in the recycle bin are regularly deleted. For details, see the introduction to the recycle bin.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DeletePermanently [<SwitchParameter>
Delete completely
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Remove-VM -VM $vm -DeletePermanently
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Remove-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VMs through the pipe (asynchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Remove-VM -RunAsync
Delete Virtual Machine Backup
Name:
Remove-VMBackup
Syntax:
Remove-VMBackup -VMBackup <IVMBackup> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM backup.
Parameters:
-VMBackup <IVMBackup>
Backup
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM backup (synchronous call)
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-VMBackup -VMBackup $vmbackup
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM backup (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmbackup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMBackup
PS > $vmbackup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-VMBackup -VMBackup $vmbackup -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM backup through the pipe (asynchronous call)
PS > Get-VMBackup -Id "xxx" | Remove-VMBackup -RunAsync
Delete VM Group
Name:
Rmove-VMGroup
Syntax:
Remove-VMGroup -VMGroup <IVMGroup> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM group.
Parameters:
-VMGroup <IVMGroup>
Search by Group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM group (synchronous call)
PS > $vmgroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMGroup
PS > $vmgroup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-VMGroup -VMGroup $vmgroup
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmgroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMGroup
PS > $vmgroup.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-VMGroup -VMGroup $vmgroup -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM group through the pipe (asynchronous call)
PS > Get-VMGroup -Id "xxx" | Remove-VMGroup -RunAsync
Delete VM NIC
Name:
Remove-VMNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
Remove-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM NIC.
Parameter:
-VMNetworkAdapter <IVMNetworkAdapter>
NIC
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM NIC (synchronous call)
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.Id = "0000000000001:eth0"
PS > Remove-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadpater
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM NIC (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmnetworkadapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMNetworkAdapter
PS > $vmnetworkadapter.Id = "0000000000001:eth0"
PS > Remove-VMNetworkAdapter -VMNetworkAdapter $vmnetworkadpater -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM NIC through the pipe (asynchronous call)
PS > Get-VMNetworkAdapter -Id "0000000000001:eth0" | Remove-VMNetworkAdapter -RunAsync
Migrate VM
Name:
Move-VM
Syntax:
Move-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [-VMHost <IVMHost>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource>] [-IsStartVMAfterMigrate] [-MigrateInterface <String>] [-IsCompressMemory] [-Groupid <String>] [-IsMigrateSpeedUnlimited] [-MigrateSpeed <Int64>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
<IDiskPolicy[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Migrate VM: Power-off migration and power-on live migration are supported. Cross-storage migration is time-consuming, because all disk data needs to be copied.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
Specified migrated VM.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHost <IVMHost>
ID of the destination running node to which the VM is migrated
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
ID of the destination storage to which the VM is migrated
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsStartVMAfterMigrate [<SwitchParameter>
Destination VM automatically started after migration?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MigrateInterface <String>
Network used for VM migration
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsCompressMemory [<SwitchParameter>
Memory compression enabled during live migration?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Groupid <String>
Migrate the VM to the target group
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsMigrateSpeedUnlimited [<SwitchParameter>
No speed limit? If there is a speed limit, it is used with the parameter MigrateSpeed
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MigrateSpeed <Int64>
VM migration speed limit, in MB/s
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policy used when migrating VMs to the destination storage
To construct, see NOTES section for STORAGEPOLICY properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DisksPolicy <IDiskPolicy[]>
Disk policy
To construct, see NOTES section for DISKSPOLICY properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Migrate VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
#Notes Obtain VM node
PS > $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Name "192.168.0.1"
#Notes Obtain storage
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
PS > Move-VM -VM $vm -VMHost $vmhost -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Migrate VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Move-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Migrate the VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Move-VM
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Migrate VM Add other parameters (asynchronous call)
PS> $vm = Get-VM -Name "vm1"
PS> $datastore = Get-Datastore -Name "Virtual datastore 1"
PS> $vmhost = Get-VMHost -Id host-005056b2117d
PS> $storagePolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StoragePolicy
PS> $storagePolicy.Id = "123456789"
PS> $diskPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DiskPolicy
PS> $diskPolicy.Id = "987465321"
PS> $diskPolicy.DiskPolicyId = "88888888"
PS> move-vm -VM $vm -Datastore $datastore -VMHost $vmhost -IsStartVMAfterMigrate -MigrateInterface "testInterface" -IsCompressMemory -GroupId "groupId0001" -IsMigrateSpeedUnlimited -MigrateSpeed 100 -StoragePolicy $storagePolicy -DisksPolicy $diskPolicy -RunAsync
Power On VM
Name:
Start-VM
Syntax:
Start-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Start VM When powering on a powered on VM, success is returned.
Parameter:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Start VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Start-VM -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Start the VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Start-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Start VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Start-VM
Recover VM From The Cecycle Bin
Name:
Restore-VM
Syntax:
Restore-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Recover VM from the recycle bin
Parameter:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM object
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover VM from the recycle bin (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Restore-VM -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover VM from the recycle bin (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Restore-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover VM from the recycle bin through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > $vm | Restore-VM
Restart VM
Name:
Restart-VM
Syntax:
Restart-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-Kill <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Restart VM.
Parameter:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Kill <String>
Force stop VM. Shutdown modes: HARD (hard shutdown), SOFT (soft shutdown), and FAST (fast shutdown)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Restart-VM -VM $vm -Kill FAST
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Restart-VM -VM $vm -Kill FAST -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Restart-V
Stop VM
Name:
Stop-VM
Syntax:
Stop-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> -Kill <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Stop the VM.
Usually, it is recommended to manually close programs such as the service system on the client side, so that the Apps can be closed normally, and then shut down the device so as to minimize program exceptions.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Kill <String>
Force stop VM. Shutdown modes: HARD (hard shutdown), SOFG (soft shutdown), and FAST (fast shutdown)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Stop VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Stop-VM -VM $vm -Kill "HARD"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Stop the VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Stop-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Stop VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Stop-VM
Suspend VM
Name:
Suspend-VM
Syntax:
Suspend-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Suspend VM.
Suspending a VM is to save the operation status of the current VM, and the VM status when the operation is recovered will be the same as the status before suspension.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Suspend the VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Suspend-VM -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Suspend the VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Suspend-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Suspend VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Suspend-VM
Recover The Suspended VM
Name:
Resume-VM
Syntax:
Resume-VM -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Recover the suspended VM.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover the suspended VM (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Resume-VM -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover the suspended VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Resume-VM -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Recover the suspended VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Resume-VM
Install The vmTools
Name:
Mount-Tools
Syntax:
Mount-Tools -VM <IVirtualMachine> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Install the vmTools
In different operating systems, you need to use different modes to continue to complete the installation (the premise is that you must call this interface to install the performance optimization toolkit):
Linux system:
- Log in to the operating system, enter the terminal, and execute the following command to start installation:
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/cdrom
sudo mount -t iso9660 /dev/sr1 /mnt/cdrom
cd /mnt/cdrom
sudo ./install.sh
- Complete the installation according to the prompts
Notes:
If the system kernel does not have a built-in virtio driver (the kernel above linux 2.6.25 has a virtio driver), the installation will fail.
If the system fails to restart, you can try to unmount vmTools from the VM details page and restart the system again.
If the error "mount: special device /dev/sr1 does not exist" is reported when mounting the CD/DVD,
The path of the CD/DVD device may be incorrect. You can try to mount another CD/DVD path (the VMOptimizationToolsLinux.tar.gz file should be in the /mnt/cdrom directory after mounting).
Windows system:
Automatic installation may not be done due to system permission restrictions.
If the installation interface does not automatically pop up on the VM desktop, it means that the installation failed.
Please follow the procedure below to complete the installation:
-
Please power on and log in to the operating system
-
Click to open my computer, and double-click the VMOptimizationTools CD/DVD, or open the CD/DVD and then run VMOptimizationTools.exe
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Install vmTools
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Mount-Tools -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Install vmTools through the pipe
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Mount-Tools
Convert The VM Into A Template
Name:
Convert-VMToTemplate
Syntax:
Convert-VMToTemplate -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Convert the VM into a template.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the VM into a template (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Convert-VMToTemplate -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the VM into a template (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Convert-VMToTemplate -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the VM into a template through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Convert-VMToTemplate
Convert The Template Into A VM
Name:
Convert-TemplateToVM
Syntax:
Convert-TemplateToVM -Template <ITemplate> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Convert the template into a VM.
Parameters:
-Template <ITemplate>
Template
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the template into a VM (synchronous call)
PS > $template = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Template
PS > $template.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Convert-TemplateToVM -Template $template
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the template into a VM (asynchronous call)
PS > $template = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Template
PS > $template.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Convert-TemplateToVM -Template $template -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Convert the template into a VM through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-Template -Id "0000000000001" | Convert-TemplateToVM
Update VM CDP Start Status
Name:
Set-VMCDPEnabledStatus
Syntax:
Set-VMCDPEnabledStatus -IsEnabled <Boolean> -VM <IVirtualMachine> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM CDP start status.
Note: The CDP can only be started when the VM is powered on.
Parameters:
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
VM CDP enabled?
Instructions for use:
-
Enabling CDP will automatically enable CDP cleanup, which cannot be disabled manually.
-
Disabling CDP will stop the CDP task of the VM. If the backed up IO logs whose retention time configured in the policy expires are not accessed within 3 days, they will be cleaned up to the recycle bin.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM CDP start status (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Set-VMCDPEnabledStatus -VM $vm -IsEnabled $true
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM CDP start status (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Set-VMCDPEnabledStatus -VM $vm -IsEnabled $true -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM CDP start status through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Set-VMCDPEnabledStatus -IsEnabled $true
The cmdlet Passes Through The Script Content To The Specified VM
Name:
Invoke-VMScript
Syntax:
Invoke-VMScript -VM <IVirtualMachine> -ScriptText <String> [-ScriptType <String>] -GuestUser <String> -GuestPassword <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The cmdlet passes through the script content to the specified VM.
When scriptType=py, the windows system must ensure that the python2.exe is in %PATH%, and the linux system need to have python2 programs in $PATH
When scriptType=py3, the windows system must ensure that the python3.exe is in %PATH%, and the linux system need to have python3 programs in $PATH
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
Specify the VM on whose operating system the script is to be run
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScriptText <String>
Specify the script content to pass through. The script content must be base64 encoded.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScriptType <String>
Specify the types of pass-through script. Types of script include: PY(Python script), PY2(Python2 script), PY3(Python3 script), SH(Shell) script, BAT(DOS script), PS1(PowerShell script)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GuestUser <String>
Guest username
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GuestPassword <String>
Guest password
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Pass through a command to the VM
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Invoke-VMScript -VM $vm -ScriptText "echo hello world" -ScriptType "PS1" -GuestUser admin -GuestPassword admin
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Pass through commands with special characters to the VM (use ` for Powershell escape characters)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Invoke-VMScript -VM $vm -ScriptText "echo "<1"" -ScriptType "PS1" -GuestUser admin -GuestPassword admin
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Pass through the script file to the VM through the pipe
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Invoke-VMScript -ScriptText "echo hello world" -ScriptType "PS1" -GuestUser admin -GuestPassword admin
Host Management
Query The Node List
Name:
Get-VMHost
Syntax:
Get-VMHost [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMHost [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the node list Query the corresponding list of node details on the HCI through the node list or the node name list.
Parameters:
-Name <String[]>
Name list. You can query the list of physical host details by name. Fuzzy query by 3 wildcards: *, ?, and [] is supported; is used to match any characters of any length, such as: 255.255.255.2.; ? is used to match any single character, such as: 255.255.255.25?; [] is used to match a single character range, such as: 255.255.255.25[0-6]. The name list can only contain one element. Exact query such as: 255.255.255.255 is supported.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Id <String[]>
Currently, the list of node IDs is based on the whole word matching rule. If the node ID does not exist, no error message is returned, but the node information is not filtered. In other words, the number of returned messages may be less than the specified number of IDs.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query by node name
PS > Get-VMHost -Name test-name
Query by multiple node names
PS > Get-VMHost -Name @("test-name1","test-name2")
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query by node ID
PS > Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
Query by multiple node IDs
PS > Get-VMHost -Id @("host-000000000001","host-000000000002")
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query storage information through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.Datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the router list through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.EdgeRouter
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the edge list through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.VDSwitch
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the log list through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.Log
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the list of alarm logs through the node
PS > $tmpHost = Get-VMHost -Id host-000000000001
PS > $tmpHost.AlarmLog
Query Physical Hosts In The LAN
Name:
Get-VMHostDiscover
Syntax:
Get-VMHostDiscover [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query physical hosts in the LAN.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query physical hosts in the LAN
PS > Get-VMHostDiscover
Query The Node DNS
Name:
Get-VMHostDNS
Syntax:
Get-VMHostDNS -VMHost <IVMHost> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the node DNS.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node DNS
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-VMHostDNS -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query node DNS through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Get-VMHostDNS
Query The List Of Node Network Information
Name:
Get-VMHostNetwork
Syntax:
Get-VMHostNetwork [-InterfaceId <String[]>] [-VMHost <IVMHost>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of node network information.
Parameters:
-InterfaceId <String[]>
Interface ID List
The specified hostID must be input to query the specified interfaceIDs, that is, only the list of specified interfaces on one node can be queried.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of node network information
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-VMHostNetwork -InterfaceId eth0,eth1 -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of node network information through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Get-VMHostNetwork -InterfaceId eth0,eth1
Query The List Of Node Physical Interfaces
Name:
Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter [-VMHost <IVMHost>] [-Role <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId <String> -Id <String[]> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of node physical interfaces.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String>
Node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
Interface ID List
The specified hostID must be input to query the specified IDs, that is, only the list of specified interfaces on one node can be queried.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Role <String[]>
Interface role list types: MGMT, VXLAN, BUSINESS, and VS
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of node physical interfaces
PS > Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node physical interface information through the role
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Role MGMT,VXLAN
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node physical interface information by ID
PS > Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Id eth0
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node physical interface information through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Get-VMHostNetworkAdapter -Role MGMT,VXLAN
Query The Node Static Route List
Name:
Get-VMHostStaticRoute
Syntax:
Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost <IVMHost> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the node static route list.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node, required parameter: node ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node static route list
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the node static route list through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Get-VMHostStaticRoute
Add Physical Host Pre-upgrade Check
Name:
Add-VMHostPreCheck
Syntax:
Add-VMHostPreCheck -AddHostConfig <IAddVMHostConfig[]> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Add physical host pre-upgrade check.
Parameters:
-AddHostConfig <IAddVMHostConfig[]>
List of physical hosts
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Add physical host pre-upgrade check
PS > $hostConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.AddVMHostConfig;
PS > $hostConfig.IP = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $hostConfig.Username = "admin"
PS > $hostConfig.Password = "00000"
PS > Add-VMHostPreCheck -AddHostConfig $hostConfig
Query The Pre-upgrade Check Progress Information By The Added Physical Host
Name:
Get-AddVMHostPreCheckReport
Syntax:
Get-AddVMHostPreCheckReport -Log <ILog> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the pre-upgrade check progress information by the added physical host.
Parameters:
-Log <ILog>
Operation logs
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the pre-upgrade check progress information by the added physical host
PS > $logObj = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Log
PS > $logObj.Id = "UPID:host-005056b28798:00003441:AEC004C:6278D419:Add node environment check::admin@vtp:"
PS > Get-AddVMHostPreCheckReport -Log $logObj
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query information through the pipe
PS > $logObj = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Log
PS > $logObj.Id = "UPID:host-005056b28798:00003441:AEC004C:6278D419:Add node environment check::admin@vtp:"
PS > $logObj | Get-AddVMHostPreCheckReport
Query The List Of Node Resource Reservation Configuration Items
Name:
Get-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Syntax:
Get-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of node resource reservation configuration items.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of node resource reservation configuration items
PS > Get-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Query The List Of Node QOS Traffic Control Information
Name:
Get-VMHostNetworkQOS
Syntax:
Get-VMHostNetworkQOS [-VMHost <IVMHost[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of node Qos traffic control information.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost[]>
Node list, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
To query a specified node qos, the specified ID must be input; otherwise, all node qos will be returned.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of node Qos traffic control information
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-VMHostNetworkQOS -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
Query The Control Node Pool Information
Name:
Get-ControllerPool
Syntax:
Get-ControllerPool [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the control node pool information.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the control node pool information
PS > Get-ControllerPool
Update Node Configuration
Name:
Set-VMHost
Syntax:
Set-VMHost -VMHost <IVMHost> [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update node configuration.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
- A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
node name
Instructions for use:
-
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node configuration
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHost -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Notes test-notes -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node configuration
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHost -Notes test-notes -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear node description
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHost -Notes $null
Update The CPU Configuration For Node Network Forwarding
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkForwardCPU
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkForwardCPU -VMHost <IVMHost> [-Cores <Int64>] [-IsExclusiveModeEnabled <Boolean>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update the CPU configuration for node network forwarding.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Cores <Int64>
CPU cores consumed by network forwarding
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsExclusiveModeEnabled <Boolean>
Enable CPU exclusive mode (in this mode, the network performance is relatively high, but the specified number of CPU cores are exclusively used by the network)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the CPU configuration for node network forwarding
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkForwardCPU -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Cores 1 -IsExclusiveModeEnabled $false
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the CPU configuration for node network forwarding (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkForwardCPU -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Cores 1 -IsExclusiveModeEnabled $true -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the CPU configuration for node network forwarding through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostNetworkForwardCPU -Cores 1 -IsExclusiveModeEnabled $false
Edit The Storage Adapter IQN Of The Node
Name:
Set-VMHostHostIQN
Syntax:
Set-VMHostHostIQN -VMHost <IVMHost> -Target <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit the storage adapter IQN of the node.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Target <String>
ISCSI target
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit the storage adapter IQN of the node
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostHostIQN -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Target test-iscsi-target:host-000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit the storage adapter IQN of the node (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostHostIQN -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Target test-iscsi-target:host-000000000001 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit the storage adapter IQN of the node through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostHostIQN -Target test-iscsi-target:host-000000000001
Update The Session Configuration For Node Network Forwarding
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkForwardSession
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkForwardSession -Count <Int64> -VMHost <IVMHost> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update the session configuration for node network forwarding.
Parameters:
-Count <Int64>
Maximum concurrent connections
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the session configuration for node network forwarding
PS > $vmhosts=Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkForwardSession -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Count 1
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the session configuration for node network forwarding (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkForwardSession -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Count 1 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the session configuration for node network forwarding through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts=Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostNetworkForwardSession -Count 1
The Node Exits The Maintenance Mode
Name:
Set-VMHostLeaveProtectMode
Syntax:
Set-VMHostLeaveProtectMode -VMHost <IVMHost> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The node exits the maintenance mode.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
The node exits the maintenance mode
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostLeaveProtectMode -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
The node exits the maintenance mode (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostLeaveProtectMode -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
The node exits the maintenance mode through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostLeaveProtectMode
The Node Enters The Maintenance Mode
Name:
Set-VMHostEnterProtectMode
Syntax:
Set-VMHostEnterProtectMode -VMHost <IVMHost> [-ShouldStopVMHost] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The node enters the maintenance mode
Instructions for use:
If you need to replace or perform other maintenance operations on the node hardware (such as CPU, memory module, and NIC), you are recommended to switch the node to the maintenance mode, so that you can bulk migrate VMs of the node. In the maintenance mode, the node will not be an available node when the system performs tasks such as DRS and HA.
To maintain the disks, please contact a Sangfor technical support representative.
Note:
-
If the VM is performing other operations (such as being backed up), it cannot enter maintenance mode. You can wait for the task to be completed and try again.
-
If the operation you selected to perform on the device was unreasonable (for example, no suitable node can be found to migrate the VMs), you can re-select or manually process it and try again later.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldStopVMHost [<SwitchParameter>
Shut down after entering maintenance mode?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
The node enters the maintenance mode
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostEnterProtectMode -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -ShouldStopVMHost
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
The node enters maintenance mode (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostEnterProtectMode -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -ShouldStopVMHost -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
The node enters maintenance mode through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostEnterProtectMode -ShouldStopVMHost
Update Node Physical Interface
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId <String> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-NetworkLinkModeType <String>] [-Netmask <String>] [-VMHostNetworkAdapterPortId <Int64>] [-Mtu <Int64>] [-NetworkBondModeType <String>] [-NetworkInterfaceRoleType <String>] [-Address <String>
[-Gateway <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update node physical interface.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
HCI node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Physical interface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkLinkModeType <String>
Link negotiation mode
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Netmask <String>
Mask
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostNetworkAdapterPortId <Int64>
VLAN subinterface ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Mtu <Int64>
Interface MTU
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkBondModeType <String>
Aggregate interface mode
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkInterfaceRoleType <String>
Interface role
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Address <String>
IP address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsFusionEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Storage network interface multiplexing
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Gateway <String>
Gateway
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node physical interface
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name eth0 -Notes test-notes -NetworkLinkModeType BASE_T_FD10 -VMHostNetworkAdapterPortId 0 -Mtu 0 -NetworkBondModeType ROUND_ROBIN -NetworkInterfaceRoleType VXLAN -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1
-IsFusionEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node physical interface (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name eth0 -Notes test-notes -NetworkLinkModeType BASE_T_FD10 -VMHostNetworkAdapterPortId 0 -Mtu 0 -NetworkBondModeType ROUND_ROBIN -NetworkInterfaceRoleType VXLAN -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1
-IsFusionEnabled -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the description of the node physical interface
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name eth0 -Notes $null
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the physical interface IP of the node
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapter -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name eth0 -Address $null -Netmask $null -Gateway $null
Update Node Static Route
Name:
Set-VMHostStaticRoute
Syntax:
Set-VMHostStaticRoute -Netmask <String> -VMHost <IVMHost> -Gateway <String> -Address <String> -VMHostStaticRoute <IVMHostStaticRoute> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update node static route.
Parameters:
-Netmask <String>
Subnet mask
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Gateway <String>
Gateway
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Address <String>
IP address
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostStaticRoute <IVMHostStaticRoute>
Static route, required parameter: Static route ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node static route
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $routes = Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
PS > Set-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1 -VMHostStaticRoute $routes[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node static route (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $routes = Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
PS > Set-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1 -VMHostStaticRoute $routes[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node static route through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $routes = Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostStaticRoute -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1 -VMHostStaticRoute $routes[0]
Update node static route through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $routes = Get-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
PS > $routes[0] | Set-VMHostStaticRoute -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -Address 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1
Switch The Node Management Interface
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdpterManagementIface
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdpterManagementIface -IP <String> -Netmask <String> -VMHostId <String> -InterfaceName <String> [-Gateway <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Switch the node management interface.
Parameters:
-IP <String>
IP address
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Netmask <String>
Subnet mask
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String>
node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-InterfaceName <String>
Management interface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Gateway <String>
Gateway
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Switch the node management interface
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdpterManagementIface -VMHostId host-000000000001 -IP 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1 -InterfaceName test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Switch the node management interface (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdpterManagementIface -VMHostId host-000000000001 -IP 192.168.0.2 -Netmask 255.255.255.0 -Gateway 192.168.0.1 -InterfaceName test-name -RunAsync
Update Node DNS
Name:
Set-VMHostDNS
Syntax:
Set-VMHostDNS -VMHost <IVMHost> -DNS <String[]> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update node DNS.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Specify the node object to be configured, required parameter: node ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DNS <String[]>
List of DNS information: You can enter up to 3 DNS in this list or leave it empty. When it is empty, it means to clear the node DNS list.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the node DNS
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostDNS -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -DNS $("8.8.8.8","114.114.114.114")
Bulk Update Node QoS Traffic Controls
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkQOS
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkQOS -VMHost <IVMHost> -InterfaceName <String> [-VxlanUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>] [-VsUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>] [-MgmtUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>] [-BusinessUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Bulk update node QoS traffic controls.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-InterfaceName <String>
Interface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VxlanUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>
Upper limit of overlay network interface traffic, in Mb/s (the minimum value is 100 and the maximum value is 10000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VsUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>
Upper limit of storage interface traffic, in Mb/s (the minimum value is 1000 and the maximum value is 40960)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MgmtUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>
Upper limit of management interface traffic, in Mb/s (the minimum value is 100 and the maximum value is 10000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BusinessUpperThresholdMbps <Int64>
Upper limit of service interface traffic, in Mb/s (the minimum value is 100 and the maximum value is 10000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Bulk update node QoS traffic controls
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkQOS -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -InterfaceName test-name -VxlanUpperThresholdMbps 100 -VsUpperThresholdMbps 1000 -MgmtUpperThresholdMbps 100 -BusinessUpperThresholdMbps 100
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Bulk update node QoS traffic controls (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkQOS -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -InterfaceName test-name -VxlanUpperThresholdMbps 100 -VsUpperThresholdMbps 1000 -MgmtUpperThresholdMbps 100 -BusinessUpperThresholdMbps 100 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Bulk update node QoS traffic controls through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostNetworkQOS -InterfaceName test-name -VxlanUpperThresholdMbps 100 -VsUpperThresholdMbps 1000 -MgmtUpperThresholdMbps 100 -BusinessUpperThresholdMbps 100
Update Node Resource Reservation Configuration Items
Name:
Set-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Syntax:
Set-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost <IVMHost> -ReservedMemoryMb <Int64> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update node resource reservation configuration items.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ReservedMemoryMb <Int64>
Reserved memory size
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node resource reservation configuration items
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Set-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -ReservedMemoryMb 1024
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update node resource reservation configuration items through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Set-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -ReservedMemoryMb 1024
Set The Control Node As An Active Node
Name:
Set-VMHostActiveController
Syntax:
Set-VMHostActiveController -VMHostId <String> -ReplacedhostId <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Set the control node as an active node.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
ID of node set as an active node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ReplacedhostId <String>
ID of the node replaced as the alternative control node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Set the control node as an active node
PS > Set-VMHostActiveController -VMHostId host-000000000001 -ReplacedhostId host-000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Set the control node as an active node (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-VMHostActiveController -VMHostId host-000000000001 -ReplacedhostId host-000000000002 -RunAsync
Update The Configuration Of Control Node Pool
Name:
Set-ControllerPool
Syntax:
Set-ControllerPool -TimeoutSeconds <Int64> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update the configuration of control node pool.
Parameters:
-TimeoutSeconds <Int64>
Fault rebuild time
Instructions for use:
- After a control node fails and goes offline, it will be automatically rebuilt after the following set period expires. If two control nodes fail at the same time during this period, automatic rebuild is not supported.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the configuration of control node pool
PS > Set-ControllerPool -TimeoutSeconds 1
Switch The Node Overlay Network Interface
Name:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdapterVXLan
Syntax:
Set-VMHostNetworkAdapterVXLan -VMHostId <String> -InterfaceName <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Switch the node overlay network interface.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-InterfaceName <String>
Overlay network interface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Switch the node overlay network interface
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapterVXLan -VMHostId host-000000000001 -InterfaceName eth0
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Switch the node overlay network interface (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-VMHostNetworkAdapterVXLan -VMHostId host-000000000001 -InterfaceName eth0 -RunAsync
Create Node Aggregate Interface
Name:
New-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond
Syntax:
New-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId <String> -Mode <String> -Members <String[]> [-Iface <IIface>] [-IsFusionenabled] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create node aggregate interface.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
HCI node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Mode <String>
The aggregate interface modes include ROUND_ROBIN, ACTIVE_BACKUP, LAYER2, LAYER23, and LAYER34.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Members <String[]>
Aggregate members: 2-8 interfaces are required for aggregation
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Iface <IIface>
Basic configuration of interface
To construct, see NOTES section for IFACE properties and create a hash table.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsFusionenabled [<SwitchParameter>
Multiplexing switch
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create node aggregate interface of the ACTIVE_BACKUP type
PS > $iface = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iface
PS > $iface.Notes = "test-notes"
PS > $iface.IsEnabled = $True
PS > $iface.NetMask = "255.255.255.0"
PS > $iface.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > New-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Mode ACTIVE_BACKUP -Members eth0,eth1 -Iface $iface -IsFusionenabled
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create node aggregate interface of the ACTIVE_BACKUP type (asynchronous call)
PS > $iface = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iface
PS > $iface.Notes = "test-notes"
PS > $iface.IsEnabled = $True
PS > $iface.NetMask = "255.255.255.0"
PS > $iface.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > New-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Mode ACTIVE_BACKUP -Members eth0,eth1 -Iface $iface -IsFusionenabled -RunAsync
Create Node VLAN Sub-interface
Name:
New-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort
Syntax:
New-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VMHostId <String> -VMHostNetworkAdapterPort <IVMHostNetworkAdapterPort> [-Iface <IIface>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create node VLAN subinterface.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
HCI node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort <IVMHostNetworkAdapterPort>
VLAN ID, required parameters: VLAN ID (Id) and the interface of the VLAN (InterfaceName)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Iface <IIface>
Basic configuration of interface
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create node VLAN subinterface
PS > $iface = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iface
PS > $iface.Notes = "test-note"
PS > $iface.IsEnabled = $True
PS > $iface.NetMask = "255.255.255.0"
PS > $iface.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $adapterPort = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHostNetworkAdapterPort
PS > $adapterPort.Id = 60
PS > $adapterPort.InterfaceName = "eth0"
PS > New-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Iface $iface -VMHostNetworkAdapterPort $adapterPort
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create node VLAN subinterface (asynchronous call)
PS > $iface = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iface
PS > $iface.Notes = "test-note"
PS > $iface.IsEnabled = $True
PS > $iface.NetMask = "255.255.255.0"
PS > $iface.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $adapterPort = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHostNetworkAdapterPort
PS > $adapterPort.Id = 60
PS > $adapterPort.InterfaceName = "eth0"
PS > New-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Iface $iface -VMHostNetworkAdapterPort $adapterPort -RunAsync
Add Node Resource Reservation Configuration Item
Name:
New-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Syntax:
New-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost <IVMHost> -ReservedMemoryMb <Int64> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Add node resource reservation configuration item
Instructions for use:
Resource reservation indicates that a certain resource space is reserved on some nodes, and these resources will not be used by the system or other VMs.
When a node fails or a disaster recovery switchover occurs, the reserved node resources can be used to recover the VM immediately, reducing the risk of failure of recovery from a service fault due to insufficient resources.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ReservedMemoryMb <Int64>
Reserved memory size
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Add node resource reservation configuration item
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > New-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost $vmhosts[0] -ReservedMemoryMb 1024
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Add node resource reservation configuration item through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | New-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -ReservedMemoryMb 1024
Add A Node To The Control Node Pool
Name:
New-ControllerPool
Syntax:
New-ControllerPool -VMHost <IVMHost> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Add a node to the control node pool.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Add a node to the control node pool
PS > New-ControllerPool -VMHost host-000000000001
Delete Node Aggregate Interface
Name:
Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond
Syntax:
Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId <String> -BondName <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete node aggregate interface.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String>
node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BondName <String>
Aggregate interface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node aggregate interface
PS > Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId host-000000000001 -BondName test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node aggregate interface (asynchronous call)
PS > Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterBond -VMHostId host-000000000001 -BondName test-name -RunAsync
Delete Node VLAN Sub-interface
Name:
Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort
Syntax:
Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VdPortName <String> -VMHostId <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete node VLAN subinterface.
Parameters:
-VdPortName <String>
VLAN subinterface name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String>
node ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node VLAN subinterface
PS > Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VMHostId host-000000000001 -VdPortName test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node VLAN subinterface (asynchronous call)
PS > Remove-VMHostNetworkAdapterPort -VMHostId host-000000000001 -VdPortName test-name -RunAsync
Delete Node Resource Reservation Configuration Item
Name:
Remove-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Syntax:
Remove-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost <IVMHost> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete node resource reservation configuration item.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node resource reservation configuration item
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Remove-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete node resource reservation configuration items through the pipe
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > $vmhosts[0] | Remove-VMHostResourceReservedConfiguration
Delete The Node From The Control Node Pool
Name:
Remove-ControllerPool
Syntax:
Remove-ControllerPool -VMHost <IVMHost> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete the node from the control node pool.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the node from the control node pool
PS > $vmhosts = Get-VMHost
PS > Remove-ControllerPool -VMHost $vmhosts[0]
Restart Node
Name:
Restart-VMHost
Syntax:
Restart-VMHost -VMHost <IVMHost> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Restart node.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart node
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > Restart-VMHost -VMHost $vmhost
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart the node (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > Restart-VMHost -VMHost $vmhost -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Restart the node through the pipe
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > $vmhost | Restart-VMHost
Shut Down Node
Name:
Stop-VMHost
Syntax:
Stop-VMHost -VMHost <IVMHost> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Shut down node.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Shut down node
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > Stop-VMHost -VMHost $vmhost
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Shut down node (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > Stop-VMHost -VMHost $vmhost -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Shut down the node through the pipe
PS > $vmhost = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMHost
PS > $vmhost.Id = "host-000000000001"
PS > $vmhost | Stop-VMHost
Add Physical Host To The Cluster
Name:
Add-VMHost
Syntax:
Add-VMHost -AddHostConfig <IAddVMHostConfig[]> [-SkipprecheckIdList <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Add physical host to the cluster.
Use the command Get-AddVMHostPreCheck to check whether the environment is normal before using this command.
Parameters:
-AddHostConfig <IAddVMHostConfig[]>
List of physical hosts
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SkipprecheckIdList <String[]>
Skip pre-upgrade check
The pre-upgrade check of the confirm type can be skipped after adding.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Add physical host to the cluster
PS > $hostConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.AddVMHostConfig
PS > $hostConfig.IP = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $hostConfig.Username = "test-name"
PS > $hostConfig.Password = "000000";
PS > $hostConfig.Roles = @("CONTROLLER")
PS > Add-VMHost -AddHostConfig $hostConfig -SkipprecheckIdList @("check-ups")
CD Drive Management
Query the CD/DVD list
Name:
Get-CDDrive
Syntax:
Get-CDDrive -VMId <String> [<CommonParameters>
Get-CDDrive [-Id <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the CD/DVD list.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
VM ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
CD/DVD ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all CD/DVDs on a specific VM
PS > Get-CDDrive -VMId "0000000000001"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the VM CD/DVD by ID
PS > Get-CDDrive -Id "0000000000001:ide2"
Query VM Image
Name:
Get-ISOImage
Syntax:
Get-ISOImage [-VM <IVirtualMachine>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query VM image
Note:
-
Specify the storage ID and VM ID at the same time: The specified VM can access the iso file in the specified storage.
-
The storage ID and VM ID are not specified at the same time: Query all images.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM: Filter the list of iso files that can be accessed by the specified VM
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Storage: The list of accessible ISO files under the specified storage can be filtered
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query ISO files that can be accessed by the specified VM on the specified storage
PS > $datastore = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $datastore.Id = "xxx"
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Get-ISOImage -VM $vm -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query ISO files that can be accessed by the specified VM on the specified storage through the pipe
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id "xxx"
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Get-ISOImage -Datastore $datastore
Update CD/DVD Information
Name:
Set-CDDrive
Syntax:
Set-CDDrive -CdDrive <ICdDrive> [-Path <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update CD/DVD information
Parameters:
-CdDrive <ICdDrive>
CD/DVD
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Path <String>
Image file storage path
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreId <String>
Storage id
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update CD/DVD information (synchronous call)
PS > $cddrive = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CdDrive
PS > $cddrive.Id = "0000000000001:ide2"
PS > Set-CDDrive -CdDrive $cddrive -Path "iso/vmtools/tftproot/WinPE.iso" -DatastoreId "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update CD/DVD information (asynchronous call)
PS > $cddrive = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CdDrive
PS > $cddrive.Id = "0000000000001:ide2"
PS > Set-CDDrive -CdDrive $cddirve -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update CD/DVD information through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-CdDrive -Id "0000000000001:ide2" | Set-CDDrive
Create CD/DVD
Name:
New-CDDrive
Syntax:
New-CDDrive -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-Path <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create CD/DVD.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Path <String>
Image file storage path
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreId <String>
Storage id
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create CD/DVD (synchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > New-CDDrive -VM $vm -Path "iso/vmtools/tftproot/WinPE.iso" -DatastoreId "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create CD/DVD (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > New-CDDrive -VM $vm -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create CD/DVD through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | New-CDDrive
Delete CD/DVD
Name:
Remove-CDDrive
Syntax:
Remove-CDDrive [-CdDrive <ICdDrive>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete CD/DVD.
Parameters:
-CdDrive <ICdDrive>
CD/DVD
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete CD/DVD (synchronous call)
PS > $cddrive = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CdDrive
PS > $cddrive.Id = "0000000000001:ide2"
PS > Remove-CDDrive -CdDrive $cddrive
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete CD/DVD (asynchronous call)
PS > $cddrive = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CdDrive
PS > $cddrive.Id = "0000000000001:ide2"
PS > Remove-CDDrive -CdDrive $cddrive -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete CD/DVD through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-CDDrive -Id "0000000000001:ide2" | Remove-CDDrive
Log
Query Operation Logs
Name:
Get-Log
Syntax:
Get-Log [-ObjectName <String>] [-Keyword <String>] [-State <String>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-StartTime <String>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-EndTime <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-Log -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query log information.
Query the task details by ID.
Returned results are sorted by time.
Parameters:
-ObjectName <String>
Operation object name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Keyword <String>
Query by keywords, fuzzy search of actions, nodes, objects, and descriptions.
Fuzzy search is a substring matching rule and does not support regular expressions or wildcard rules.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Operation log ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-State <String>
Operation log status
Including UNDEFINED (unknown), WAITING (waiting), RUNNING (running), CANCELING (canceling), FAILED (executed but failed), and SUCCESS (successfully executed)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Size of each page (the default value is 50, the minimum value is 1, and the maximum value is 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StartTime <String>
Query by the start time of operation logs.
It does not match the whole word, but filters all operation logs whose start time is after the specified time, and the results are sorted in descending order of time by default.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Page start position, whose default value and minimum value are both 0.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EndTime <String>
Sorted by the end time of operation logs.
It does not match the whole word, but filters all operation logs whose end time is before the specified time, and the results are sorted in descending order of time by default.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all operation logs
PS > Get-Log
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of operation logs by object name
PS > Get-Log -ObjectName "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query operation logs by keywords
PS > Get-Log -Keyword "VM"
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of operation logs by task status
PS > Get-Log -State "FAILED"
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of operation logs by page start position and page size
PS > Get-Log -Offset 0 -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of operation logs by task start time and end time
PS > Get-Log -StartTime "2022-05-25T01:30:31+08:00" -EndTime "2022-05-25T01:30:36+08:00"
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of operation logs by ID
PS > Get-Log -Id "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through operation logs
PS > $logs = Get-Log -Keyword "VM"
PS > $logs[0].VM
Drill-down query storage through operation logs
PS > $logs = Get-Log -Keyword "Datastore"
PS > $logs[0].Datastore
Drill-down query nodes through operation logs
PS > $logs = Get-Log -Keyword "node"
PS > $logs[0].VMHost
Drill-down query edges through operation logs
PS > $logs = Get-Log -Keyword "Edge"
PS > $logs[0].VDSwitch
Drill-down query switches through operation logs
PS > $logs = Get-Log -Keyword "Switch"
PS > $logs[0].DistributeSwitch
Create Operation Log
Name:
New-Log
Syntax:
New-Log [-Id <String>] -Objectname <String> -Action <String> -ObjectId <String> -Objecttype <String> [-CreatorIP <String>] [-Notes <String>] [-Creatorname <String>] [-Progress <Int64>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create operation log.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
Operation log id
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Objectname <String>
The name of operation object
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Action <String>
Operation object action
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectId <String>
Operation object ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Objecttype <String>
Operation object type
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CreatorIP <String>
IP of creator
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Creatorname <String>
Username of creator
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Progress <Int64>
Progress
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create operation log (synchronous call)
PS > New-Log -Id "xxx" -ObjectName "test-name" -Action "Create" -ObjectId "0000000000001" -Objecttype "vm" -Notes "test-notes" -Creatorname "admin" -Progress 100
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create operation log (asynchronous call)
PS > New-Log -Objectname "test-name" -Action "Create" -Objecttype "vm" -RunAsync
Task Management
Query Task Information
Name:
Get-Task
Syntax:
Get-Task [-State <String>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-Offset <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-Task -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query task information.
Parameters:
-State <String>
Operation task status
Including UNDEFINED (unknown), WAITING (waiting), RUNNING (running), CANCELING (canceling), FAILED (executed but failed), and SUCCESS (successfully executed)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Size of each page (the default value is 50, the minimum value is 1, and the maximum value is 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Page start position, whose default value and minimum value are both 0.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Operation task ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all task information
PS > Get-Task
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of task information by task status
PS > Get-Task -State "UNDEFINED"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of task information by page start position and page size
PS > Get-Task -Offset 0 -Limit 50
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of task information by task ID
PS > Get-Task -Id "xxx"
Query Task Progress Information
Name:
Get-TaskProcess
Syntax:
Get-TaskProcess -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query task progress information.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
Operation log ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query task progress information
PS > Get-TaskProcess -Id "xxx"
Cancel Task
Name:
Stop-Task
Syntax:
Stop-Task -Task <ITask> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Cancel task.
Parameters:
-Task <ITask>
Task
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Cancel task (synchronous call)
PS > $task = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Task
PS > $task.Id = "xxx"
PS > Stop-Task -Task $task
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Cancel task (asynchronous call)
PS > $task = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Task
PS > $task.Id = "xxx"
PS > Stop-Task -Task $task -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Cancel the task through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-Task -Id "xxx" | Stop-Task
Storage Management
Query The Storage List In The Cluster
Name:
Get-Datastore
Syntax:
Get-Datastore [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-Datastore [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
This interface queries the storage list in the cluster, including system disks and other disks. However, if the system disk capacity does not exceed 256G, system disks cannot be found through this interface, while other disks still can be found.
Parameters:
-Name <String[]>
List of storage names, for filtering by name based on the whole word matching rule.
If not matched, no error message is returned, but the storage information is not filtered. In other words, the number of returned messages may be less than the specified number of names.
Fuzzy matching and exact matching are supported. See the wildcardDatastoreName instruction for details.
Currently, only one name can be input.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Id <String[]>
Specify the list of storage IDs to be searched
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query storage
PS > Get-Datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query storage by name
PS > Get-Datastore -Name "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query storage by ID
PS > Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
PS > $datastore.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the node information
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
PS > $datastore.VMHost
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the user information
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
PS > $datastore.User
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the log information
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
PS > $datastore.Log
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the alarm log information
PS > $datastore = Get-Datastore -Id testId0001
PS > $datastore.AlarmLog
Scan For Disks
Name:
Scan-Datastore
Syntax:
Scan-Datastore [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Scan for disks
Instructions for use:
If a disk is not listed when adding storage, you can call this interface to scan the disk.
Parameters:
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Scan for disks
PS > Scan-Datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Scan for disks (asynchronous call)
PS > Scan-Datastore -RunAsync
Query NFS Server Information
Name:
Get-NFSServer
Syntax:
Get-NFSServer -IPAddress <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query NFS server information.
Parameters:
-IPAddress <String>
NFS server address
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query NFS server information
Get-NFSServer -IPAddress "192.168.0.1"
Query The List Of Storage Policy Information For The Virtual Storage
Name:
Get-StoragePolicy
Syntax:
Get-StoragePolicy [-VolumeId <String>] [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-StoragePolicy [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of storage policy information for the virtual storage.
Parameters:
-VolumeId <String>
Filter by virtual datastore ID, with shared disks created on this virtual datastore only.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Filter by storage policy name, supporting fuzzy matching and exact matching. For details, see the wildcardStoragePolicyName instruction.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
List of storage policy IDs, for filtering by ID based on the whole word matching rule.
If the storage policy ID does not exist, no error message is returned, but the storage policy information is not filtered. In other words, the number of returned messages may be less than the specified number of IDs.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of storage policy information for the virtual storage
PS > Get-StoragePolicy -VolumeId volumeid0001 -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of storage policy information for the virtual storage by ID
PS > Get-StoragePolicy -Id policyId0001
Query The List Of iSCSI Server Connection Information
Name:
Get-ISCSIServerConnection
Syntax:
Get-ISCSIServerConnection [<CommonParameters>
Get-ISCSIServerConnection -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of iSCSI server connection information.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
iSCSI server connection information ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of iSCSI server connection information
PS > Get-ISCSIServerConnection
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of iSCSI server connection information by ID
PS > Get-ISCSIServerConnection -Id testId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of iSCSI server connection information through the pipe
PS > "testId0001" | Get-ISCSIServerConnection
Update Storage
Name:
Set-Datastore
Syntax:
Set-Datastore -Datastore <IStorageResource> [-Name <String>] [-AttachToVMHostId <String[]>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update storage.
Parameters:
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Datastore
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Storage name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AttachToVMHostId <String[]>
List of IDs of nodes that mount this storage
Instructions for use:
1.
When multiple nodes can access the current storage, which nodes can be configured to mount the current storage?
2.
If not specified, all nodes that can access the current storage will be added to the list.
3.
Nodes that cannot access this storage cannot be added to the list.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update storage
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > Set-Datastore -Datastore $storages[0] -Name test-name -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update storage (asynchronous call)
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > Set-Datastore -Datastore $storages[0] -Name test-name -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update storage through the pipe
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > $storages[0] | Set-Datastore -Name test-name -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001
Update Storage Policy
Name:
Set-StoragePolicy
Syntax:
Set-StoragePolicy -StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy> [-Notes <String>] [-QosPriority <String>] [-Replicaplacement <String>] [-Replica <String>] [-Stripewidth <Int64>] [-Replicadefrag <String>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update storage policy. This is a synchronous request that returns the storage policy details.
Parameters:
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Usage restrictions as follows:
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
-
The maximum length is 255 characters or 85 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-QosPriority <String>
Automated QoS types of storage policy: NORMAL (default performance), LOW (low performance), and HIGH (high performance)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replicaplacement <String>
Replica placement
Usage restrictions as follows:
- 3 replicas (only support stretched datastore)
Replica placement modes: NORMAL (normal allocation), PRIMARY_FAULT_DOMAIN (primary fault domain priority), and SECONDARY_FAULT_DOMAIN (secondary fault domain priority)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replica <String>
Replicas. Storage policy replica types: REPLICA_TWO (2 replicas), REPLICA_THREE_NORMAL (3 replicas (ordinary datastore)), and REPLICA_THREE_STRETCHED (3 replicas (stretched datastore))
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Stripewidth <Int64>
Number of stripes
Function description:
Striping is to divide data into small pieces and save them to different physical disks. The stripe width reflects the number of physical disks that can be used by a VM at the same time. There is a normal curve relationship between the performance of the VM and the stripe width, and an
appropriate stripe width is required to maximize IO performance.
Suggested use:
In most scenarios, you can use the default "Adaptive".
In an all-flash scenario, you can set the number of stripes to the number of SSDs on a single node, so that the VM can use the concurrent performance of all SSDs on this node.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replicadefrag <String>
Replica defrag. The storage policy replica defrag status includes AUTO (adaptive), ENABLED (replica defrag enabled), and DISABLED (replica defrag disabled).
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Storage policy name.
Usage restrictions as follows:
-
Can only contain digits, underscores (_), letters, and Chinese characters.
-
The maximum length is 64 characters or 21 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update storage policy
PS > $policy = Get-StoragePolicy -Id policyId0001
PS > Set-StoragePolicy -StoragePolicy $policy -Notes test-note -QosPriority "NORMAL" -Replicaplacement "NORMAL" -Replica "REPLICA_TWO" -Stripewidth 1 -Replicadefrag "AUTO" -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update storage policy through the pipe
PS > $policy = Get-StoragePolicy -Id policyId0001
PS > $policy | Set-StoragePolicy -Notes test-note -QosPriority "NORMAL" -Replicaplacement "NORMAL" -Replica "REPLICA_TWO" -Stripewidth 1 -Replicadefrag "AUTO" -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear storage policy description
PS > $policy = Get-StoragePolicy -Id policyId0001
PS > $policy | Set-StoragePolicy -Notes $null
Update iSCSI Server Connection Information
Name:
Set-ISCSIServerConnection
Syntax:
Set-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection <IIscsiServerConnection> [-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [-ShouldReconnect <Boolean>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update iSCSI server connection information.
Parameters:
-IscsiServerConnection <IIscsiServerConnection>
iSCSI server connection information
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Server authenticates initiator (one-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
1.
The authentication account used to connect this device to the iSCSI server is provided by the iSCSI server, and only local connection to iSCSI server is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Initiator authenticates the server (two-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
1.
The authentication account used to connect the iSCSI server to this device is provided by this device, and only iSCSI connection is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldReconnect <Boolean>
Rescanned?
Instructions for use:
1.
Rescanning will cause the LUN mounted on the iSCSI storage server to be offline for a short time, and cause the VM running on the storage server to be suspended or restarted due to IO error, thus affecting the service. You can migrate the running VM to another storage or shut down and try again!
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update iSCSI server connection information
PS > $iscsiServers = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > Set-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection $iscsiServers[0] -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap -ShouldReconnect $true
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update iSCSI server connection information
PS > $iscsiServers = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > Set-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection $iscsiServers[0] -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap -ShouldReconnect $true -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update iSCSI server connection information through the pipe
PS > $iscsiServers = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $iscsiServers[0] | Set-ISCSIServerConnection -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap -ShouldReconnect $true -RunAsync
Mount Storage To The Platform
Name:
New-Datastore
Syntax:
New-Datastore -Datastore <IStorageResource> -Name <String> [-ShouldImportVM] [-Notes <String>] [-AttachToVMHostId <String[]>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-Datastore -Server <IAttachNfsDatastoreServer> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-AttachToVMHostId <String[]>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Mount storage to the platform
Instructions for use:
If the storage has not been added by the platform before (the platform has not formatted the storage), it will be formatted and the original data will be lost. Please check before operation.
If the storage has been added by the platform before (the platform has formatted the storage), it will no longer be formatted and can be used directly after mounting. If you want to reformat the storage, please call the formatting interface to reformat it.
Add NFS storage.
Parameters:
-Server <IAttachNfsDatastoreServer>
Add input parameter information of the nfs storage server
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Storage to be added
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Storage Name
Instructions for use:
-
Can only contain digits, letters, underscores (_), decimal points, and horizontal lines (-), and must start and end with a digit or letter.
-
The length is 2-16 characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldImportVM [<SwitchParameter>
VMs in storage imported?
Instructions for use:
-
If the storage has been used by the Sangfor HCI Platform with VMs on this storage, when the VMs are re-added to the platform, this parameter can be used to control whether to import the VMs in the storage to the platform.
-
The default is false, that is, no import.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
-
The length is limited to 255 characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AttachToVMHostId <String[]>
List of IDs of nodes that mount this storage
Instructions for use:
-
When multiple nodes can access the current storage, which nodes can be configured to mount the current storage?
-
If not specified, all nodes that can access the current storage will be added to the list.
-
Nodes that cannot access this storage cannot be added to the list.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount storage to the platform through Datastore
PS > $storage = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $storage.Id = ((Get-HardDisk).id)[0]
PS > New-Datastore -Datastore $storage -Name test-name -ShouldImportVM -Notes test-note -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount storage to the platform through Datastore (asynchronous call)
PS > $storage = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $storage.Id = ((Get-HardDisk).id)[0]
PS > New-Datastore -Datastore $storage -Name test-name -ShouldImportVM -Notes test-note -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount storage to the platform through the server
PS > $server = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.AttachNfsDatastoreServer
PS > $server.Id = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $server.Path = "serverPath"
PS > New-Datastore -Server $server -Name test-name -Notes test-note -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount storage to the platform through the server (asynchronous call)
PS > $server = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.AttachNfsDatastoreServer
PS > $server.Id = "192.168.0.1"
PS > $server.Path = "serverPath"
PS > New-Datastore -Server $server -Name test-name -Notes test-note -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount the storage to the platform through the pipe
PS > $storage = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $storage.Id = ((Get-HardDisk).id)[0]
PS > $storage | New-Datastore -Name test-name -ShouldImportVM -Notes test-note -AttachToVMHostId host-000000000001
Create Storage Policy
Name:
New-StoragePolicy
Syntax:
New-StoragePolicy -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-QosPriority <String>] [-Replicaplacement <String>] [-Replica <String>] [-Stripewidth <Int64>] [-Replicadefrag <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create a storage policy. This is a synchronous request that returns the storage policy details.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Storage policy name.
Usage restrictions as follows:
-
Can only contain digits, underscores (_), letters, and Chinese characters.
-
The maximum length is 64 characters or 21 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Usage restrictions as follows:
-
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
-
The maximum length is 255 characters or 85 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-QosPriority <String>
Automated QoS types of storage policy: NORMAL (default performance), LOW (low performance), and HIGH (high performance)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replicaplacement <String>
Replica placement
Usage restrictions as follows:
- 3 replicas (only support stretched datastore)
Replica placement modes: NORMAL (normal allocation), PRIMARY_FAULT_DOMAIN (primary fault domain priority), and SECONDARY_FAULT_DOMAIN (secondary fault domain priority)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replica <String>
Replicas. Storage policy replica types: REPLICA_TWO (2 replicas), REPLICA_THREE_NORMAL (3 replicas (ordinary datastore)), and REPLICA_THREE_STRETCHED (3 replicas (stretched datastore))
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Stripewidth <Int64>
Number of stripes
Function description:
Striping is to divide data into small pieces and save them to different physical disks. The stripe width reflects the number of physical disks that can be used by a VM at the same time. There is a normal curve relationship between the performance of the VM and the stripe width, and an
appropriate stripe width is required to maximize IO performance.
Suggested use:
In most scenarios, you can use the default "Adaptive".
In an all-flash scenario, you can set the number of stripes to the number of SSDs on a single node, so that the VM can use the concurrent performance of all SSDs on this node.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Replicadefrag <String>
Replica defrag. The storage policy replica defrag status includes AUTO (adaptive), ENABLED (replica defrag enabled), and DISABLED (replica defrag disabled).
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create storage policy
PS > New-StoragePolicy -Name test-name -Notes test-note -QosPriority "NORMAL" -Replicaplacement "NORMAL" -Replica "REPLICA_TWO" -Stripewidth 1 -Replicadefrag "AUTO"
Create iSCSI Server Connection Information
Name:
New-ISCSIServerConnection
Syntax:
New-ISCSIServerConnection -Port <Int64> -Address <String> [-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create iSCSI server connection information.
Parameters:
-Port <Int64>
Port of iSCSI server
Instructions for use:
- The default open port of the iSCSI server is 3260. For details, please check the relevant configuration of the iSCSI server.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Address <String>
IP address of ISCSI Server
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Server authenticates initiator (one-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
- The authentication account used to connect this device to the iSCSI server is provided by the iSCSI server, and only local connection to iSCSI server is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Initiator authenticates the server (two-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
- The authentication account used to connect the iSCSI server to this device is provided by this device, and only iSCSI connection is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create iSCSI server connection information
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > New-ISCSIServerConnection -Port 5555 -Address 192.168.0.1 -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap
Unmount Storage
Name:
Remove-Datastore
Syntax:
Remove-Datastore -Datastore <IStorageResource> [-IsEnforced] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Unmount storage
Instructions for use:
Unmounting storage will only delete the storage configuration, and will not clear the data in the storage. Afterwards, you can recover the storage through "Add storage".
Parameters:
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Datastore
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnforced [<SwitchParameter>
Force unmounted?
Instructions for use:
-
If the storage is forcibly unmounted, the system will automatically shut down "all VMs running on this storage" and disassociate "other VMs using the ISO image on this storage". If the VMs running on this storage are encrypted, when the storage is mounted to another cluster, these encrypted VMs cannot be recovered and powered on.
-
The default is to not force unmount.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > Remove-Datastore -Datastore $storages[0] -IsEnforced
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > Remove-Datastore -Datastore $storages[0] -IsEnforced -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > $storages = Get-Datastore
PS > $storages[0] | Remove-Datastore -IsEnforced
Delete Storage Policy
Name:
Remove-StoragePolicy
Syntax:
Remove-StoragePolicy -StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete a storage policy. This is a synchronous request. Successful deletion gets normal return, and an error is reported when the deletion fails.
Parameters:
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete storage policy
PS > $policys = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > Remove-StoragePolicy -StoragePolicy $policys[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete storage policy
PS > $policys = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $policys[0] | Remove-StoragePolicy
Delete iSCSI Server Connection Information
Name:
Remove-ISCSIServerConnection
Syntax:
Remove-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection <IIscsiServerConnection> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete iSCSI server connection information.
Parameters:
-IscsiServerConnection <IIscsiServerConnection>
iSCSI server connection information
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete iSCSI server connection information
PS > $iscsiServers = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > Remove-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection $iscsiServers[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete iSCSI server connection information (asynchronous call)
PS > $connection = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > Remove-ISCSIServerConnection -IscsiServerConnection $iscsiServers[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete iSCSI server connection information through the pipe
PS > $connection = Get-ISCSIServerConnection
PS > $iscsiServers[0] | Remove-ISCSIServerConnection -RunAsync
Format Storage
Name:
Format-Datastore
Syntax:
Format-Datastore -Datastore <IStorageResource> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Formatted storage
Instructions for use:
After formatting, all data on the storage will be cleared and cannot be recovered.
Parameters:
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
Datastore
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Formatted storage
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > Format-Datastore -Datastore $datastores[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Formatted storage
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > Format-Datastore -Datastore $datastores[0] -RunAsync
Authenticate iSCSI Target
Name:
Authenticate-ISCSITarget
Syntax:
Authenticate-ISCSITarget -ServerId <String> -TargetId <String> [-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Authenticate iSCSI target.
Parameters:
-ServerId <String>
iSCSI server ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetId <String>
The unique ID of the target in the platform
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-UnidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Server authenticates initiator (one-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
- The authentication account used to connect this device to the iSCSI server is provided by the iSCSI server, and only local connection to iSCSI server is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BidirectionalChap <IIscsichap>
Initiator authenticates the server (two-way authentication)
Instructions for use:
- The authentication account used to connect the iSCSI server to this device is provided by this device, and only iSCSI connection is required.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Authenticate iSCSI target
PS > $iscsiServer = Get-ISCSIServerConnection -Id testId0001
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > Authenticate-ISCSITarget -ServerId $iscsiServer.Id -TargetId testTargetId -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Authenticate iSCSI target (asynchronous authentication)
PS > $iscsiServer = Get-ISCSIServerConnection -Id testId0001
PS > $uChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $uChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $uChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > $bChap = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.Iscsichap
PS > $bChap.Username = "test-name"
PS > $bChap.Password = "12345678"
PS > Authenticate-ISCSITarget -ServerId $iscsiServer.Id -TargetId testTargetId -UnidirectionalChap $uChap -BidirectionalChap $bChap -RunAsync
Alert Management
Query The List Of Alarm Logs
Name:
Get-AlarmLog
Syntax:
Get-AlarmLog [-State <String[]>] [-ObjectId <String>] [-EventType <String>] [-Priority <String>] [-IsDistinct] [-Limit <Int64>] [-StartTime <String>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-EndTime <String>] [-ObjectType <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-AlarmLog [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-AlarmLog [-Keyword <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of alarm logs. When the resources in the platform are abnormal, the corresponding alarm information is recorded, and the alarms are divided into different levels according to the severity.
The returned results are sorted by time.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
List of alarm log IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Keyword <String>
Query by keywords. You can fuzzy query alarm events, objects, and descriptions.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-State <String[]>
Alarm handling status: UNHANDLED (unhandled), CONFIRMED (confirmed), and AUTO_RECOVERED (automatically recovered)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectId <String>
Alarm object ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EventType <String>
Alarm event type.
Different entity types are located to different alarm events to distinguish between different alarms.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Priority <String>
Alarm urgency: NORMAL and URGENT
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDistinct [<SwitchParameter>
"Duplicate alarms merged?" is "No" by default. If merged, only the latest alarm of the same type is displayed.
The alarm module periodically detects the resource status. After an alarm is triggered when the resource is abnormal, if the resource does not automatically return to normal within a period of time, multiple alarms of the same type may be triggered during this period.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Size of each page: The default value is 50, the minimum value is 1, and the maximum value is 1000.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StartTime <String>
Start time, the time when the alarm is triggered.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Page start position, whose default value and minimum value are 0.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EndTime <String>
The end time, which is the time recorded to the system when the alarm is triggered, is basically the same as the start time.
This time is not the time when the resources have been recovered after the alarm.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectType <String>
Alarm object type (host, datastore, vm, vnet, sn, and others)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of alarm logs
PS > Get-AlarmLog
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of alarm logs
PS > Get-AlarmLog -State UNHANDLED -ObjectId objectId00001 -EventType Storage Offline -Priority URGENT -IsDistinct -StartTime 2000-01-01T01:01:01+08:00 -Offset 0 -Limit 50 -EndTime 2001-01-01T01:01:01+08:00 -ObjectType datastore.
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of alarm logs by ID
PS > Get-AlarmLog -Id alarmLogId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of alarm logs by fuzzy matching
PS > Get-AlarmLog -Keyword test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $alarmLog = Get-AlarmLog -Id alarmLogId0001
PS > $alarmLog.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the node information
PS > $alarmLog = Get-AlarmLog -Id alarmLogId0001
PS > $alarmLog.VMHost
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the storage information
PS > $alarmLog = Get-AlarmLog -Id alarmLogId0001
PS > $alarmLog.Datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the object information
PS > $alarmLog = Get-AlarmLog -Id alarmLogId0001
PS > $alarmLog.Object
Query Alarm Settings
Name:
Get-AlarmConfig
Syntax:
Get-AlarmConfig [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query alarm settings.
Parameter:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > Get-AlarmConfig
Update Alarm Settings
Name:
Set-AlarmConfig
Syntax:
Set-AlarmConfig [-RunAsync] [-NetworkAlarmConfig <INetworkAlarmConfig>] [-VMAlarmConfig <IVMAlarmConfig>] [-ClusterAlarmConfig <IClusterAlarmConfig>] [-HostAlarmConfig <IHostAlarmConfig>] [-DatastoreAlarmConfig <IDatastoreAlarmConfig>] [-VirtualNetworkAlarmConfig <IVirtualNetworkAlarmConfig>
[<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update alarm settings.
Parameters:
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-NetworkAlarmConfig <INetworkAlarmConfig>
Physical network alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMAlarmConfig <IVMAlarmConfig>
VM alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ClusterAlarmConfig <IClusterAlarmConfig>
Cluster alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-HostAlarmConfig <IHostAlarmConfig>
node alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreAlarmConfig <IDatastoreAlarmConfig>
Storage alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VirtualNetworkAlarmConfig <IVirtualNetworkAlarmConfig>
Virtual network alarm settings
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update alarm settings
PS > $alarmConfig = Get-AlarmConfig
PS > $vmAlarmConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMAlarmConfig
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.CpuUsageIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.CpuUsageIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.AbnormalShutdownIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.AbnormalShutdownIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.PhysicalNetworkIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.PhysicalNetworkIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.SoftShutdownIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.SoftShutdownIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.MemoryUsageIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.MemoryUsageIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.MemoryUsagePercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.MemoryUsagePercentThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.MemoryUsageTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.MemoryUsageTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualDiskIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualDiskIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.CpuUsagePercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.CpuUsagePercentThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.CpuUsageTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.CpuUsageTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.AdapterSessionCountThreshold = $alarmConfig.AdapterSessionCountThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.AdapterSessionIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.AdapterSessionIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.AdapterSessionTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.AdapterSessionTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.BackupIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.BackupIsEnabled
PS > $clusterAlarmConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ClusterAlarmConfig
PS > $clusterAlarmConfig.HealthCheckReminderIntervalSeconds = $alarmConfig.HealthCheckReminderIntervalSeconds
PS > $clusterAlarmConfig.HealthCheckReminderIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.HealthCheckReminderIsEnabled
PS > $clusterAlarmConfig.LicenseKeyErrorIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.LicenseKeyErrorIsEnabled
PS > $clusterAlarmConfig.LicenseExpirationIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.LicenseExpirationIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DatastoreAlarmConfig
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.BackupPoolUsagePercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.BackupPoolUsagePercentThreshold
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.IoBusyIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.IoBusyIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.BackupDatastoreIoBusyIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.BackupDatastoreIoBusyIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.StateIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.StateIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.ConnectionIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.ConnectionIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.BackupPoolUsageIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.BackupPoolUsageIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.IoBusyTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.IoBusyTimeoutSeconds
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.UsageIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.UsageIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.UsagePercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.UsagePercentThreshold
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.IoLatencyIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.IoLatencyIsEnabled
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.IoLatencyTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.IoLatencyTimeoutSeconds
PS > $datastoreAlarmConfig.RaidStateIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.RaidStateIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkAlarmConfig
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgPercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgPercentThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.NfvLicenseErrorIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.NfvLicenseErrorIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDevicePhysicalNetworkIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDevicePhysicalNetworkIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuPercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuPercentThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceCpuTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualRouterStateIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualRouterStateIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceAlgTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceVirtualDiskIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceVirtualDiskIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossIsEnabled
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossPercentThreshold = $alarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossPercentThreshold
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossTimeoutSeconds = $alarmConfig.VirtualInterfacePacketLossTimeoutSeconds
PS > $vmAlarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceInternalErrorIsEnabled = $alarmConfig.VirtualNetworkDeviceInternalErrorIsEnabled
PS > Set-AlarmConfig -NetworkAlarmConfig $alarmConfig.Network -VMAlarmConfig $vmAlarmConfig -ClusterAlarmConfig $clusterAlarmConfig -HostAlarmConfig $alarmConfig.VMHost -DatastoreAlarmConfig $datastoreAlarmConfig -VirtualNetworkAlarmConfig $vmAlarmConfig -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update alarm settings (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-AlarmConfig -NetworkAlarmConfig $alarmConfig.Network -VMAlarmConfig $vmAlarmConfig -ClusterAlarmConfig $clusterAlarmConfig -HostAlarmConfig $alarmConfig.VMHost -DatastoreAlarmConfig $datastoreAlarmConfig -VirtualNetworkAlarmConfig $vmAlarmConfig -RunAsync
Write Alarm
Name:
New-AlarmAction
Syntax:
New-AlarmAction -Notes <String> -ObjectName <String> -EventType <String> -ObjectId <String> -ObjectType <String> [-Priority <String>] [-State <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Write alarm.
Parameters:
-Notes <String>
Alarm event description
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectName <String>
Alarm object name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EventType <String>
Alarm event type
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectId <String>
Alarm object identifier
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ObjectType <String>
Alarm object type
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Priority <String>
Alarm urgency
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-State <String>
Alarm processing status
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Write alarm
PS > New-AlarmAction -Notes test-note -ObjectName test-name -EventType "Storage Network Anomaly" -ObjectId "Storage network" -ObjectType "datastore" -Priority URGENT1 -State UNHANDLED
Cluster Management
Query Cluster Configuration Information.
Name:
Get-Cluster
Syntax:
Get-Cluster [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the information of cluster configuration, which is general configuration for the entire cluster.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query cluster configuration information
PS > Get-Cluster
Query Cluster Summary
Name:
Get-ClusterSummary
Syntax:
Get-ClusterSummary [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query cluster summary.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query cluster summary
PS > Get-ClusterSummary
Query Resource Scheduling Configuration (DRS)
Name:
Get-ClusterDRS
Syntax:
Get-ClusterDRS [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query resource scheduling configuration (DRS).
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query resource scheduling configuration (DRS)
PS > Get-ClusterDRS
Query Automated HHhh Hot Add (DRX) Configuration Information
Name:
Get-ClusterDRX
Syntax:
Get-ClusterDRX [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query automated hot add (DRX) configuration information.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query automated hot add (DRX) configuration information
PS > Get-ClusterDRX
Query High Availability (HA)
Name:
Get-ClusterHA
Syntax:
Get-ClusterHA [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query high availability (HA).
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query high availability (HA)
PS > Get-ClusterHA
Update Cluster Access Configuration
Name:
Set-ClusterAccess
Syntax:
Set-ClusterAccess [-Name <String>] [-Network <IClusterNetwork>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update cluster access configuration.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Cluster name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Network <IClusterNetwork>
Cluster network information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update cluster access configuration information (synchronous call)
PS > $clusternetwork = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ClusterNetwork
PS > $clusternetwork.Mask = "255.255.255.0"
PS > $clusternetwork.Address = "192.168.0.1"
PS > Set-ClusterAccess -Name "test-name" -Network $clusternetwork
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update cluster access configuration information (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-ClusterAccess -RunAsync
Update Cluster CPU Overcommitment
Name:
Set-ClusterCpuOvercommit
Syntax:
Set-ClusterCpuOvercommit [-VMHostCpuOvercommit <IClusterVMHostCpuovercommit[]>] -IsEnabled <Boolean> [-GlobalPercent <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update cluster CPU overcommitment.
Parameters:
-VMHostCpuOvercommit <IClusterVMHostCpuovercommit[]>
node overcommitment configuration list
When isEnabled is false, the overcommitment configuration of the corresponding node is overwritten.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
No limit to overcommitment?
If the parameter is set to true, the VMHostCpuOvercommit and GlobalPercent parameter settings are invalid.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GlobalPercent <Int64>
Globally unified overcommitment ratio
Safe range [100%, 150%, 200% (default)], alarm range [250%, 300%, 350%], and dangerous range [400%, 500%]
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the host CPU overcommitment of the cluster
PS > $vmhostcpuovercommit = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ClusterVMHostCpuovercommit
PS > $vmhostcpuovercommit.VMHostId = "host-0000000000001"
PS > $vmhostcpuovercommit.Percent = 100
PS > Set-ClusterCpuOvercommit -VMHostCpuOvercommit $vmhostcpuovercommit -IsEnabled $false
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the globally unified CPU overcommitment of the cluster
PS > Set-ClusterCpuOvercommit -IsEnabled $false -GlobalPercent 100
Update The Memory Overcommitment Of The Cluster
Name:
Set-ClusterMemoryOvercommit
Syntax:
Set-ClusterMemoryOvercommit [-VMHostMemoryOvercommit <IClusterVMHostMemoryOvercommit[]>] [-GlobalPercent <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update the memory overcommitment of the cluster.
Parameters:
-VMHostMemoryOvercommit <IClusterVMHostMemoryOvercommit[]>
node overcommitment configuration list
Overwrite the overcommitment configuration of the corresponding node
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-GlobalPercent <Int64>
Globally unified overcommitment ratio
Memory overcommitment range: Safe range [100%, 120%], alarm range [140%, 160%, 180%], and dangerous range [200%].
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the host memory overcommitment of the cluster
PS > $vmhostmemoryovercommit = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ClusterVMHostMemoryOvercommit
PS > $vmhostmemoryovercommit.VMHostId = "host-0000000000001"
PS > $vmhostmemoryovercommit.Percent = 100
PS > Set-ClusterMemoryOvercommit -VMHostMemoryOvercommit $vmhostmemoryovercommit
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the globally unified memory overcommitment of the cluster
PS > Set-ClusterMemoryOvercommit -GlobalPercent 100
Update Cluster NTP Server
Name:
Set-ClusterNtpServer
Syntax:
Set-ClusterNtpServer -IsEnabled <Boolean> [-ServerAddress <String>] [-IsImmediately] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update cluster NTP server.
Parameters:
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Synchronized with the NTP server?
When the value is false, the ServerAddress and IsImmediately settings are invalid.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ServerAddress <String>
NTP server address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsImmediately [<SwitchParameter>
Time synchronized immediately?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update cluster NTP server (synchronous call)
PS > Set-ClusterNtpServer -IsEnabled $false -ServerAddress "192.168.0.1" -IsImmediately
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update cluster NTP server (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-ClusterNtpServer -IsEnabled $true -RunAsync
Update Resource Scheduling Configuration (DRS)
Name:
Set-ClusterDRS
Syntax:
Set-ClusterDRS [-VMConfig <IDrsvmConfig[]>] [-SensitivityType <String>] [-IsEnabled] [-IsPredictionEnabled] [-CpuConfig <IDrscpuConfig>] [-MemoryConfig <IDrsMemoryConfig>] [-ScheduleType <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update resource scheduling configuration (DRS).
Parameters:
-VMConfig <IDrsvmConfig[]>
Specific VM scheduling
Instructions for use:
1.
The scheduling mode (manual/auto/disable) for specific VMs is configurable during resource scheduling.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SensitivityType <String>
DRS sensitivity (grading policy)
Including CONSERVATIVE, MODERATE, AGGRESSIVE, and VERY_AGGRESSIVE
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
DRS enabled?
Instructions for use:
1.
After cluster resource scheduling is enabled, the system intelligently schedules the run location of VMs according to the resource load of each node to ensure continuous and stable service operation.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsPredictionEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
AI intelligent prediction enabled?
Instructions for use:
1.
The AI algorithm is used to predict and analyze the resource load for more accurate scheduling.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CpuConfig <IDrscpuConfig>
Configuration of CPU metrics
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MemoryConfig <IDrsMemoryConfig>
Configuration of memory metrics
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScheduleType <String>
Scheduling modes, including AUTO and MANUAL
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update resource scheduling configuration (DRS)
#Notes Create specific VM scheduling object
PS > $drsvmconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrsvmConfig
PS > $drsvmconfig.IsEnabled = $true
PS > $drsvmconfig.VMId = "0000000000001"
PS > $drsvmconfig.ScheduleType = "AUTO"
#Notes Create CPU metrics configuration object
PS > $cpuconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrscpuConfig
PS > $cpuconfig.IsEnabled = $true
#Notes Create memory metrics configuration object
PS > $memoryconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrsMemoryConfig
PS > $memoryconfig.IsEnabled = $true
PS > Set-ClusterDRS -VMConfig $drsvmconfig -SensitivityType "MODERATE" -IsEnabled -IsPredictionEnabled -CpuConfig $cpuconfig -MemoryConfig $memoryconfig -ScheduleType "AUTO"
Update DRX Configuration Items
Name:
Set-ClusterDRX
Syntax:
Set-ClusterDRX [-VMConfigList <IDrxvmConfig[]>] [-CpuConfig <IDrxcpuConfig>] [-MemoryConfig <IDrxMemoryConfig>] [-SensitivityType <String>] [-IsEnabled <Boolean>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update DRX configuration items.
Parameters:
-VMConfigList <IDrxvmConfig[]>
VM configuration of automated hot add (DRX)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CpuConfig <IDrxcpuConfig>
Configuration of CPU metrics
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-MemoryConfig <IDrxMemoryConfig>
Configuration of memory metrics
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SensitivityType <String>
Sensitivity level of automated hot add (DRX)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Automated hot add (DRX) enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update DRX configuration items
#Notes Create DRX VM configuration object
PS > $drxvmconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrxvmConfig
PS > $drxvmconfig.VMId = "0000000000001"
#Notes Create CPU metrics configuration object
PS > $drxcpuconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrxcpuConfig
PS > $drxcpuconfig.UsagePercentThreshold = 80
PS > $drxcpuconfig.IsEnabled = $true
#Notes Create memory metrics configuration object
PS > $drxmemoryconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DrxMemoryConfig
PS > $drxmemoryconfig.UsagePercentThreshold = 80
PS > $drxmemoryconfig.IsEnabled = $true
PS > Set-ClusterDRX -VMConfigList $drxvmconfig -CpuConfig $drxcpuconfig -MemoryConfig $drxmemoryconfig -SensitivityType "CONSERVATIVE" -IsEnabled
Update High Availability (HA)
Name:
Set-ClusterHA
Syntax:
Set-ClusterHA -SensitivityLevelType <String> [-IsEdgeConnectedIfaceDown <Boolean>] [-IsManagementAndEdgeConnectedIfaceDown <Boolean>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update high availability (HA).
Parameters:
-SensitivityLevelType <String>
Sensitivity levels: LOW, MEDIUM_LOW, MEDIUM, MEDIUM_HIGH, and HIGH
The HA shuts down the VM on the failed node according to the level and tries to restore the operation of the VM on other nodes in the cluster.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEdgeConnectedIfaceDown <Boolean>
Abnormal service interface
Scenario 1: Separation of service network and overlay network interfaces
When the service network fails, the node service cannot access terminal devices outside the cluster. If the service needs to access terminal devices outside the cluster, it is recommended to enable HA;
In this scenario, the overlay network is not affected. If service traffic is only accessed between VMs in the cluster, it is not necessary to enable HA.
Scenario 2: Reuse of service network and overlay network interfaces
When the service network fails, the node service cannot access terminal devices outside the cluster and VMs on other nodes. If the service needs to access terminal devices outside the cluster or VMs on other nodes, it is recommended to enable HA;
Traffic access in the same node is not affected. If service traffic is only accessed in the same node, it is not necessary to enable HA.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsManagementAndEdgeConnectedIfaceDown <Boolean>
Abnormal management interface and service interface
When it is set to true, this condition only takes effect on two-node clusters, and does not take effect on three-node and above clusters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? False
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update high availability (HA) (synchronous call)
PS > Set-ClusterHA -SensitivityLevelType "LOW" -IsNotEdgeConnectedIfaceDown $false -IsNotManagementAndEdgeConnectedIfaceDown $true
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update high availability (HA) (asynchronous call)
PS > Set-ClusterHA -SensitivityLevelType "LOW" -RunAsync
Disk Management
Query The List Of Physical Disks
Name:
Get-HardDisk
Syntax:
Get-HardDisk [-Id <String[]>] [-Name <String[]>] [-Type <String>] [-AccessibleHostId <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of physical disks.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
The ID list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Physical disk name
For fuzzy matching, see the wildcardName instruction.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Type <String>
Hard disk types: ISCSI, FC and LOCAL
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AccessibleHostId <String[]>
List of accessible node IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of physical disks
PS > Get-HardDisk
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of physical disks
PS > Get-HardDisk -Id testHardDiskId0001 -Name test-name -Type LOCAL -AccessibleHostId host-000000000001
Query The List Of VS Shared Disks
Name:
Get-Sharedisk
Syntax:
Get-Sharedisk [-Id <String[]>] [-Name <String[]>] [-VM <IVirtualMachine>] [-VolumeId <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of VS shared disks.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
The ID list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
List of shared disk names
For detailed restrictions, see the wildcardSharediskName instruction.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Query available shared disks of the VM
The shared disk is available for the VM only when the storage policy of the VM is consistent with that of the shared disk.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VolumeId <String>
Virtual datastore ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VS shared disks
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Name test-name
PS > Get-Sharedisk -Id shardiskId0001 -Name test-name -VM $vm -VolumeId volumeId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VS shared disks through the pipe
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Name test-name
PS > $vm | Get-Sharedisk -Id shardiskId0001 -Name test-name -VolumeId volumeId0001
Query The List Of Virtual Disks
Name:
Get-VDisk
Syntax:
Get-VDisk -VM <IVirtualMachine[]> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of virtual disks.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine[]>
VM. It is used to query the information of virtual disks mounted to this VM and the mount information between the virtual disks.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual disks
PS > Get-VDisk
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual disks
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Name test-name
PS > Get-VDisk -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual disks through the pipe
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Name test-name
PS > $vm | Get-VDisk
Query VM Disk Mount Information
Name:
Get-VMDisk
Syntax:
Get-VMDisk -VM <IVirtualMachine> [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMDisk -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the mount information list of virtual disks, physical disks, and shared disks mounted to a VM.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Mount information ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM disk mount information
PS > $vm = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualMachine
PS > $vm.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > Get-VMDisk -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query VM disk mount information through the pipe
PS > Get-VM -Id "0000000000001" | Get-VMDisk
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of VM disk mount information by ID
PS > Get-VMDisk -Id "xxx"
Update Disk Information
Name:
Set-Disk
Syntax:
Set-Disk -VMDiskAttachment <IVMDiskAttachment> [-IoConfig <IIoConfig>] [-AdapterType <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Set-Disk -VirtualDisk <IVirtualDisk> [-AdvancedConfig <IVirtualDiskAdvancedConfig>] [-SizeGb <Int64>] [-FormatType <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Set-Disk -Sharedisk <ISharedisk> [-Name <String>] [-FormatType <String>] [-ConnectableVMId <String[]>] [-Notes <String>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
- Update the mount information of physical disks, shared disks, and virtual disks mounted to a VM.
- Edit shared disk.
- Update virtual disk information.
Parameters:
-VirtualDisk <IVirtualDisk>
Virtual disk
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Sharedisk <ISharedisk>
sharedisk
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AdvancedConfig <IVirtualDiskAdvancedConfig>
Advanced configuration information of disk
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
For detailed restrictions, see the sharediskName instruction.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SizeGb <Int64>
Disk size
1.
Expansion is supported and shrinkage is not supported, so the capacity must be greater than the original capacity.
2.
The minimum and maximum disk sizes are 1 and 64512 respectively.
3.
The capacity of a disk that has not installed vmTools and has not enabled Virtio cannot be greater than or equal to 2048GB.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FormatType <String>
The shared disk allocation mode refers to how the shared disk allocates space on virtual storage.
Pre-allocating will improve hard disk performance but take up a lot of storage space; dynamic provisioning will allocate storage space on demand according to the actual data usage.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ConnectableVMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs with shared access
Specify a list of VMs for the shared disk, which indicates that the shared disk is allowed to be used only by these specified VMs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
Storage policies supported by the virtual storage where the shared disk is located
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMDiskAttachment <IVMDiskAttachment>
Mount information of disks mounted to a VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IoConfig <IIoConfig>
Disk IO limit
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AdapterType <String>
Disk controller types: IDE and VIRTIO
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information
PS > $attachment = Get-VMDisk -Id "vmdisk0001"
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > Set-Disk -VMDiskAttachment $attachment -IoConfig $IoConfig -AdapterType VIRTIO
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information (asynchronous call)
PS > $attachment = Get-VMDisk -Id "vmdisk0001"
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > Set-Disk -VMDiskAttachment $attachment -IoConfig $IoConfig -AdapterType VIRTIO -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information
PS > $virtualdisk = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDisk
PS > $virtualdisk.Id = "2371477601538:ide0"
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > Set-Disk -VirtualDisk $virtualdisk -AdvancedConfig $config -SizeGb 1 -FormatType "OFF"
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information (asynchronous call)
PS > $virtualdisk = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDisk
PS > $virtualdisk.Id = "2371477601538:ide0"
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > Set-Disk -VirtualDisk $virtualdisk -AdvancedConfig $config -SizeGb 1 -FormatType "OFF" -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information
PS > $sharedisks = Get-Sharedisk
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > Set-Disk -Sharedisk $sharedisks[0] -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -StoragePolicy $storagepolicies[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information through the pipe
PS > $virtualdisk = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDisk
PS > $virtualdisk.Id = "2371477601538:ide0"
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > $virtualdisk | Set-Disk -AdvancedConfig $config -SizeGb 1 -FormatType "OFF"
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information through the pipe
PS > $sharedisks = Get-Sharedisk
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $sharedisks[0] | Set-Disk -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -StoragePolicy $storagepolicies[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information through the pipe
PS > $sharedisks = Get-Sharedisk
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $storagepolicies[0] | Set-Disk -Sharedisk $sharedisks[0] -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Update disk information
PS > $attachment = Get-VMDisk -Id "vmdisk0001"
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > $attachment | Set-Disk -IoConfig $IoConfig -AdapterType VIRTIO
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear disk description
PS > $sharedisks = Get-Sharedisk
PS > $sharedisks[0] | Set-Disk -Notes $null
Create Virtual Disk
Name:
New-Disk
Syntax:
New-Disk -VM <IVirtualMachine> -DiskId <String> -DiskType <String> [-IoConfig <IIoConfig>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-Disk -VolumeId <String> -Name <String> [-FormatType <String>] [-ConnectableVMId <String[]>] [-Notes <String>] [-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>] -SizeGb <Int64> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-Disk [-FormatType <String>] -Attachment <IVMDiskAttachment[]> -SizeGb <Int64> [-AdvancedConfig <IVirtualDiskAdvancedConfig>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-Disk -Path <String> -Datastore <IStorageResource> -Attachment <IVMDiskAttachment[]> [-AdvancedConfig <IVirtualDiskAdvancedConfig>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
- Physical disks, shared disks, and virtual disks mounted to a VM.
- Create shared disk.
- Create virtual disk.
- Manage free disks.
Parameters:
-VolumeId <String>
VS ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
For detailed restrictions, see the sharediskName instruction.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FormatType <String>
Allocation mode
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ConnectableVMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs with shared access
Specify a list of VMs for the shared disk, which indicates that the shared disk is allowed to be used only by these specified VMs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-StoragePolicy <IStoragePolicy>
A storage policy supported by VS {volumeID}
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Path <String>
The path of a disk file relative to the specified storage
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
The storage where the VM is located
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Attachment <IVMDiskAttachment[]>
Disk mount information
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SizeGb <Int64>
Disk size
1.
The minimum and maximum disk sizes are 1 and 64512 respectively.
2.
The capacity of a disk that has not installed vmTools and has not enabled Virtio cannot be greater than or equal to 2048GB.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-AdvancedConfig <IVirtualDiskAdvancedConfig>
Advanced configuration information of disk
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DiskId <String>
The disk ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DiskType <String>
Disk type
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IoConfig <IIoConfig>
IO limit
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Physical disks, shared disks, and virtual disks mounted to a VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > New-Disk -VM $vm -DiskId testDiskId0001 -DiskType VIRTUAL_DISK -IoConfig $ioConfig
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Physical disks, shared disks, and virtual disks (asynchronous call) mounted to a VM
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > New-Disk -VM $vm -DiskId testDiskId0001 -DiskType VIRTUAL_DISK -IoConfig $ioConfig -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create shared disk
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > New-Disk -VolumeId volumeId0001 -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -StoragePolicy $storagepolicies[0] -SizeGb 1
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Create shared disk (asynchronous call)
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > New-Disk -VolumeId volumeId0001 -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -StoragePolicy $storagepolicies[0] -SizeGb 1 -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Create virtual disk
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $vdisk = Get-VDisk -VM $vm
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > New-Disk -FormatType METADATA -Attachment $vdisk.Attachments -SizeGb 1 -AdvancedConfig $config
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Create virtual disk (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $vdisk = Get-VDisk -VM $vm
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > New-Disk -FormatType METADATA -Attachment $vdisk.Attachments -SizeGb 1 -AdvancedConfig $config -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Manage free disks
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $vdisk = Get-VDisk -VM $vm
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > New-Disk -Path "/testPath/test.qcow2" -Datastore $datastores[0] -Attachment $vdisk.Attachments -AdvancedConfig $config
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Manage free disks (asynchronous call)
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $vdisk = Get-VDisk -VM $vm
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > New-Disk -Path "/testPath/test.qcow2" -Datastore $datastores[0] -Attachment $vdisk.Attachments -AdvancedConfig $config -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Create shared disk through the pipe
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $storagepolicies[0] | New-Disk -VolumeId volumeId0001 -Name test-name -FormatType METADATA -ConnectableVMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -SizeGb 1
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Create shared disk through the pipe
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $vdisk = Get-VDisk -VM $vm
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $storagepolicies = Get-StoragePolicy
PS > $config = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualDiskAdvancedConfig
PS > $config.PolicyId = $storagepolicies[0].Id
PS > $config.SerialNumber = "12323"
PS > $datastores[0] | New-Disk -Path "/testPath/test.qcow2" -Attachment $vdisk.Attachments -AdvancedConfig $config
————————– EXAMPLE 11 ————————–
PS > ####
Mount physical disks, shared disks, and virtual disks to a VM through the pipe
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > $ioConfig = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IoConfig
PS > $ioConfig.WriteKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadKBps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.ReadIOps = 256
PS > $ioConfig.WriteIOps = 256
PS > $vm | New-Disk -DiskId testDiskId0001 -DiskType VIRTUAL_DISK -IoConfig $ioConfig
Backup Management
Query Backup Policy
Name:
Get-BackupPolicy
Syntax:
Get-BackupPolicy [-Limit <Int64>] [-Keyword <String>] [-Offset <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query backup policy information.
Parameters:
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Keyword <String>
Filter by name (fuzzy query)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all backup policies
PS > Get-BackupPolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup policies by keywords
PS > Get-BackupPolicy -Keyword "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup policies by page start position and page size
PS > Get-BackupPolicy -Offset 0 -Limit 50
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the backup policy
PS > (Get-BackupPolicy)[0].VM
Query All Backup Repositories
Name:
Get-BackupPool
Syntax:
Get-BackupPool [-DatastoreName <String>] [-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>] [-Keyword <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query backup repositories information.
Parameters:
-DatastoreName <String>
Storage name (exact query)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource[]>
The storage where the VM is located
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Keyword <String>
Filter by storage name (fuzzy query)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query backup repositories
PS > Get-BackupPool
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup repositories by storage name
PS > Get-BackupPool -DatastoreName "test-name"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup repositories by specifying storage
PS > $datastore = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.StorageResource
PS > $datastore.Id = "xxx"
PS > Get-BackupPool -Datastore $datastore
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup repositories by specifying storage through the pipe
PS > Get-Datastore | Get-BackupPool
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Filter the list of backup repositories by keywords
PS > Get-BackupPool -Keyword "xxx"
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VM backups through the backup repositories
PS > $backuppool = Get-BackupPool
PS > $backuppool.Backup
Update Backup And CDP Policies
Name:
Set-BackupPolicy
Syntax:
Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy> -CdpPolicy <IBackupPolicyCdp> [-Notes <String>] [-FullBackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-Name <String>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy> -WeeklyPolicy <IBackupPolicyWeekly> [-Notes <String>] [-FullBackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-Name <String>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy> -DailyPolicy <IBackupPolicyDaily> [-Notes <String>] [-FullBackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-Name <String>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy> -HourlyPolicy <IBackupPolicyHourly> [-Notes <String>] [-FullBackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-Name <String>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-DatastoreId <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update backup and CDP policies.
Parameters:
-BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy>
Backup/CDP policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-HourlyPolicy <IBackupPolicyHourly>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is hourly.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DailyPolicy <IBackupPolicyDaily>
The backup schedule is the policy configuration information in days.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-WeeklyPolicy <IBackupPolicyWeekly>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is weekly.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CdpPolicy <IBackupPolicyCdp>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is CDP (seconds).
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 120 characters or 40 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FullBackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>
Full backup related configuration input parameters
Instruction for use:
1.
The priority of the regular full backup task is higher than that of the normal backup task.
2.
Even if no incremental data is generated, the VM will be backed up according to the regular full backup policy and will not be canceled when it times out.
3.
Enabling regular full backup consumes more storage resources. It may take a long time to complete backup, and incremental backup cannot be performed during this period. However, the length of the backup chain of the VM can be reduced to improve IO performance in the data sorting stage after the VM is recovered.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>
Archive backup: Merge backup files and save them to the specified archive repository.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
Specify which VMs are added to this backup policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Backup policy name
Instructions for use:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RetentionPolicy <String>
Backup merge policy (backup retention mode)
Introduction:
Automatically merge backup points to save storage space. The last backup in the selected period is retained by default, and all backups beyond the selected period are merged to save a lot of space: To ensure the reliability of VM data, the platform will retain at least 5 backup points.
Instructions for use:
1.
The policy is set with the minimum granularity of day. Greater granularities include week, month, and year.
2.
The filling format is A-B-C-D-E, indicating:
-
All retained before time period A
-
Retain one per day within the period of A-B
-
Retain one per week within the period of B-C
-
Retain one per month within a period of C-D
-
Retain one per year within the period of D-E
3.
The time units include days (d), weeks (w), months (m), and years (y), which can be used at each time point, while the unit for the next period cannot be smaller than that for the previous period.
For example: If the value of A is 3w, indicating 3 weeks, the unit of B cannot be days.
4.
If a time point is 0, no processing policy is available for this period of time.
For example: A-B-0-D-E, indicating that the policy to retain one per week is skipped, and one is retained per month within the period of B-D
5.
Complete introduction to example 1: 3d-4w-0-12w-2y
-
All are retained within a period of 0-3 days.
-
Retain one per day within a period of 3 days to 4 weeks
-
Retain one per month within a period of 4 to 12 weeks
-
Retain one per year within a period of 12 weeks to 2 years
6.
Complete introduction to example 2: 1m-0-0-0-0
- All are retained within a period of 0-1 month.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreId <String>
Backup repository
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? False
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update CDP policy (synchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create CDP policy configuration object
PS > $cdppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyCdp
PS > $cdppolicy.IologRetentionHours = 48
PS > $cdppolicy.IologIntervalMilliseconds = 5000
PS > $cdppolicy.FrequencySeconds = 3600
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoAlertByWarningFrequencyInSeconds = 300
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoAlertThresholdSeconds = 300
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoWarningThresholdSeconds = 100
#Notes Create VM IO log datastore configuration object
PS > $vmconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyVmcdpConfig
PS > $vmconfig.VMId = "0000000000001"
PS > $vmconfig.DatastoreId = "yyy"
PS > $vmconfig.IologMaxCacheBytes = 2147483648
PS > $vmconfig.IologMaxUsageBytes = 107374182400
PS > $cdppolicy.VMConfigs = $vmconfig
#Notes Create full backup configuration object
PS > $fullbackuppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.FullBackupPolicy
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.FrequencyType = "WEEKLY"
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.WeeklyPolicyAtDay = "MONDAY"
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.WeeklyPolicyAtHour = 23
#Notes Create archive backup configuration object
PS > $archivepolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ArchivePolicy
PS > $archivepolicy.DatastoreId = "zzz"
PS > $archivepolicy.Months = "JANUARY", "APRIL"
PS > $archivepolicy.DayPredicate = "LAST"
PS > $archivepolicy.AtDay = "FRIDAY"
PS > $archivepolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $archivepolicy.RetentionPolicy = "3m-18m"
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -CdpPolicy $cdppolicy -Notes "test-notes" -FullBackupPolicy $fullbackuppolicy -ArchivePolicy $archivepolicy -VMId "0000000000001" -Name "test-name" -RetentionPolicy "3d-4w-0-12w-2y" -DatastoreId "yyy"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update weekly backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create weekly backup policy configuration object
PS > $weeklypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyWeekly
PS > $weeklypolicy.AtDays = "MONDAY", "FRIDAY"
PS > $weeklypolicy.TimeoutHours = 23
PS > $weeklypolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $weeklypolicy.ShouldCancelAfterTimeout = $true
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -WeeklyPolicy $weeklypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update daily backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create daily backup policy configuration object
PS > $dailypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyDaily
PS > $dailypolicy.TimeoutHours = 23
PS > $dailypolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $dailypolicy.ShouldCancelAfterTimeout = $true
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -DailyPolicy $dailypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Update hourly backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create hourly backup policy configuration object
PS > $hourlypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyHourly
PS > $hourlypolicy.IntervalHours = 8
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -HourlyPolicy $hourlypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Update hourly backup policy (asynchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create hourly backup policy configuration object
PS > $hourlypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyHourly
PS > $hourlypolicy.IntervalHours = 8
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -HourlyPolicy $hourlypolicy -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear backup policy description (synchronous call)
PS > $backupPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backupPolicy.Id = "xxx"
#Notes Create hourly backup policy configuration object
PS > $hourlypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyHourly
PS > $hourlypolicy.IntervalHours = 8
PS > Set-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backupPolicy -HourlyPolicy $hourlypolicy -Notes $null
Update The Enabled Status Of The Backup Policy
Name:
Set-BackupPolicyEnabledStatus
Syntax:
Set-BackupPolicyEnabledStatus -IsEnabled <Boolean> -Id <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update the enabled status of the backup policy.
Parameters:
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
This policy enabled?
Instructions for use:
1.
This is a global configuration switch. When disabled, all VMs in the policy will not be backed up.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Backup/CDP policy ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the enabled status of the backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > Set-BackupPolicyEnabledStatus -Id "xxx" -IsEnabled $true
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the enabled status of the backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > Set-BackupPolicyEnabledStatus -Id "xxx" -IsEnabled $true -RunAsync
Create Backup And CDP Policies
Name:
Create backup and CDP policies
Syntax:
New-BackupPolicy -Name <String> -DatastoreId <String> [-Notes <String>] [-FullbackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] -CdpPolicy <IBackupPolicyCdp> [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-BackupPolicy -Name <String> -DatastoreId <String> [-Notes <String>] [-FullbackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] -WeeklyPolicy <IBackupPolicyWeekly> [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-BackupPolicy -Name <String> -DatastoreId <String> [-Notes <String>] [-FullbackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] -HourlyPolicy <IBackupPolicyHourly> [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
New-BackupPolicy -Name <String> -DatastoreId <String> [-Notes <String>] [-FullbackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>] -DailyPolicy <IBackupPolicyDaily> [-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-RetentionPolicy <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create backup and CDP policies.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Backup policy name
Instructions for use:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DatastoreId <String>
Backup repository
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 120 characters or 40 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FullbackupPolicy <IFullBackupPolicy>
Full backup related configuration input parameters
Instruction for use:
1.
The priority of the regular full backup task is higher than that of the normal backup task.
2.
Even if no incremental data is generated, the VM will be backed up according to the regular full backup policy and will not be canceled when it times out.
3.
Enabling regular full backup consumes more storage resources. It may take a long time to complete backup, and incremental backup cannot be performed during this period. However, the length of the backup chain of the VM can be reduced to improve IO performance in the data sorting stage after the VM is recovered.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-WeeklyPolicy <IBackupPolicyWeekly>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is weekly.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-HourlyPolicy <IBackupPolicyHourly>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is hourly.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DailyPolicy <IBackupPolicyDaily>
The backup schedule is the policy configuration information in days.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CdpPolicy <IBackupPolicyCdp>
Policy configuration information whose backup schedule is CDP (seconds).
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ArchivePolicy <IArchivePolicy>
Archive backup: Merge backup files and save them to the specified archive repository.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs
Specify which VMs are added to this backup policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RetentionPolicy <String>
Backup merge policy (backup retention mode)
Introduction:
Automatically merge backup points to save storage space. The last backup in the selected period is retained by default, and all backups beyond the selected period are merged to save a lot of space: To ensure the reliability of VM data, the platform will retain at least 5 backup points.
Instructions for use:
1.
The policy is set with the minimum granularity of day. Greater granularities include week, month, and year.
2.
The filling format is A-B-C-D-E, indicating:
-
All retained before time period A
-
Retain one per day within the period of A-B
-
Retain one per week within the period of B-C
-
Retain one per month within a period of C-D
-
Retain one per year within the period of D-E
3.
The time units include days (d), weeks (w), months (m), and years (y), which can be used at each time point, while the unit for the next period cannot be smaller than that for the previous period.
For example: If the value of A is 3w, indicating 3 weeks, the unit of B cannot be days.
4.
If a time point is 0, no processing policy is available for this period of time.
For example: A-B-0-D-E, indicating that the policy to retain one per week is skipped, and one is retained per month within the period of B-D
5.
Complete introduction to example 1: 3d-4w-0-12w-2y
-
All are retained within a period of 0-3 days.
-
Retain one per day within a period of 3 days to 4 weeks
-
Retain one per month within a period of 4 to 12 weeks
-
Retain one per year within a period of 12 weeks to 2 years
6.
Complete introduction to example 2: 1m-0-0-0-0
- All are retained within a period of 0-1 month.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create CDP policy (synchronous call)
#Notes Create CDP policy configuration object
PS > $cdppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyCdp
PS > $cdppolicy.IologRetentionHours = 48
PS > $cdppolicy.IologIntervalMilliseconds = 5000
PS > $cdppolicy.FrequencySeconds = 3600
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoAlertByWarningFrequencyInSeconds = 300
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoAlertThresholdSeconds = 300
PS > $cdppolicy.RpoWarningThresholdSeconds = 100
#Notes Create VM IO log datastore configuration object
PS > $vmconfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyVmcdpConfig
PS > $vmconfig.VMId = "0000000000001"
PS > $vmconfig.DatastoreId = "yyy"
PS > $vmconfig.IologMaxCacheBytes = 2147483648
PS > $vmconfig.IologMaxUsageBytes = 107374182400
PS > $cdppolicy.VMConfigs = $vmconfig
#Notes Create full backup configuration object
PS > $fullbackuppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.FullBackupPolicy
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.FrequencyType = "WEEKLY"
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.WeeklyPolicyAtDay = "MONDAY"
PS > $fullbackuppolicy.WeeklyPolicyAtHour = 23
#Notes Create archive backup configuration object
PS > $archivepolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ArchivePolicy
PS > $archivepolicy.DatastoreId = "zzz"
PS > $archivepolicy.Months = "JANUARY", "APRIL"
PS > $archivepolicy.DayPredicate = "LAST"
PS > $archivepolicy.AtDay = "FRIDAY"
PS > $archivepolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $archivepolicy.RetentionPolicy = "3m-18m"
PS > New-BackupPolicy -Name "test-name" -DatastoreId "yyy" -Notes "test-notes" -FullBackupPolicy $fullbackuppolicy -CdpPolicy $cdppolicy -ArchivePolicy $archivepolicy -VMId "0000000000001" -RetentionPolicy "3d-4w-0-12w-2y"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create weekly backup policy (synchronous call)
#Notes Create weekly backup policy configuration object
PS > $weeklypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyWeekly
PS > $weeklypolicy.AtDays = "MONDAY", "FRIDAY"
PS > $weeklypolicy.TimeoutHours = 23
PS > $weeklypolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $weeklypolicy.ShouldCancelAfterTimeout = $true
PS > New-BackupPolicy -Name "test-name" -DatastoreId "yyy" -WeeklyPolicy $weeklypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create daily backup policy (synchronous call)
#Notes Create daily backup policy configuration object
PS > $dailypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyDaily
PS > $dailypolicy.TimeoutHours = 23
PS > $dailypolicy.AtHour = 23
PS > $dailypolicy.ShouldCancelAfterTimeout = $true
PS > New-BackupPolicy -Name "test-name" -DatastoreId "yyy" -DailyPolicy $dailypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Create hourly backup policy (synchronous call)
#Notes Create hourly backup policy configuration object
PS > $hourlypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyHourly
PS > $hourlypolicy.IntervalHours = 8
PS > New-BackupPolicy -Name "test-name" -DatastoreId "yyy" -HourlyPolicy $hourlypolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Create hourly backup policy (asynchronous call)
#Notes Create hourly backup policy configuration object
PS > $hourlypolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicyHourly
PS > $hourlypolicy.IntervalHours = 8
PS > New-BackupPolicy -Name "test-name" -DatastoreId "yyy" -HourlyPolicy $hourlypolicy -RunAsync
Delete Backup And CDP Policies
Name:
Remove-BackupPolicy
Syntax:
Remove-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy> [-ShouldDeleteRelatedBackups] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete backup and CDP policies.
Parameters:
-BackupPolicy <IBackupPolicy>
Backup/CDP policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldDeleteRelatedBackups [<SwitchParameter>
Backup files in the backup policy storage deleted at the same time?
1.
If the VM only has backup files generated from automatic backup, the backup files will be retained in the recycle bin for 30 days by default;
2.
The backup data in the policy backup storage is deleted to the recycle bin.
3.
To further clean up the remaining VM backups, you can go to the backup file page to delete them.
4.
Archive files are processed in the same way as backup files.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete backup policy (synchronous call)
PS > $backuppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backuppolicy.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -ShouldDeleteRelatedBackups
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete backup policy (asynchronous call)
PS > $backuppolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BackupPolicy
PS > $backuppolicy.Id = "xxx"
PS > Remove-BackupPolicy -BackupPolicy $backuppolicy -ShouldDeleteRelatedBackups -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete backup policy through the pipe (synchronous call)
PS > Get-BackupPolicy | Remove-BackupPolicy
Snapshot Management
Query The List Of VM Snapshots
Name:
Get-Snapshot
Syntax:
Get-Snapshot -VM <IVirtualMachine> [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-Snapshot [-Id <String[]>] -VM <IVirtualMachine> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of VM snapshots.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
Snapshot
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine>
VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Snapshot Name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM snapshots
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM snapshots
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > Get-Snapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -VM $vms[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM snapshots through the pipe
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > "snapshotId0001" | Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $snapshot = Get-Snapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -VM $vms[0]
PS > $snapshot.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the snapshot policy information
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $snapshot = Get-Snapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -VM $vms[0]
PS > $snapshot.SnapshotPolicy
Query The List Of Consistency Group Information
Name:
Get-ConsistencyGroup
Syntax:
Get-ConsistencyGroup [-Offset <Int64>] [-Limit <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-ConsistencyGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
Query the list of consistency group information.
Query the list of consistency group information by ID.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
ID of the Consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Page start position, whose default value and minimum value are 0.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Size of each page: The default value is 50, the minimum value is 1, and the maximum value is 1000.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of consistency group information
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroup -Offset 0 -Limit 50
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of consistency group information
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroup -Id groupId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the snapshot policy information
PS > $cGroup = Get-ConsistencyGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > $cGroup.SnapshotPolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $cGroup = Get-ConsistencyGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > $cGroup.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the consistency group snapshot information
PS > $cGroup = Get-ConsistencyGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > $cGroup.ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
Query The Snapshot List Of The Specified Consistency Group
Name:
Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
Syntax:
Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId <String> [-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot <IConsistencyGroupSnapshot[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -Id <String> -ConsistencyGroupId <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
Query the snapshot list of the specified consistency group.
Query the snapshot details of the specified consistency group.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
Snapshot ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ConsistencyGroupId <String>
Consistency group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot “<IConsistencyGroupSnapshot[]>
Snapshot
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the snapshot list of the specified consistency group
PS > $cGroup = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
PS > $cGroup.Id = "cgrpupId0001"
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -ConsistencyGroupSnapshot $cGroup
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the snapshot list of the specified consistency group
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $cGroupSnapshot = Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001
PS > $cGroupSnapshot.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the consistency group information
PS > $cGroupSnapshot = Get-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -Id snapshotId0001 -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001
PS > $cGroupSnapshot.ConsistencyGroup
Query The List Of Consistency Group Summary Information
Name:
Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary
Syntax:
Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary [-VM <IVirtualMachine[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of consistency group summary information.
Parameters:
-VM <IVirtualMachine[]>
VM
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
List of consistency group IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of consistency group summary information
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of consistency group summary information
PS > $vm = Get-VM -Id 0000000000001
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary -VM $vm
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of consistency group summary information
PS > Get-ConsistencyGroupSummary -Id groupId0001
Query The List Of Timed Snapshot Policies
Name:
Get-SnapshotPolicy
Syntax:
Get-SnapshotPolicy [-TargetId <String[]>] [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-SnapshotPolicy [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of timed snapshot policies.
Parameters:
-TargetId <String[]>
List of target IDs
VM ID and consistency snapshot group ID are supported.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Fuzzy query by name
Usage restrictions:
1.
Wildcards are supported. See the name instruction.
2.
You can only input a name for query now.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
List of snapshot policy IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of timed snapshot policies
PS > Get-SnapshotPolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of timed snapshot policies
PS > Get-SnapshotPolicy -TargetId targetId0001 -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of timed snapshot policies
PS > Get-SnapshotPolicy -Id policyId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the VM information
PS > $snapshotPolicy = Get-SnapshotPolicy -Id policyId0001
PS > $snapshotPolicy.VM
Edit Snapshot
Name:
Set-Snapshot
Syntax:
Set-Snapshot -VMId <String> -Snapshot <ISnapshot> [-IsProtected] [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit snapshot.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
VM of the snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsProtected [<SwitchParameter>
Set as protection type snapshot?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Snapshot Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Snapshot Name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit snapshot
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Set-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Snapshot $shapshot -IsProtected -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Set-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Snapshot $shapshot -IsProtected -Notes test-note -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear snapshot description
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Set-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Snapshot $shapshot -Notes $null
Edit Consistency Group
Name:
Set-ConsistencyGroup
Syntax:
Set-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup> [-VMId <String[]>] [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit consistency group.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup>
Consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
The list of VM IDs contained in the consistency group
Usage restrictions:
1.
Contain at least one VM
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description of consistency group
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
2.
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Consistency group name
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > Set-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $consistencyGroups[0] -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group (asynchronous call)
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > Set-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $consistencyGroups[0] -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group through the pipe
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $consistencyGroups[0] | Set-ConsistencyGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear consistency group description
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $consistencyGroups[0] | Set-ConsistencyGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes $null
Edit Consistency Group Snapshot
Name:
Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
Syntax:
Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId <String> -Snapshot <ISnapshot> [-IsProtected] [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit consistency group snapshot.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroupId <String>
The ID of the consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsProtected [<SwitchParameter>
Protection enabled?
When selected, snapshots automatically created through the snapshot policy will not be deleted by the automatic cleanup mechanism. Manually created snapshots are selected by default and will not be automatically deleted.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
The description of snapshot
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
2.
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
The name of snapshot
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: (),.!()【】,。!@._-+、¥……“”‘’:.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group snapshot
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Snapshot $shapshot -IsProtected -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Snapshot $shapshot -IsProtected -Notes test-note -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit consistency group snapshots through the pipe
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $shapshot | Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -IsProtected -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear consistency group snapshot description
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $shapshot | Set-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Notes $null
Modify Snapshot Policy
Name:
Set-SnapshotPolicy
Syntax:
Set-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy <ISnapshotPolicy> -PolicyType <String> [-Notes <String>] [-IsEnabled] [-VMGroupType <String>] [-EffectivePolicy <IEffectivePolicy>] [-TargetId <String[]>] [-ReservePolicy <IReservePolicy[]>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Modify snapshot policy.
Parameters:
-SnapshotPolicy <ISnapshotPolicy>
Policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyType <String>
Snapshot policy type: Disk snapshot policy or storage snapshot policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Policy description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMGroupType <String>
VM group type
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EffectivePolicy <IEffectivePolicy>
Execution policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetId <String[]>
Target ID (consistency group ID or VM ID)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ReservePolicy <IReservePolicy[]>
Retention policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Policy name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify snapshot policy
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > Set-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy policies[0] -Notes test-note -IsEnabled -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -TargetId targetId0001 -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name [-RunAsync]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify snapshot policy (asynchronous call)
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > Set-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy policies[0] -Notes test-note -IsEnabled -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -TargetId targetId0001 -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify snapshot policy through the pipe
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > "targetId0001" | Set-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy policies[0] -Notes test-note -IsEnabled -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear snapshot policy description
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > Set-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy policies[0] -Notes $null
Take Snapshot
Name:
New-Snapshot
Syntax:
New-Snapshot -VMId <String> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Take snapshot.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
ID of the VM from which a snapshot is created
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Snapshot name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Snapshot description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Take snapshot
PS > New-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > New-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note -RunAsync
Create Consistency Group
Name:
New-ConsistencyGroup
Syntax:
New-ConsistencyGroup -VMId <String[]> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create consistency group.
Parameters:
-VMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs contained in the consistency group
Usage restrictions:
1.
Contain at least one VM
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Consistency group name
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description of consistency group
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
2.
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create consistency group
PS > New-ConsistencyGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create consistency group (asynchronous call)
PS > New-ConsistencyGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note -RunAsync
Create Consistency Group Snapshot
Name:
New-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
Syntax:
New-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId <String> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create consistency group snapshot
A snapshot is taken for all VMs in the consistency group to ensure that all VMs are in the same status.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroupId <String>
The ID of the consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
The name of snapshot
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: (),.!()【】,。!@._-+、¥……“”‘’:.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
The description of snapshot
Usage restrictions:
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
2.
The maximum length is 100 characters or 33 Chinese characters.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create consistency group snapshot
PS > New-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Name test-name -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create consistency group snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > New-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Name test-name -Notes test-notes -RunAsync
Create Snapshot Policy
Name:
New-SnapshotPolicy
Syntax:
New-SnapshotPolicy -VMGroupType <String> -PolicyType <String> -EffectivePolicy <IEffectivePolicy> -TargetId <String[]> -ReservePolicy <IReservePolicy[]> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-IsEnabled] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create snapshot policy.
Parameters:
-VMGroupType <String>
Group type
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyType <String>
Snapshot policy type: Disk snapshot policy or storage snapshot policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-EffectivePolicy <IEffectivePolicy>
Execution rules
To construct, see NOTES section for EFFECTIVEPOLICY properties and create a hash table.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetId <String[]>
Target identifier, VM ID or consistency group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ReservePolicy <IReservePolicy[]>
Retention policy rules
For example, [
{"effectiveSeconds":172800, "reserveMethod":"ALL"},
{"effectiveSeconds":864000, "reserveMethod":"DAILY"}
]
Retention rule: All snapshots are reserved within a period of 0-2 days, and 1 snapshot is reserved per day within a period of 2-10 days
Implicit rule: The startAt in the first position of the array must be 0, and the startAt of the next interval must be equal to the endAt of the previous interval.
To construct, see NOTES section for RESERVEPOLICY properties and create a hash table.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Policy name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Policy description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled [<SwitchParameter>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create snapshot policy
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > New-SnapshotPolicy -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -TargetId targetId0001 -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name -Notes test-note -IsEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create snapshot policy (asynchronous call)
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > New-SnapshotPolicy -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -TargetId targetId0001 -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name -Notes test-note -IsEnabled -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create snapshot policy through the pipe
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > "targetId0001" | New-SnapshotPolicy -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name -Notes test-note -IsEnabled
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Create snapshot policy through the pipe
PS > $eff = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.EffectivePolicy
PS > $eff.Frequency = "DAILY"
PS > $eff.TargetDate = 1
PS > $eff.TargetHour = 10
PS > $eff.Interval = 1
PS > $reserve = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.ReservePolicy
PS > $reserve.EffectiveSeconds = 2
PS > $reserve.ReserveMethod = "DAILY"
PS > "policyId0001" | New-SnapshotPolicy -VMGroupType VM -PolicyType VS -EffectivePolicy $eff -TargetId targetId0001 -ReservePolicy $reserve -Name test-name -Notes test-note -IsEnabled
Delete Snapshot
Name:
Remove-Snapshot
Syntax:
Remove-Snapshot -VMId <String> -Snapshot <ISnapshot> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete snapshot.
Parameters:
-VMId <String>
VM ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete snapshot
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Remove-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Snapshot $shapshot
Delete snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Remove-Snapshot -VMId 0000000000001 -Snapshot $shapshot -RunAsync
Delete Consistency Group
Name:
Remove-ConsistencyGroup
Syntax:
Remove-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete consistency group.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup>
Consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > Remove-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $consistencyGroups[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group (asynchronous call)
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > Remove-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $consistencyGroups[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group through the pipe
PS > $consistencyGroups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $consistencyGroups[0] | Remove-ConsistencyGroup
Delete Consistency Group Snapshot
Name:
Remove-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot
Syntax:
Remove-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId <String> -Snapshot <ISnapshot> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete consistency group snapshot.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroupId <String>
The ID of the consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group snapshot
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Remove-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Snapshot $shapshot
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > Remove-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001 -Snapshot $shapshot -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete consistency group snapshots through the pipe
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $shapshot | Remove-ConsistencyGroupSnapshot -ConsistencyGroupId groupId0001
Delete Snapshot Policy
Name:
Remove-SnapshotPolicy
Syntax:
Remove-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy <ISnapshotPolicy> -PolicyType <String> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete snapshot policy.
Parameters:
-SnapshotPolicy <ISnapshotPolicy>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyType <String>
Snapshot policy type: Disk snapshot policy or storage snapshot policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete snapshot policy
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > Remove-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy $policies[0] -PolicyType VS
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete snapshot policy (asynchronous call)
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > Remove-SnapshotPolicy -SnapshotPolicy $policies[0] -PolicyType VS -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete snapshot policy through the pipe
PS > $policies = Get-SnapshotPolicy
PS > $policies[0] | Remove-SnapshotPolicy
Clone Consistency Group From The Snapshot
Name:
Clone-ConsistencyGroup
Syntax:
Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup> -Name <String> -VMConfig <ICloneConsistencyVMConfig> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup> -Snapshot <ISnapshot> [-Notes <String>] [-ShouldStartAfterClone] [-VMCloneConfiguration <ICloneConsistencyGroupVMConfiguration[]>] -Name <String> [-ShouldConnectNiCs] [-FolderId <String>] [-CloneType <String>
<IStorageResource>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Clone consistency group from the snapshot.
Parameters:
-ConsistencyGroup <IConsistencyGroup>
Consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Snapshot <ISnapshot>
Snapshot
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description of the new consistency group
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldStartAfterClone [<SwitchParameter>
Powered on automatically after the clone?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMCloneConfiguration <ICloneConsistencyGroupVMConfiguration[]>
VM configuration
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ShouldConnectNiCs [<SwitchParameter>
All NICs disconnected?
To prevent the IP address conflict between the cloned VM and the original VM, the default is false.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-FolderId <String>
ID of the group where the cloned new VM is located
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-CloneType <String>
Clone type
FULL
Full clone: A complete clone of a VM is not associated with the original VM, and the use of the two VMs will not affect each other. This clone type is the slowest.
LINK
Linked clone: A new VM can be quickly cloned through the underlying technology, and there is a relationship called link between the new VM and the original VM. The original VM and the new VM can be used normally, but the original VM cannot be deleted; Otherwise, the cloned VM can no longer be used.
FAST
Quick clone: A new VM can be quickly cloned through the underlying technology, and the new VM is associated with the original VM, which cannot be deleted. However, the original VM and the new VM can be used normally. During the start and use of the new VM, the data of the original VM is automatically migrated to the new VM. After all data is migrated, the new VM is no longer associated with the original VM, and the effect is the same as that of full clone. Quick clone is a compromise between full clone and linked clone.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Datastore <IStorageResource>
The storage where the cloned new VM is located
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMConfig <ICloneConsistencyVMConfig>
Configuration input parameters for VMs in the cloned consistency group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $groups[0] -Name test-name -VMConfig $vmConfig
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $groups[0] -Name test-name -VMConfig $vmConfig -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $groups[0] -Snapshot $shapshot -Notes test-note -ShouldStartAfterClone -VMCloneConfiguration $vmConfig -Name test-name -ShouldConnectNiCs -FolderId folderId0001 -CloneType FULL -Datastore $datastores[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot (asynchronous call)
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $groups[0] -Snapshot $shapshot -Notes test-note -ShouldStartAfterClone -VMCloneConfiguration $vmConfig -Name test-name -ShouldConnectNiCs -FolderId folderId0001 -CloneType FULL -Datastore $datastores[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot through the pipe
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > $groups[0] | Clone-ConsistencyGroup -Name test-name -VMConfig $vmConfig
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Clone consistency group from the snapshot
PS > $groups = Get-ConsistencyGroup
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $shapshot = Get-Snapshot -VM $vms[0] -Name test-name
PS > $datastores = Get-Datastore
PS > $vmConfig = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyVMConfig
PS > $cGroup = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneConsistencyGroupVMCustomizedInput
PS > $cGroup.Id = "group0000000001"
PS > $adapter = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.CloneVMNetworkAdapterInput
PS > $adapter.DeviceId = "deveiceId0001"
PS > $cGroup.VMNetworkAdapters = $adapter
PS > $vmConfig.Configurations = $cGroup
PS > $shapshot | Clone-ConsistencyGroup -ConsistencyGroup $groups[0] -Notes test-note -ShouldStartAfterClone -VMCloneConfiguration $vmConfig -Name test-name -ShouldConnectNiCs -FolderId folderId0001 -CloneType FULL -Datastore $datastores[0]
Network Management
Query The List Of Available Virtual Networks
Name:
Get-Network
Syntax:
Get-Network [-VMHost <IVMHost[]>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of available virtual networks.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost[]>
Node, required parameter: Node ID (Id)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of available virtual networks
PS > $v = Get-VMHost
PS > Get-Network -VMHost $v
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual networks available by specifying the node through the pipe
PS > Get-VMHost | Get-Network
Query The Group List
Name:
Get-NetworkGroup
Syntax:
Get-NetworkGroup [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-NetworkGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the group list.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Group name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the group list by name
PS > Get-NetworkGroup -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the group list by ID
PS > Get-NetworkGroup -Id 0000000000001
Query The List Of Distributed Firewall IP Group Information
Name:
Get-DFWIPGroup
Syntax:
Get-DFWIPGroup [-Name <String>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-IsTemporary] [<CommonParameters>
Get-DFWIPGroup [-Id <String[]>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-Offset <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of distributed firewall IP group information.
Query the list of distributed firewall IP group information by ID.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Filter by IP group name, supporting fuzzy matching and exact matching
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
List of IP group IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsTemporary [<SwitchParameter>
A temporary distributed firewall IP group?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall IP group information by name
PS > Get-DFWIPGroup -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall IP group information by Id
PS > Get-DFWIPGroup -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query temporary distributed firewall IP group
PS > Get-DFWIPGroup -IsTemporary
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of the list of distributed firewall IP group information
PS > Get-DFWIPGroup -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall IP group information with an offset of 1
PS > Get-DFWIPGroup -Offset 1
Query The List Of Distributed Firewall Policies
Name:
Get-DFWPolicy
Syntax:
Get-DFWPolicy [-Name <String>] [-DstScopeValue <String[]>] [-PolicyService <IPolicyService[]>] [-RuleName <String>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-SrcScopeValue <String[]>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-Action <String>] [-SrcScopeType <String>] [-DstScopeType <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-DFWPolicy -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
Query the list of distributed firewall policies.
Query distributed firewall information by ID.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
Distributed firewall policy ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Distributed firewall policy name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-DstScopeValue <String[]>
List of distributed firewall rule destination information values
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyService <IPolicyService[]>
Policy service, required parameter: Policy service ID (Id)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RuleName <String>
Distributed firewall rule name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SrcScopeValue <String[]>
List of distributed firewall rule source information values
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Action <String>
Protective action types of distributed firewall: ALLOW and DROP
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-SrcScopeType <String>
Source information type of distributed firewall rules
Including IPRANGE (IP range), IPGROUP (IP group), VM, VMGROUP (VM group), VMLABEL (VM label), and ALLIP (all IPs)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DstScopeType <String>
Destination information type of distributed firewall rules
Including IPRANGE (IP range), IPGROUP (IP group), VM, VMGROUP (VM group), VMLABEL (VM label), and ALLIP (all IPs)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query distributed firewall policy information by ID
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information by name
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information through the distributed firewall destination information
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -DstScopeValue "123.23.1.1-123.23.1.100" -DstScopeType IPRANGE
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information through the distributed firewall source information
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -SrcScopeValue "123.23.1.1-123.23.1.100" -SrcScopeType IPRANGE
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information by the distributed firewall action type
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -Action ALLOW
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information by rule name
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -RuleName test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information through the policy service
PS > $s = Get-PolicyService
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -PolicyService $s[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the distributed firewall policy information on the specified policy sever through the pipe
PS > Get-PolicyService | Get-DFWPolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 distributed firewall policies
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Query distributed firewall policy information with an offset of 10
PS > Get-DFWPolicy -Offset 10
————————– EXAMPLE 11 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the firewall
PS > $policy = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > $policy.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 12 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query IP groups through the firewall
PS > $policy = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > $policy.DfwipGroup
Query The List Of Distributed Firewall Rules
Name:
Get-DFWRule
Syntax:
Get-DFWRule [-Id <String[]>] [-Name <String>] [-PolicyId <String>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-Limit <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of distributed firewall rules.
Parameters:
-Id <String[]>
List of distributed firewall rule IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Distributed firewall rule name
Fuzzy matching
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-PolicyId <String>
Policy ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall rules by ID
PS > Get-DFWRule -Id 0000000000001, 0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall rules by name
PS > Get-DFWRule -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of the list of distributed firewall rules
PS > Get-DFWRule -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall rules with an offset of 1
PS > Get-DFWRule -Offset 1
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of distributed firewall rules according to the distributed firewall policy ID
PS > Get-DFWRule -PolicyId 0000000000001
Query The Edge List
Name:
Get-VDSwitch
Syntax:
Get-VDSwitch [-VMId <String[]>] [-Offset <Int32>] [-Limit <Int32>] [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VDSwitch -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Function:
Query the edge list.
Query edge details.
Parameters:
-VMId <String[]>
The list of the VM IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int32>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int32>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Name list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Id <String>
Edge ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query edge information by VM ID
PS > Get-VDSwitch -VMId xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx1
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the edge information after the first entry
PS > Get-VDSwitch -Offset 1
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of edge information
PS > Get-VDSwitch -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query edge information according to the name list
PS > Get-VDSwitch -Name test-nam1,test-name2
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query edge information according to the edge ID
PS > Get-VDSwitch -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the edge
PS > $vs = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $vs[0].VM
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query the associated node interfaces through the edge
PS > $vs = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $vs[0].VMHostNetworkAdapter
Query The List Of VLAN Port Groups
Name:
Get-VDPortGroup
Syntax:
Get-VDPortGroup [-VMId <String[]>] [-Name <String[]>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-IdList <String[]>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-VdSwitch <IVdSwitch[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VDPortGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of VLAN port groups.
Parameters:
-VMId <String[]>
The list of the VM IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
List of port group names
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IdList <String[]>
ID list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VdSwitch <IVdSwitch[]>
Edge, required parameter: Edge ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Port group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups by name
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries in the VLAN port group list
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups through the list of VLAN port group IDs
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -IdList 0000000000001,0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query data after the first entry of the list of VLAN port groups
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -Offset 1
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups through the edge list
PS > $vs = Get-VDSwitch
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -VdSwitch $vs
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups on the specified edge through the pipe
PS > Get-VDSwitch | Get-VDPortGroup
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups through the VLAN port group ID
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VLAN port groups by VM ID
PS > Get-VDPortGroup -VMId 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vp.VM
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query routers through the port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vp.EdgeRouter
————————– EXAMPLE 11 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query switches through the port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vp.DistributeSwitch
————————– EXAMPLE 12 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query edges through the port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vp.BorderSwitch
Query The List Of Policy Service Information
Name:
Get-PolicyService
Syntax:
Get-PolicyService [-IsBuildIn] [-ScopeType <String>] [-ScopeVrId <String>] [-Keyword <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-PolicyService [-Id <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of policy service information.
Parameters:
-IsBuildIn [<SwitchParameter>
Is it a built-in service?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScopeType <String>
Policy service scope types: DFW (distributed firewall) and VR (router)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScopeVrId <String>
Router ID for which the scope takes effect
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Keyword <String>
Fuzzy matching
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String[]>
List of service IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of policy service information by keywords
PS > Get-PolicyService -Keyword test-keyword
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of policy service information whose scope is fire wall
PS > Get-PolicyService -ScopeType DFW
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of policy service information whose scope is router
PS > $router = Get-EdgeRouter
PS > Get-PolicyService -ScopeType VR -ScopeVrId $router[0].Id
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of policy service information by ID
PS > Get-PolicyService -Id 0000000000001, 0000000000002
Query The Switch List
Name:
Get-DistributeSwitch
Syntax:
Get-DistributeSwitch [-VMId <String[]>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-Name <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-DistributeSwitch -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the switch list.
Parameters:
-VMId <String[]>
The list of the VM IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
List of switch names
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Switch ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the switch list through the name list
PS > Get-DistributeSwitch -Name test-name1,test-name2
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the switch list by VM ID
PS > Get-DistributeSwitch -VMId 0000000000001,0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of the switch list
PS > Get-DistributeSwitch -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the switch list after the first entry
PS > Get-DistributeSwitch -Offset 1
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query switch data by ID
PS > Get-DistributeSwitch -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query VMs through the switch
PS > $ds = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $ds[0].VM
Query The Router List
Name:
Get-EdgeRouter
Syntax:
Get-EdgeRouter [-Name <String[]>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-Limit <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-EdgeRouter -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the router list.
Parameters:
-Name <String[]>
List of router names
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query the start position (the minimum value is 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries (minimum value: 1, maximum value: 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Router ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the router list by name
PS > Get-EdgeRouter -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of the router list
PS > Get-EdgeRouter -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of routers after the first entry
PS > Get-EdgeRouter -Offset 10
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the router list by ID
PS > Get-EdgeRouter -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query edges through the router
PS > $r = Get-EdgeRouter
PS > $r[0].BorderSwitch
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Drill-down query switches through the router
PS > $r = Get-EdgeRouter
PS > $r[0].DistributeSwitch
Query The List Of Virtual Interfaces
Name:
Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
Syntax:
Get-VirtualNetworkInterface [-DeviceType <String[]>] [-DeviceId <String[]>] [-Ids <String[]>] [-PeerDeviceType <String[]>] [-Limit <Int64>] [-Name <String[]>] [-VdPortGroupId <String[]>] [-Offset <Int64>] [-PeerDeviceId <String[]>] [-PeerVdPortGroupId <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query the list of virtual interfaces.
Parameters:
-DeviceType <String[]>
List of local device types
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DeviceId <String[]>
List of local device IDs. Note: In the case of a VM template, please subtract 1 from the device ID and assign the result to DeviceId.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ids <String[]>
ID list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PeerDeviceType <String[]>
List of peer device types
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Limit of queries
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String[]>
Name list
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VdPortGroupId <String[]>
List of port group IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Query start position
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PeerDeviceId <String[]>
List of peer device IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PeerVdPortGroupId <String[]>
List of peer port group IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
Virtual interface ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces whose local device type is router
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType EVR
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces by this device ID
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceId 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces through the ID list
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Ids 0000000000001,0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces whose peer device type is node
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -PeerDeviceType HOST
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces by peer device ID
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -PeerDeviceId 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the top 10 entries of the list of virtual interfaces
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Limit 10
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Query data after the first entry of the virtual interface list
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Offset 1
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces by virtual interface name
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces through the list of port group IDs
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -VdPortGroupId 0000000000001, 0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces through the list of peer port group IDs
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -PeerVdPortGroupId 0000000000001, 0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 11 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces by ID
PS > Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -Id 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 12 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of virtual interfaces by specifying ID through the pipe
PS > $id = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxx1"
PS > $id | Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
Edit Network Group
Name:
Set-NetworkGroup
Syntax:
Set-NetworkGroup -NetworkGroup <INetworkGroup> -Name <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit network group.
Parameters:
-NetworkGroup <INetworkGroup>
Network group, required parameter: Network group ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Group name
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit network group name
PS > $ng = Get-NetworkGroup
PS > Set-NetworkGroup -NetworkGroup $ng[0] -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Edit the specified network group name through the pipe
PS > $ng = Get-NetworkGroup
PS > $ng[0] | Set-NetworkGroup -Name test-name
Update Distributed Firewall Policy
Name:
Set-DFWPolicy
Syntax:
Set-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy> [-Priority <Int64>] [-Position <IDfwPolicyOffset>] [-Rule <IDfwRule[]>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update distributed firewall policy.
Parameters:
-DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy>
Distributed firewall policy ID, required parameter: Distributed firewall policy ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Priority <Int64>
Distributed firewall policy priority (the minimum value is 0, and the maximum value is 2147483647)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Position <IDfwPolicyOffset>
Distributed firewall policy location
You can select UP or DOWN in Direction when action is SHIFT.
You can select BEFORE or AFTER in Direction when action is MOVE.
Required parameters: TargetPolicyId and Direction
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Rule <IDfwRule[]>
Rule list, required parameters: Rule ID (id), distributed firewall rule source scope type (SrcType), distributed firewall source scope list (SrcValues), policy service ID list (PolicyServiceIDs), distributed firewall rule destination scope type (DstType), distributed firewall destination
scope list (SrcValues), enabled or not (IsEnabled), and distributed firewall protection action type (Action)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Distributed firewall policy name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update distributed firewall policy rules
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRule
PS > $service = Get-PolicyService
PS > $rule.PolicyServiceIDs = $service[0].Id
PS > $rule.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule.IsEnabled = 1
PS > $rule.Name = "test-name"
PS > $rule.DstType = "VMGROUP"
PS > $rule.DstValues = "default"
PS > $rule.SrcType = "IPRANGE"
PS > $rule.SrcValues = "123.23.1.1"
PS > $rule.Id = "0000000000001"
PS > $rule.PolicyServiceIDs = $service[0].Id
PS > $p = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > Set-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $p[0] -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Where to update distributed firewall policy
PS > $position = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwPolicyOffset
PS > $position.TargetPolicyId = "0000000000001"
PS > $position.Direction = "BEFORE"
PS > $service = Get-PolicyService
PS > Set-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $p[0] -Position $position
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update distributed firewall policy name
PS > $service = Get-PolicyService
PS > Set-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $p[0] -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the priority of distributed firewall policy
PS > $p = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > Set-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $p[0] -Priority 12314123
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the priority of the specified distributed firewall policy through the pipe
PS > $p = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > $p[0] | Set-DFWPolicy -Priority 12314123
Update Distributed Firewall Rules
Name:
Set-DFWRule
Syntax:
Set-DFWRule -DfwRule <ISecurityRule> [-Src <IDfwRuleScope>] [-TargetPolicyId <String>] [-Name <String>] [-PolicyServiceId <String[]>] [-Dst <IDfwRuleScope>] [-Priority <Int64>] [-Action <String>] [-Position <IDfwRuleOffset>] [-IsEnabled <Boolean>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update distributed firewall rules.
Parameters:
-DfwRule <ISecurityRule>
Rule
Required parameter: Rule ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Src <IDfwRuleScope>
Source information, required parameters: Distributed firewall rule source information type (Type) and distributed firewall rule source information domain list (Values)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetPolicyId <String>
Point to the associated distributed firewall policy ID
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Rule name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyServiceId <String[]>
List of service IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Dst <IDfwRuleScope>
Destination information, required parameters: Distributed firewall rule destination information type (Type) and distributed firewall rule destination information domain list (Values)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Priority <Int64>
Rule priority (the minimum value is 0, and the maximum value is 2147483647)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Action <String>
Protective action type of distributed firewall
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Position <IDfwRuleOffset>
Rule location, required parameters: Rule location type (Direction) and target rule ID (TargetRuleID)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Enabled?
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the destination information of distributed firewall rules
PS > $position_dst = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleScope
PS > $position_dst.Type = "IPRANGE"
PS > $position_dst.Values = "123.23.1.1-123.23.1.100"
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -Dst $position_dst
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the source information of distributed firewall rules
PS > $position_src = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleScope
PS > $position_src.Type = "IPRANGE"
PS > $position_src.Values = "123.23.1.1-123.23.1.100"
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -Src $position_src -IsEnabled $true
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the source information of distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -TargetPolicyId 0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Update distributed firewall rule name
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -Name xxxxxxx
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Update distributed firewall policy IDs associated with distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -TargetPolicyId 0000000000002
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the policy service of distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -PolicyServiceId xxxxxxx1
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the protective action type of distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -Action ALLOW
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Where to update distributed firewall rules
PS > $p = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleOffset
PS > $p.Direction = "BEFORE"
PS > $p.TargetRuleId = "xxxxxx"
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -Position $p
————————– EXAMPLE 9 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the enabled status of distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Set-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0] -IsEnabled $false
————————– EXAMPLE 10 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the enabled status of specified distributed firewall rules through the pipe
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > $r[0] | Set-DFWRule -IsEnabled $false
Update Edge
Name:
Set-VDSwitch
Syntax:
Set-VDSwitch -VdSwitch <IVdSwitch> [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update edge.
Parameters:
-VdSwitch <IVdSwitch>
Edge, required parameter: Edge ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Edge description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Edge name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update edge name
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > Set-VDSwitch -VdSwitch $swtich[0] -Notes test_note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update edge remarks
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > Set-VDSwitch -VdSwitch $swtich[0] -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the description of the specified edge through the pipe
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $swtich[0] | Set-VDSwitch -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the description of the specified edge
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $swtich[0] | Set-VDSwitch -Notes $null
Update VLAN Port Group
Name:
Set-VDPortGroup
Syntax:
Set-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup <IVdPortGroup> [-PortType <String>] [-VlanRange <String>] [-PvId <Int64>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VLAN port group.
Parameters:
-VdPortGroup <IVdPortGroup>
Port group, required parameter: Port group ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PortType <String>
Port group types: TRUNK and ACCESS
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VlanRange <String>
Range of trunk type ports
1.
vlanRange must be a VLANID or VLANID range. The VLAN value should be 1-4094 in the format of 100,105-110 for example, or you can directly enter all, which means the full range.
2.
A maximum of 10 VLAN ranges are supported.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PvId <Int64>
The default VLANID of the trunk type port, or the VLANID of the save access type port (the minimum value is 1 and the maximum value is 4094)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
The name of the port group
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify the VLAN port group type to ACCESS
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > Set-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup $vp[0] -PortType ACCESS -VlanRange 23
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify the PvId of VLAN port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > Set-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup $vp[0] -PvId 14
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify VLAN port group name
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > Set-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup $vp[0] -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify the specified VLAN port group name through the pipe
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vp[0] | Set-VDPortGroup -Name test-name
Edit Policy Service
Name:
Set-PolicyService
Syntax:
Set-PolicyService -PolicyService <IPolicyService> [-Rule <IPolicyServiceRule[]>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Edit policy service.
Parameters:
-PolicyService <IPolicyService>
Service to be updated, required parameter: Policy service ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Rule <IPolicyServiceRule[]>
New service rule list, required parameter: Rule protocol No. (Protocol)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
New service name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
# Modify policy service rule
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rule.Protocol = 6
PS > $rule.PortRange = 53
PS > $ps = Get-PolicyService
PS > Set-PolicyService -PolicyService $ps[0] -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify policy service name
PS > $ps = Get-PolicyService
PS > Set-PolicyService -PolicyService $ps[0] -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Modify the name of the specified policy service through the pipe
PS > $ps = Get-PolicyService
PS > $ps[0] | Set-PolicyService -Name test-name
Update Switch
Name:
Set-DistributeSwitch
Syntax:
Set-DistributeSwitch -DistributeSwitch <IDistributeSwitch> [-BroadCast <IBroadCast>] [-Name <String>] [-Notes <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update switch.
Parameters:
-DistributeSwitch <IDistributeSwitch>
Switch, required parameter: switch ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BroadCast <IBroadCast>
BroadCast function
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Switch name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Switch description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update switch
PS > $b = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BroadCast
PS > $b.IsSuppressionKbpsEnabled = $false
PS > $b.QosKbps = $null
PS > $b.IsSuppressionPpsEnabled = $true
PS > $b.QosPps = 700
PS > $s = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > Set-DistributeSwitch -DistributeSwitch $s[0] -BroadCast $b -Name test-name -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the specified switch through the pipe
PS > $b = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BroadCast
PS > $b.IsSuppressionKbpsEnabled = $false
PS > $b.QosKbps = $null
PS > $b.IsSuppressionPpsEnabled = $true
PS > $b.QosPps = 700
PS > $s = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $s[0] | Set-DistributeSwitch -BroadCast $b -Name test-name -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the description of the specified switch
PS > $s = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $s[0] | Set-DistributeSwitch -Notes $null
Update Virtual Interface
Name:
Set-VirtualNetworkInterface
Syntax:
Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface <IVirtualNetworkInterface> [-Macaddress <String>] [-Ipv4 <IIPAddress[]>] [-VdPortGroupId <String>] [-IsEnabled <Boolean>] [-Location <String[]>] [-IsConnected <Boolean>] [-Ipv6 <IIPAddress[]>
<IVirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice>] [-Notes <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update virtual interface.
Parameters:
-VirtualNetworkInterface <IVirtualNetworkInterface>
Interface, required parameter: Interface ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Macaddress <String>
Interface MAC address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv4 <IIPAddress[]>
List of IPv4 information, required parameters: IPv4 prefix length (PrefixLength) and IPv4 address (Address)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VdPortGroupId <String>
Port group ID. Note: It needs to be input only when the local device type is edge.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Location <String[]>
The run location (which node) of the device to which the interface belongs to
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsConnected <Boolean>
Device connected?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv6 <IIPAddress[]>
List of IPv6 information, required parameters: IPv6 prefix length (PrefixLength) and IPv6 address (Address)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PeerDevice <IVirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice>
Peer device information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a connection between the VM and the switch
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $ifaces = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceId $vms[0].Id
PS > $switch = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $peerDevice = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice
PS > $peerDevice.Type = "DVS"
PS > $peerDevice.Id = $switch[0].Id
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $ifaces[0] -PeerDevice $peerDevice
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a connection between the VM and the edge (port group)
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $ifaces = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceId $vms[0].Id
PS > $ports = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $peerDevice = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice
PS > $peerDevice.Type = "EVS"
PS > $peerDevice.Id = $ports[0].VdSwitchId
PS > $peerDevice.VdPortGroupId = $ports[0].Id
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $ifaces[0] -PeerDevice $peerDevice
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a connection between the router and the switch
PS > $iface = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType EVR -Name ethx -DeviceId edgeRouterId0001
PS > $peerDevice = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice
PS > $peerDevice.Type = "DVS"
PS > $peerDevice.Id = $switch[0].Id
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $iface -PeerDevice $peerDevice
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Update the list of IPv4 information for the virtual interface
PS > $vs = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
PS > $ip = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.IPAddress
PS > $ip.PrefixLength = 24
PS > $ip.Dns = "114.114.114.114"
PS > $ip.Address = "10.103.242.144"
PS > $ip.Gateway = "10.103.240.1"
PS > $vs = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $vs[0] -Ipv4 $ip
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
The VM is disassociated from the connected device.
PS > $iface = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceId vmId0001 -Name netx
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $iface -IsConnected $false
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
The router is disassociated from the connected device.
PS > $iface = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType EVR -Name ethx -DeviceId edgeRouterId0001
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $iface -IsConnected $false
————————– EXAMPLE 7 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear virtual interface IP
PS > $vs = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $vs[0] -Ipv4 @()
————————– EXAMPLE 8 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear virtual interface description
PS > $vs = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
PS > Set-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $vs[0] -Notes $null
Create Network Group
Name:
New-NetworkGroup
Syntax:
New-NetworkGroup -Name <String> -ParentId <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create network group.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Group name
1.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
2.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-ParentId <String>
Parent group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create network group
PS > New-NetworkGroup -Name test-name -ParentId 0000000000001
Create Distributed Firewall Rule
Name:
New-DFWRule
Syntax:
New-DFWRule -Src <IDfwRuleScope> -TargetPolicyId <String> -PolicyServiceId <String[]> -Dst <IDfwRuleScope> -Action <String> -IsEnabled <Boolean> [-Name <String>] [-Priority <Int64>] [-Position <IDfwRuleOffset>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create distributed firewall rule.
Parameters:
-Src <IDfwRuleScope>
Source information
Distributed firewall rule source types: IPRANGE (IP range), IPGROUP (IP group), VM, VMGROUP (VM group), VMLABEL (VM tag), and ALLIP (all IPs)
When the type is ALLIP, the value should be set to 0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255.
Required parameters:
-
Distributed firewall rule source information type (Type):MUST BE ONE OF IPRANGE, IPGROUP, VM, VMGROUP, VMLABEL, ALL IP.
-
Distributed firewall rule source information domain list (Values).
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetPolicyId <String>
Point to the associated distributed firewall policy ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyServiceId <String[]>
List of service IDs
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Dst <IDfwRuleScope>
Destination information
Distributed firewall rule destination information types: IPRANGE (IP range), IPGROUP (IP group), VM, VMGROUP (VM group), VMLABEL (VM label), and ALLIP (all IPs)
When the type is ALLIP, the value should be set to 0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255.
Required parameters: Distributed firewall rule destination information type (Type) and distributed firewall rule destination information domain list (Values)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Action <String>
Protective action types of distributed firewall: ALLOW and DROP
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Enabled?
Required? true
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Rule name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Priority <Int64>
Rule priority (the minimum value is 0, and the maximum value is 2147483647)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Position <IDfwRuleOffset>
Rule position, the relative position type of the distributed firewall rule includes BEFORE (before), AFTER (after), mandatory parameters: rule position type (Direction), target rule ID (TargetRuleID)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create distributed firewall rule
PS > $posi_src = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleScope
PS > $posi_src.Type = "IPRANGE"
PS > $posi_src.Values = "192.168.1.10-192.168.1.100"
PS > $posi_tar = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleScope
PS > $posi_tar.Values = "10.103.1.1-10.103.1.100"
PS > $posi_tar.Type = "IPRANGE"
PS > $ps = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRuleOffset
PS > $ps.Direction = "AFTER"
PS > $ps.TargetRuleId = "0000000000001"
PS > $s = Get-PolicyService
PS > New-DFWRule -Src $posi_src -TargetPolicyId 0000000000001 -Dst $posi_tar -Action ALLOW -Name test-name -Position $ps -PolicyServiceId $s[1].Id -IsEnabled $true
Create Edge
Name:
New-VDSwitch
Syntax:
New-VDSwitch -Name <String> [-Bridge <INetworkBridge[]>] [-DefaultVlanGroupId <String>] [-Notes <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create edge.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Edge name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-Bridge <INetworkBridge[]>
Bridge information
Required parameters: Bridged host ID (HostId) and bridged node physical interface name (InterfaceName) in the format of ethx or ethx.x
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DefaultVlanGroupId <String>
Default port group
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create edge
PS > $b = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.NetworkBridge
PS > $b.InterfaceName ="eth1"
PS > $b.HostId = "host-xxxxxxxxxx"
PS > New-VDSwitch -Name test-name -Bridge $b -DefaultVlanGroupId 0000000000001 -Notes test-notes
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create edge by specifying the default port group through the pipe
PS > $b = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.NetworkBridge
PS > $b.InterfaceName ="eth1"
PS > $b.HostId = "host-xxxxxxxxxx"
PS > $port_id = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
PS > $port_id | New-VDSwitch -Name test-name -Bridge $b -Notes test-notes
Create VLAN Port Group
Name:
New-VDPortGroup
Syntax:
New-VDPortGroup -PortType <String> -VlanRange <String> -Name <String> -VdSwitch <IVdSwitch> [-PvId <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VLAN port group.
Parameters:
-PortType <String>
Port group types: TRUNK and ACCESS
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VlanRange <String>
Range of trunk type ports
1.
vlanRange must be a VLANID or VLANID range. The VLAN value should be 1-4094 in the format of 100,105-110 for example, or you can directly enter all, which means the full range.
2.
A maximum of 10 VLAN ranges are supported.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Port group name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? true
-VdSwitch <IVdSwitch>
Edge, required parameter: Edge ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PvId <Int64>
The default VLANID of the trunk type port, or the VLANID of the save access type port (the minimum value is 1 and the maximum value is 4094)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VLAN port group
PS > $vs = Get-VDSwitch
PS > New-VDPortGroup -PortType TRUNK -VlanRange all -Name test-name -VdSwitch $vs[0] -PvId 13
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a VLAN port group by specifying an edge through the pipe
PS > $vs = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $vs | New-VDPortGroup -PortType TRUNK -VlanRange all -Name test-name -PvId 13
Create Policy Service
Name:
New-PolicyService
Syntax:
New-PolicyService -ScopeType <String> [-ScopeVrId <String>] -Name <String> [-Rule <IPolicyServiceRule[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create policy service.
Parameters:
-ScopeType <String>
Policy service scope types: DFW (distributed firewall) and VR (router)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-ScopeVrId <String>
Router ID for which the scope takes effect
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Create service name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Rule <IPolicyServiceRule[]>
List of service rule information, required parameter: Rule protocol No. (Protocol)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a policy service with UDP protocol and port number 53
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rule.PortRange = 53
PS > $rule.Protocol = 17
PS > New-PolicyService -Name test-name -ScopeType DFW -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create ICMP service, with the rule of network unreachable
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rule.Protocol = 1
PS > $rule.IcmpCode = 0
PS > $rule.IcmpType = 3
PS > New-PolicyService -Name test-name -ScopeType DFW -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a policy service with TCP protocol and port number 80
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rule.PortRange = 80
PS > $rule.Protocol = 6
PS > New-PolicyService -ScopeType DFW -Name test-name -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a policy service whose scope type is router, protocol type is TCP, and port number is 8
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rule.PortRange = 80
PS > $rule.Protocol = 6
PS > $router = Get-EdgeRouter
PS > New-PolicyService -ScopeType VR -ScopeVrId $router[0].Id -Name test-name -Rule $rule
Create Switch
Name:
New-DistributeSwitch
Syntax:
New-DistributeSwitch -Name <String> [-BroadCast <IBroadCast>] [-Notes <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create switch.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Switch name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-BroadCast <IBroadCast>
Broad Cast function
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Switch description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create switch
PS > $b = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.BroadCast
PS > $b.IsSuppressionKbpsEnabled = $true
PS > $b.QosKbps = 600
PS > $b.IsSuppressionPpsEnabled = $true
PS > $b.QosPps = 500
PS > New-DistributeSwitch -BroadCast $b -Name test-name -Notes test-notes
Create Virtual Interface
Name:
New-VirtualNetworkInterface
Syntax:
New-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType <String> -DeviceId <String> [-Macaddress <String>] [-Ipv4 <IIPAddressInput[]>] [-Name <String>] [-VdPortGroupId <String>] [-IsEnabled <Boolean>] [-RouterVlan <IRouterVlan>] [-Location <String[]>] [-Ipv6 <IIPAddressInput[]>
<IVirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice>] [-Notes <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create virtual interface.
Parameters:
-DeviceType <String>
Device type of interface
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-DeviceId <String>
Device ID of interface
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Macaddress <String>
Interface MAC address
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv4 <IIPAddressInput[]>
List of IPv4 information, required parameters: IPv4 prefix length (PrefixLength) and IPv4 address (Address)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Interface name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VdPortGroupId <String>
Port group ID. Note: It needs to be input only when the local device type is edge.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsEnabled <Boolean>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RouterVlan <IRouterVlan>
VLAN information. Note: For the router. Required parameters: VLAN ID (Id) and parent adapter ID (ParentAdapterID) of VLAN subinterface
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Location <String[]>
The run location (which node) of the device to which the interface belongs to
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Ipv6 <IIPAddressInput[]>
List of IPv6 information, required parameters: IPv6 prefix length (PrefixLength) and IPv6 address (Address)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PeerDevice <IVirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice>
Peer device information
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
Description
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a connection between the edge and the switch
PS > $port = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $switch = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $peerDevice = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice
PS > $peerDevice.Type = "DVS"
PS > $peerDevice.Id = $switch[0].Id
PS > New-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType "EVS" -DeviceId $port[0].VdSwitchId -VdPortGroupId $port[0].Id -PeerDevice $peerDevice
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
The edge is connected to the node interface.
PS > $peerDevice = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VirtualNetworkInterfacePeerDevice
PS > $peerDevice.Type = "HOST"
PS > $peerDevice.VlinkId = "ethx"
PS > New-VirtualNetworkInterface -DeviceType EVS -DeviceId VdSwitchId0001 -PeerDevice $peerDevice -Location "host-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
Create Distributed Firewall Policy
Name:
New-DFWPolicy
Syntax:
New-DFWPolicy -Name <String> [-Priority <Int64>] [-Position <IDfwPolicyOffset>] [-Rule <IDfwRule[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create distributed firewall policy.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Distributed firewall policy name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Priority <Int64>
Distributed firewall policy priority (the minimum value is 0, and the maximum value is 2147483647)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Position <IDfwPolicyOffset>
Distributed firewall policy location, required parameters: TargetPolicyId and Direction
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Rule <IDfwRule[]>
Rule list, required parameters: rule ID (id), distributed firewall rule source scope type (SrcType), distributed firewall source scope list (SrcValues), policy service ID list (PolicyServiceIDs), distributed firewall rule purpose role Domain Type (DstType), Distributed Firewall Purpose Scope List (SrcValues), Whether to Enable (IsEnabled), Distributed Firewall Protection Action Type (Action)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create distributed firewall policy
PS > $position = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwPolicyOffset
PS > $position.Direction="AFTER"
PS > $default = Get-DfwPolicy
PS > $position.TargetPolicyId = $default[1].Id
PS > $service = Get-PolicyService
PS > $rule = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRule
PS > $rule.PolicyServiceIDs = $service[1].Id
PS > $rule.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule.Name = "test-name"
PS > $rule.SrcType = "IPRANGE"
PS > $rule.SrcValues = "123.23.1.1-123.23.1.100"
PS > $rule.DstType = "IPRANGE"
PS > $rule.DstValues = "145.45.1.1-145.45.1.100"
PS > $rule.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule.IsEnabled = 1
PS > New-DfwPolicy -Name test-name -Position $position -Rule $rule
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create a firewall policy for the VM to open port 22 and close other port accesses
PS > $rules = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.PolicyServiceRule
PS > $rules.PortRange = 22
PS > $rules.Protocol = 6
PS > New-PolicyService -ScopeType DFW -Name service20 -Rule $rules
PS > $service = Get-PolicyService -Keyword service20
PS > $all_service = Get-PolicyService -ScopeType DFW -Keyword "All services" -IsBuildIn
PS > $vms = Get-VM
PS > $rule1 = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRule
PS > $rule1.PolicyServiceIDs =$service.Id
PS > $rule1.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule1.Name = "allow_22_service"
PS > $rule1.SrcType = "IPRANGE"
PS > $rule1.SrcValues = "0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255"
PS > $rule1.DstType = "VM"
PS > $rule1.DstValues = $vms[0].Id
PS > $rule1.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule1.IsEnabled = 1
PS > $rule2 = New-Object Sangfor.Acloud.Models.DfwRule
PS > $rule2.PolicyServiceIDs =$all_service.Id
PS > $rule2.Action = "ALLOW"
PS > $rule2.Name = "drop_all_service"
PS > $rule2.SrcType = "IPRANGE"
PS > $rule2.SrcValues = "0.0.0.0-255.255.255.255"
PS > $rule2.DstType = "VM"
PS > $rule2.DstValues = $vms[0].Id
PS > $rule2.Action = "DROP"
PS > $rule2.IsEnabled = 1
PS > New-DfwPolicy -Name test-22-service-policy -Rule $rule1,$rule2
Delete Network Group
Name:
Remove-NetworkGroup
Syntax:
Remove-NetworkGroup -NetworkGroup <INetworkGroup> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete network group.
Parameters:
-NetworkGroup <INetworkGroup>
Network group, required parameter: Network group ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete network group
PS > $ng = Get-NetworkGroup
PS > Remove-NetworkGroup -NetworkGroup $ng[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the specified network group through the pipe
PS > $ng = Get-NetworkGroup
PS > $mg[0] | Remove-NetworkGroup
Delete Distributed Firewall Policy
Name:
Remove-DFWPolicy
Syntax:
Remove-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete distributed firewall policy.
Parameters:
-DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy>
Distributed firewall policy, required parameter: Distributed firewall policy ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete distributed firewall policy
PS > $p = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > Remove-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $p[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the specified distributed firewall policy through the pipe
PS > $p = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > $p[0] | Remove-DFWPolicy
Bulk Delete Distributed Firewall Rules
Name:
Remove-DFWRule
Syntax:
Remove-DFWRule -DfwRule <ISecurityRule[]> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Bulk delete distributed firewall rules.
Parameters:
-DfwRule <ISecurityRule[]>
Distributed firewall rule, required parameter: Distributed firewall rule ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Bulk delete distributed firewall rules
PS > $r = Get-DFWRule
PS > Remove-DFWRule -DfwRule $r[0],$r[1]
Delete Edge
Name:
Remove-VDSwitch
Syntax:
Remove-VDSwitch -VdSwitch <IVdSwitch> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete edge.
Parameters:
-VdSwitch <IVdSwitch>
Edge, required parameter: Edge ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete edge
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > Remove-VDSwitch -VdSwitch $switch[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete edge through the pipe
PS > $swtich = Get-VDSwitch
PS > $swtich[0] | Remove-VDSwitch
Delete VLAN Port Group
Name:
Remove-VDPortGroup
Syntax:
Remove-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup <IVdPortGroup> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VLAN port group.
Parameters:
-VdPortGroup <IVdPortGroup>
Port group, required parameter: Port group ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VLAN port group
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > Remove-VDPortGroup -VdPortGroup $vp[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the specified VLAN port group through the pipe
PS > $vp = Get-VDPortGroup
PS > $vs[0] | Remove-VDPortGroup
Delete Policy Service
Name:
Remove-PolicyService
Syntax:
Remove-PolicyService -PolicyService <IPolicyService> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete policy service.
Parameters:
-PolicyService <IPolicyService>
Policy service, required parameter: Policy service ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete policy service
PS > $ps = Get-PolicyService
PS > Remove-PolicyService -PolicyService $ps[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the specified policy service through the pipe
PS > $ps = Get-PolicyService
PS > $ps[0] | Remove-PolicyService
Delete Switch
Name:
Remove-DistributeSwitch
Syntax:
Remove-DistributeSwitch -DistributeSwitch <IDistributeSwitch> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete switch.
Parameters:
-DistributeSwitch <IDistributeSwitch>
Switch, required parameter: switch ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete switch
PS > $s = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > Remove-DistributeSwitch -DistributeSwitch $s[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete the specified switch through the pipe
PS > $s = Get-DistributeSwitch
PS > $s[0] | Remove-DistributeSwitch
Delete Virtual Interface
Name:
Remove-VirtualNetworkInterface
Syntax:
Remove-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface <IVirtualNetworkInterface> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete virtual interface.
Parameters:
-VirtualNetworkInterface <IVirtualNetworkInterface>
Interface, required parameter: Interface ID (Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Disassociation between the edge and the node interface
PS > $iface = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface -PeerDeviceType HOST -DeviceId VdSwitchId0001
PS > Remove-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $iface
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete virtual interface
PS > $vs = Get-VirtualNetworkInterface
PS > Remove-VirtualNetworkInterface -VirtualNetworkInterface $vs[0]
Move Distributed Firewall Policy
Name:
Move-DFWPolicy
Syntax:
Move-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy> -Action <String> -Direction <String> [-TargetpolicyId <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Move distributed firewall policy.
Parameters:
-DfwPolicy <IDfwPolicy>
Distributed firewall policy, required parameter: Distributed firewall policy ID(Id)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Action <String>
Distributed firewall policy action types: SHIFT (move up and down) and MOVE (move before or after the associated policy)
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Direction <String>
Associated position
You can select UP or DOWN when action is SHIFT.
You can select BEFORE or AFTER when action is MOVE.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-TargetpolicyId <String>
Associated distributed firewall policy ID, which can be entered only when action is MOVE
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Move the distributed firewall policy down
PS > $d = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > Move-DFWPolicy -DfwPolicy $d[1] -Action SHIFT -Direction DOWN -TargetpolicyId 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Move down the distributed firewall policy by specifying a policy through the pipe
PS > $d = Get-DFWPolicy
PS > $d[0] | Move-DFWPolicy -Action SHIFT -Direction DOWN -TargetpolicyId 0000000000001
Other Features
Set The Log Level
Name:
Switch-LogLevel
Syntax:
Switch-LogLevel [-LogLevel <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The cmdlet sets the log level.
Parameters:
-LogLevel <String>
Specify the log level to be set.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Set the Info log level
Switch-LogLevel -LogLevel "Info"
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Set debug log level
Switch-LogLevel -LogLevel "Debug"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Set error log level
Switch-LogLevel -LogLevel "Error"
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Set Warn log level
Switch-LogLevel -LogLevel "Warn"
————————– EXAMPLE 5 ————————–
PS > ####
Set Off log level
Switch-LogLevel -LogLevel "Off"
————————– EXAMPLE 6 ————————–
PS > ####
Set the info log level through the pipe
"Info" | Switch-LogLevel
Query Privacy Policy
Name:
Get-PrivacyPolicy
Syntax:
Get-PrivacyPolicy [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The cmdlet queries the privacy policy.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query privacy policy
PS > Get-PrivacyPolicy
Obtain The Report Information Of The HCI Platform, Including VMs And Nodes
Name:
Get-View
Syntax:
Get-View -VMHostId <String[]> [-IsTrendIncluded <Boolean>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-View -VMHost <IVMHost[]> [-IsTrendIncluded <Boolean>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-View -VM <IVirtualMachine[]> [-Limit <Int64>] [-IsTrendIncluded <Boolean>] [-Offset <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-View -VMId <String[]> [-Limit <Int64>] [-IsTrendIncluded <Boolean>] [-Offset <Int64>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Obtain the report information of the HCI platform, including VMs and nodes.
Parameters:
-VMHost <IVMHost[]>
node
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String[]>
node Id
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VM <IVirtualMachine[]>
VM ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
VM Id
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Limit <Int64>
Size of each page (the default value is 50, the minimum value is 0, and the maximum value is 1000)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsTrendIncluded <Boolean>
Historical trend information included? Not included by default
When true is input, the number of objects is limited, and each object can only obtain the trend information of one object.
So you need to specify the input parameter vmIDs, hostIDs or datastoreIDs, and only input one ID.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Offset <Int64>
Page start position (the default value and minimum value are 0)
Required? false
Position? named
Default value 0
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Obtain VM status information
PS > (Get-View -VMId 5137159212710).State | fl
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Obtain VM trend
PS > (Get-View -VMId 5137159212710 -IsTrendIncluded 1 ).Trend | fl
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Obtain node status information
PS > Get-View -VMHostId host-005056b2117d | fl
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Obtain node trend
PS > (Get-View -VMHostId host-005056b2117d -IsTrendIncluded 1).Trend | fl
Settings
Name:
Set-Config
Syntax:
Set-Config [-Language <String>] [-WithoutRebootPrompt] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Settings.
Parameters:
-Language <String>
Specify the language to be set.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-WithoutRebootPrompt [<SwitchParameter>
Whether the system does not prompt a restart. Default is true.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Set system language
PS > Set-Config -Language Chinese
Schedule Management
List Of VM Scheduling VM Group Details
Name:
Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
Syntax:
Get-VMScheduleVMGroup [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMScheduleVMGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
List of VM scheduling VM group details.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
VM scheduling VM group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
List of VM scheduling VM group details
PS > Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
List of VM scheduling VM group details
PS > Get-VMScheduleVMGroup -Id vmGroupId0001
List Of VM Scheduling Policies
Name:
Get-VMSchedulePolicy
Syntax:
Get-VMSchedulePolicy [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMSchedulePolicy -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
List of VM scheduling policies.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
VM scheduling policy ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
List of VM scheduling policies
PS > Get-VMSchedulePolicy
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
List of VM scheduling policies
PS > Get-VMSchedulePolicy -Id policyId0001
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the list of VM scheduling policies through the pipe
PS > "policyId0001" | Get-VMSchedulePolicy
List Of VM Scheduling Node Group Details
Name:
Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup
Syntax:
Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup [<CommonParameters>
Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id <String> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
List of VM scheduling node group details.
Parameters:
-Id <String>
VM scheduling node group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
PS > Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
Update VM Scheduling VM Group
Name:
Set-VMScheduleVMGroup
Syntax:
Set-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup <IVMScheduleVmgroup> [-VMId <String[]>] [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM scheduling VM group.
Parameters:
-VMScheduleVmgroup <IVMScheduleVmgroup>
VM scheduling VM group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length of the input item is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling VM group
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > Set-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup $groups[0] -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > Set-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup $groups -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling VM group
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > $groups[0] | Set-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name
————————– EXAMPLE 4 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the VM scheduling VM group description
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > $groups[0] | Set-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMId 0000000000001 -Notes $null
Update VM Scheduling Policy
Name:
Set-VMSchedulePolicy
Syntax:
Set-VMSchedulePolicy -VMSchedulePolicy <IVMSchedulePolicy> [-VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy>] [-IsDisabled] [-VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy>] -PolicyType <String>
<IVMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy>] [-VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy>] [-Name <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM scheduling policy.
Parameters:
-VMSchedulePolicy <IVMSchedulePolicy>
VM scheduling policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy>
VM anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDisabled [<SwitchParameter>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy>
VM group anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyType <String>
Policy type
Instructions for use:
1.
Please specify vmAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_AFFINITY
2.
Please specify vmAntiAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_ANTI_AFFINITY
3.
Please specify vmGroupAntiAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_GROUP_ANTI_AFFINITY
4.
Please specify vmHostAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_HOST_AFFINITY
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy>
Node group anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy>
Affinity VM scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling policy
PS > $policies = Get-VMSchedulePolicy
PS > $tAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy
PS > $tAffPolicy.AutomationType = "MUST"
PS > $tAffPolicy.VMIDs = @("0000000000001")
PS > $gAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy
PS > $gAffPolicy.VMGroupIDs = @("groupId0001")
PS > $hAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy
PS > $hAffPolicy.VMGroupIDs = @("vmGroupId0001")
PS > $hAffPolicy.HostGroupId = @("hostGroupId0001")
PS > $vAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy
PS > $vAffPolicy.AutomationType = "MUST"
PS > $vAffPolicy.VMIDs = @("0000000000001")
PS > Set-VMSchedulePolicy -VMSchedulePolicy $policies[0] -VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy $tAffPolicy -IsDisabled -VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy $gAffPolicy -PolicyType VM_AFFINITY -VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy $hAffPolicy -VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy $vAffPolicy -Name test-name
Update VM Scheduling Node Group
Name:
Set-VMScheduleVMHostGroup
Syntax:
Set-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup <IVMScheduleVmhostGroup> [-VMHostId <String[]>] [-Notes <String>] [-Name <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Update VM scheduling node group.
Parameters:
-VMScheduleVmhostGroup <IVMScheduleVmhostGroup>
VM scheduling node group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMHostId <String[]>
List of node IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length of the input item is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling node group
PS > $vmHostGroup = Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > Set-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup $vmHostGroup -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name [-RunAsync]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Update VM scheduling node group (asynchronous call)
PS > $vmHostGroup = Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > Set-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup $vmHostGroup -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Notes test-note -Name test-name -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Clear the VM scheduling node group description
PS > $vmHostGroup = Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > Set-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup $vmHostGroup -Notes $null
Create VM Scheduling VM Group
Name:
New-VMScheduleVMGroup
Syntax:
New-VMScheduleVMGroup -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-VMId <String[]>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM scheduling VM group
Instructions for use:
For the same VM group, the run location must be configured in the same fault domain or automatically selected. The run location cannot be set if the VM is running.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Name
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length of the input item is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMId <String[]>
List of VM IDs
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM scheduling VM group
PS > New-VMScheduleVMGroup -Name test-name -Notes test-note -VMId 0000000000001
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM scheduling VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > New-VMScheduleVMGroup -Name test-name -Notes test-note -VMId 0000000000001 -RunAsync
Create VM Scheduling Policy
Name:
New-VMSchedulePolicy
Syntax:
New-VMSchedulePolicy -Name <String> -PolicyType <String> [-IsDisabled] [-VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy>] [-VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy>] [-VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy>
[-VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM scheduling policy.
Parameters:
-Name <String>
Name
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-PolicyType <String>
Policy type
Instructions for use:
1.
Please specify vmAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_AFFINITY
2.
Please specify vmAntiAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_ANTI_AFFINITY
3.
Please specify vmGroupAntiAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_GROUP_ANTI_AFFINITY
4.
Please specify vmHostAffinityPolicy when the policy type is VM_HOST_AFFINITY
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-IsDisabled [<SwitchParameter>
Enabled?
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy>
VM group anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy>
Node group anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy>
Affinity VM scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy <IVMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy>
VM anti-affinity scheduling policy
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM scheduling policy
PS > $gAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy
PS > $gAffPolicy.VMGroupIDs = @("groupId0001")
PS > $hAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy
PS > $hAffPolicy.VMGroupIDs = @("vmGroupId0001")
PS > $hAffPolicy.HostGroupId = @("hostGroupId0001")
PS > $vAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy
PS > $vAffPolicy.AutomationType = "MUST"
PS > $vAffPolicy.VMIDs = @("0000000000001")
PS > $tAffPolicy = New-Object -TypeName Sangfor.Acloud.Models.VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy
PS > $tAffPolicy.AutomationType = "MUST"
PS > $tAffPolicy.VMIDs = @("0000000000001")
PS > New-VMSchedulePolicy -Name test-name -PolicyType VM_AFFINITY -IsDisabled -VMScheduleVmgroupAntiAffinityPolicy $gAffPolicy -VMScheduleVmhostAffinityPolicy $hAffPolicy -VMScheduleVmaffinityPolicy $vAffPolicy -VMScheduleVmantiAffinityPolicy $tAffPolicy
Create VM Scheduling Node Group
Name:
New-VMScheduleVMHostGroup
Syntax:
New-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMHostId <String[]> -Name <String> [-Notes <String>] [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Create VM scheduling node group.
Parameters:
-VMHostId <String[]>
List of node IDs
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Name <String>
Name
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length of the input item is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ()【】_-.+()@.
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Notes <String>
description
Instructions for use:
1.
The maximum length is 90 characters or 30 Chinese characters.
2.
Can only contain digits, letters, spaces, Chinese characters, and the following special characters: ,。!¥……()【】“”‘’:;_-:.+=()@!~,/.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM scheduling node group
PS > New-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Create VM scheduling node group (asynchronous call)
PS > New-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMHostId host-000000000001 -Name test-name -Notes test-note -RunAsync
Delete VM Scheduling VM Group
Name:
Remove-VMScheduleVMGroup
Syntax:
Remove-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup <IVMScheduleVmgroup> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM scheduling VM group.
Parameters:
-VMScheduleVmgroup <IVMScheduleVmgroup>
VM scheduling VM group ID
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? true (ByValue)
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameter:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling VM group
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > Remove-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup $groups[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling VM group (asynchronous call)
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > Remove-VMScheduleVMGroup -VMScheduleVmgroup $groups[0] -RunAsync
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling VM group through the pipe
PS > $groups = Get-VMScheduleVMGroup
PS > $groups[0] | Remove-VMScheduleVMGroup
Delete VM Scheduling Policy
Name:
Remove-VMSchedulePolicy
Syntax:
Remove-VMSchedulePolicy -VMSchedulePolicy <IVMSchedulePolicy> [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM scheduling policy.
Parameters:
-VMSchedulePolicy <IVMSchedulePolicy>
VM scheduling policy
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling policy
PS > $policies = Get-VMSchedulePolicy
PS > Remove-VMSchedulePolicy -VMSchedulePolicy $policies[0]
Delete VM Scheduling Node Group
Name:
Remove-VMScheduleVMHostGroup
Syntax:
Remove-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup <IVMScheduleVmhostGroup> [-RunAsync] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Delete VM scheduling node group.
Parameters:
-VMScheduleVmhostGroup <IVMScheduleVmhostGroup>
VM scheduling node group
Required? true
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-RunAsync [<SwitchParameter>
The command is returned immediately without waiting.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value False
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling node group
PS > $vmHostGroup = Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > Remove-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup $vmHostGroup[0]
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Delete VM scheduling node group
PS > $vmHostGroup = Get-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -Id groupId0001
PS > Remove-VMScheduleVMHostGroup -VMScheduleVmhostGroup $vmHostGroup[0] -RunAsync
User Management
Query the Terms Of Use
Name:
Get-UserProtocol
Syntax:
Get-UserProtocol [<CommonParameters>
Description:
The cmdlet queries the Terms of Use.
Parameters:
N/A.
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query the Terms of Use
PS > Get-UserProtocol
Query User
Name:
Get-User
Syntax:
Get-User [-Ids <String[]>] [<CommonParameters>
Get-User [-Id <String>] [<CommonParameters>
Description:
Query user group information.
Parameters:
-Ids <String[]>
A set of user IDs.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
-Id <String>
User ID.
Currently, the interface does not support custom query of user information, and it can only query the current user information.
Required? false
Position? named
Default value
Accept pipeline input? false
Accept wildcard characters? false
Output Parameters:
Example:
————————– EXAMPLE 1 ————————–
PS > ####
Query all users
PS > Get-User
————————– EXAMPLE 2 ————————–
PS > ####
Query a group of users through the ID list
PS > Get-User -Ids "xxx", "yyy"
————————– EXAMPLE 3 ————————–
PS > ####
Query a single user by ID
PS > Get-User -Id "xxx"