【HCI】Virtual Storage Deployment Guide_V6.8.0
Background
Sangfor HCI virtual storage is the pooling of physical storage from multiple nodes into what appears to be a single storage device that is managed from a central console. It provided data copies across nodes and data tiering and caching technology to ensure high availability and performance on customer production.

Definition of Virtual Storage
-
Minimum of 2 nodes to build a Virtual Storage.
-
Integrate all the cluster nodes’ hard disks into one Virtual Storage.
-
Virtual Storage is based on a Distributed File System.
-
Storage Virtualization requires a valid aSAN license.
Limitations of Virtual Storage
-
Minimum 2 data copies and HCI 6.0.1 and above supports up to 3 data copies.
-
A Virtual Storage must have an SSD cache disk. (Not necessary on a full flash data disk deployment).
Note:
For HCI version 6.0.1 below, the number of copies cannot be changed after Virtual Storage initialization.
Storage Policy allows the virtual machines’ data copy to be modified between 2-copies and 3-copies.
Types of Virtual Datastore
HCI supports multiple volume management, ordinary volumes, and stretched volumes that can coexist in a cluster simultaneously.
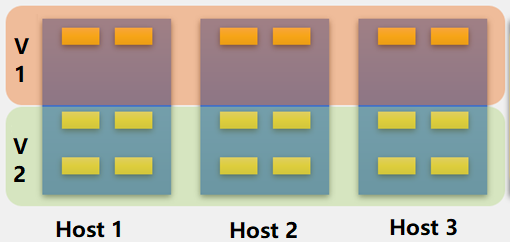
A host-based multi-volume requires at least six hosts, three hosts for a volume and the other three for a volume. Three or more hosts can divide multiple volumes for multi-volume based on disks.
Therefore, a single host can create an all-flash volume based on creating a mixed volume, which will require high disk performance. All services run on all-flash volumes to improve disk usage. Host multi-volume and disk multi-volume methods can coexist on an HCI cluster.
As an example, the supported group multi-volume mode for three hosts is shown in the figure.
Precautions
-
The newly added volume will be formatted when it is created. Before adding, please ensure that no data needs to be preserved on the disk used to add the new volume.
-
A cluster is allowed to have a maximum of six virtual datastores, of which a maximum of one stretched volume is allowed.
-
A volume consists of hard disks on at least three hosts, and a host can be divided into two volumes at most.
-
Virtual storage does not support a single copy. When a single copy is used, the virtual storage is not redundant, and there is a risk of data loss.
-
Two hosts do not support data balancing.
-
Striping is not supported for virtual machines on two hosts.
-
Virtual storage is a full HDD deployment and does not support upgrades or new deployments.
-
If the capacity of three hosts is too large, the deployment of virtual storage will be limited. It is required that the capacity of one host cannot exceed the sum of the capacities of the other hosts. For example, host A is 1TB, host B is 1TB, and host C is 5TB. Deployment is not supported.
-
A host spanned by one volume cannot belong to two other volumes.
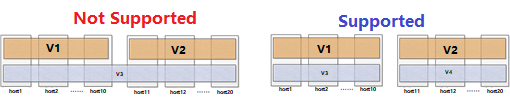
-
Stretched clusters do not support multiple volumes. A host cannot belong to extended and normal volumes, as shown below:
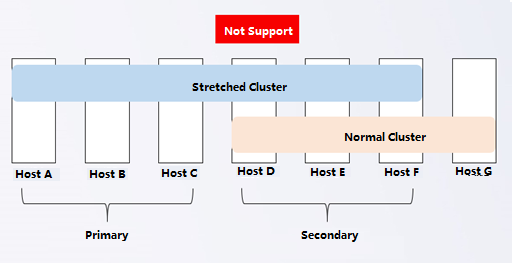
-
All-flash volumes (compression) do not support hard disk volumes but only host volumes.
-
A single host in an ordinary volume has at least one SSD, and a single host in an all-flash volume has at least two SSDs.
Ordinary Datastore
Ordinary datastore use automated tiering to give full advantage of the SSD and HDD and achieve excellent performance.
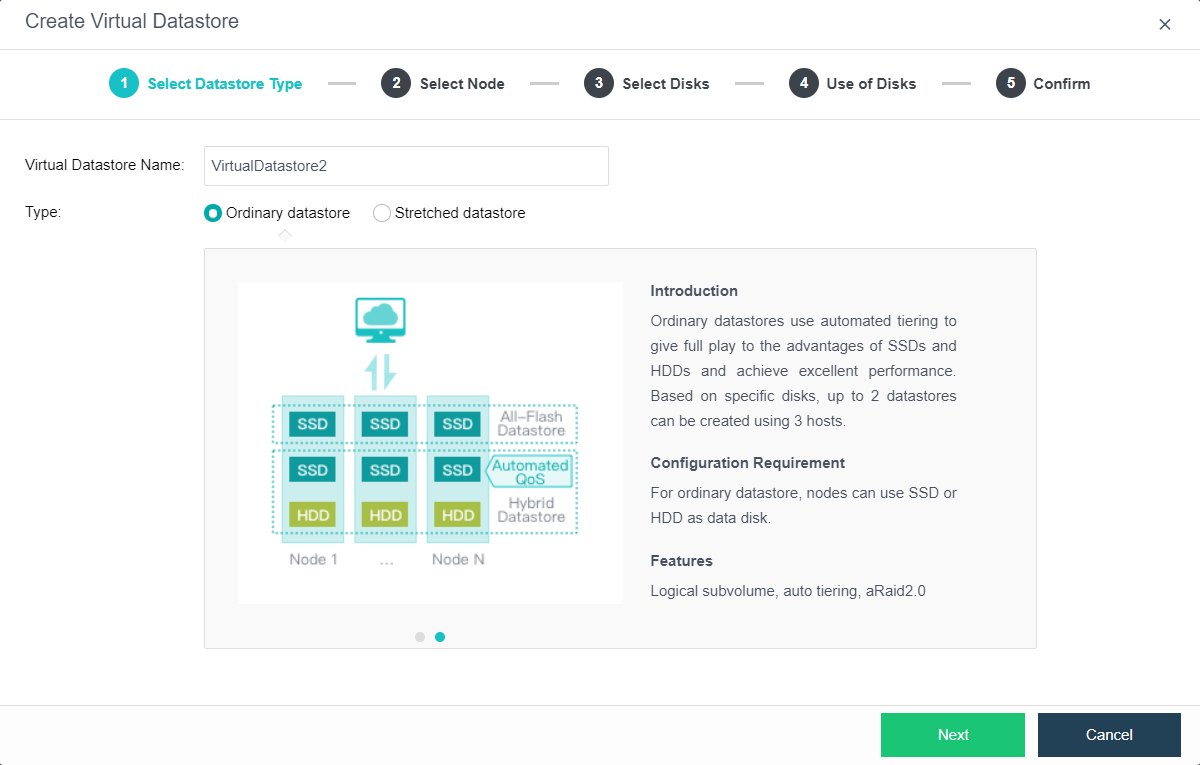
Note:
To set up multiple volumes, each volume requires at least three hosts.
At least three hosts are required to form multiple disk volumes.
The expansion host’s management interface, storage interface, overlay network interface, and service interface have been connected to the network.
Stretched Datastore
A stretched cluster starts with at least four hosts plus one witness node. In actual deployment, ensuring that the node location configured on the page is consistent with the actual physical location is necessary. Otherwise, it cannot achieve the computer room level protection. The two fault domain computer rooms must be connected at Layer 2, and the link of the witness node does not need to be connected at Layer 2, but make sure it is reachable by the network.
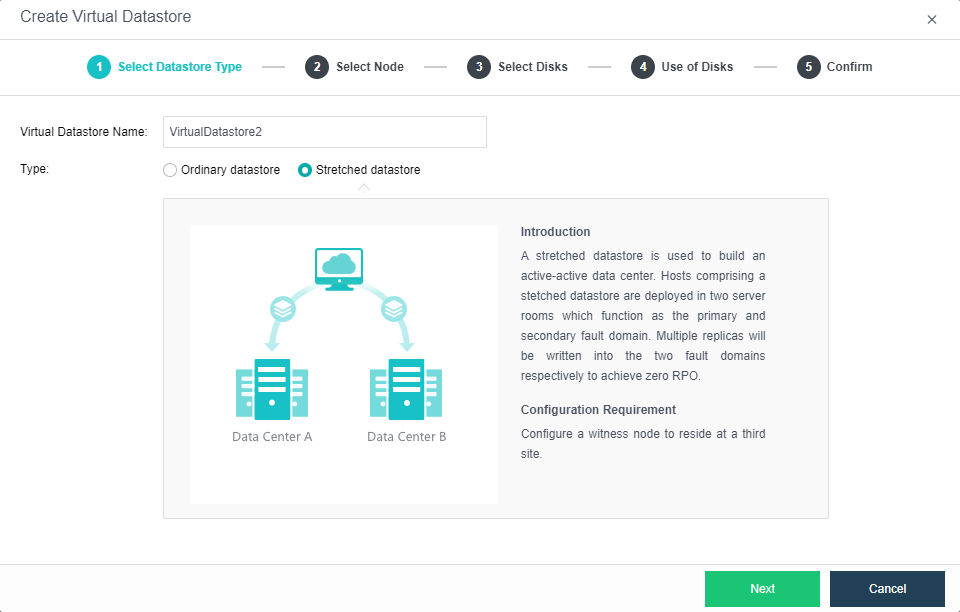
Note:
The newly added volume will be formatted when it is created. Before adding, please ensure that no data needs to be preserved on the disk used to add the new volume.
HCI builds volumes based on the host as the basic unit. Therefore, please plan ahead to create a cluster.
The deployment mode of the witness node supports physical machine deployment and VMware virtualization deployment. Using the management interface to communicate with the data node is recommended.
Types of disks in Sangfor Virtual Storage
Cache Disk
- Must use Enterprise SSD as Cache Disk.
- Recommended SSD with 256GB or above.
- Recommended cache/data disk ratio 1:3 (SSD:HDD).
- Recommended cache/data disk volume ratio 1:10. (Cannot be lower than 1:20).
- Suggests using 512GB SSD when each data disk is over 2TB.
- It is used to speed up the read-and-write process.
Data Disk
- Recommended to use HDD as Data Disk. (Supports SSD, SAS & NVMe PCIe).
- HDD Enterprise Edition and >7200 RPM.
- Forms Virtual Storage with all Data Disks on the cluster.
- Virtual Machines and other data will be stored in Virtual Storage.
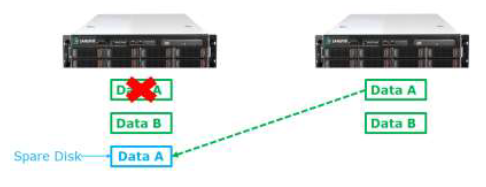
Spare Disk
-
A spare disk stays on standby and is used when the data disk fails.
Configuration Guide
- Setup Storage Network Interface.
Go to Storage > Virtual Storage > Storage Area Network Settings and click Edit Storage Area Network. It will pop out an alert message. If you want to proceed, enter the admin’s password to configure the storage deployment mode.
Deployment Mode:
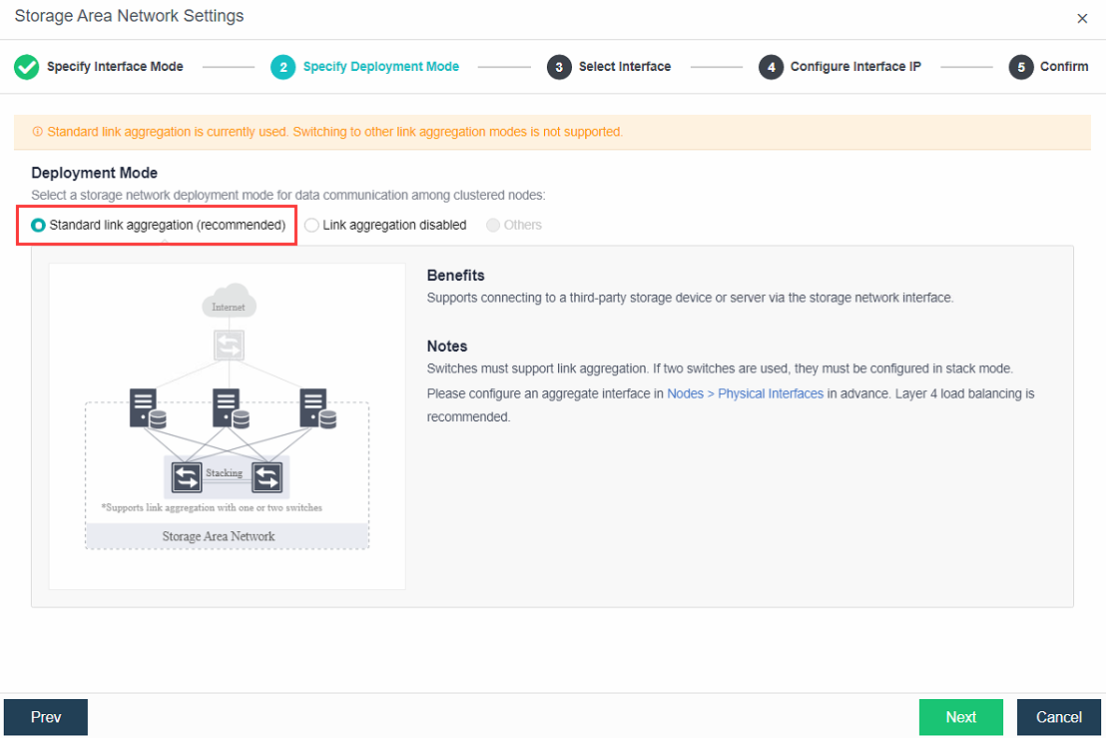
- Standard link aggregation (recommended): By configuring interface aggregation on the node and switch, the node can connect to the third-party storage or third-party server through the virtual storage interface. If you use two switches, the switches also must be configured into stacking mode. Select the Layer 4 load balancing as the interface load balance mode is recommended.
-
Link aggregation disabled: The network storing data communication is independent, and the switch is not required. It can be an ordinary layer 2 switch, and there is no need to make any configuration. However, when a link fails, the storage on the connected host will be directly unavailable.
-
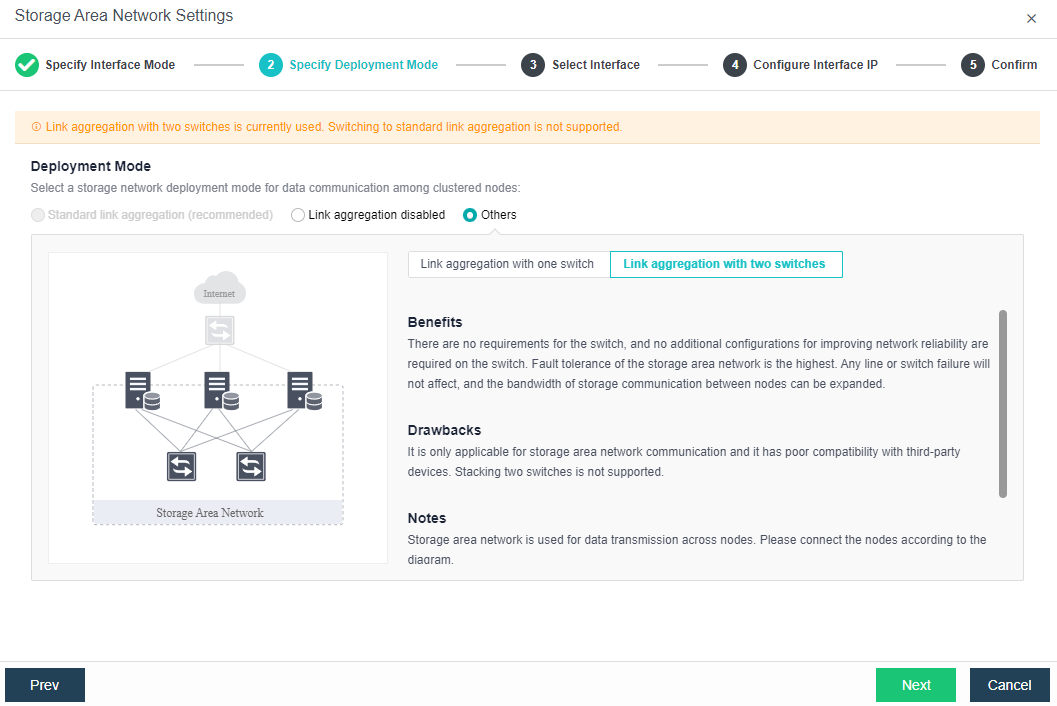
Others:
a) Link Aggregation with One Switch: A single storage network link aggregation switch. There is no requirement for the switch. It can be an ordinary layer 2 switch, and there is no need to make any configuration. The failure of a single link does not affect storage communication.
b) Link Aggregation with two switches: Two switches are used for storage network link aggregation. There is no requirement for switches. Ordinary layer 2 switches do not need to make any configuration on the switches. They have high fault tolerance. Any line or switch failure will not affect storage communication.
Note:
To deploy standard link aggregation, select Link aggregation disabled and save, then edit the storage area network to switch to standard link aggregation mode.
- Configuring Datastore Type and Disks
The virtual storage volume is divided into Ordinary Datastore and Stretched Datastore. When the HCI cluster is planned to be a standard cluster, select Ordinary Datastore. When planning an HCI cluster as a Stretched Cluster, select Stretched Datastore.
Note:
When deploying a stretched cluster, you need to deploy a witness node. The witness node can be deployed on a physical server or a VMware virtualization environment.
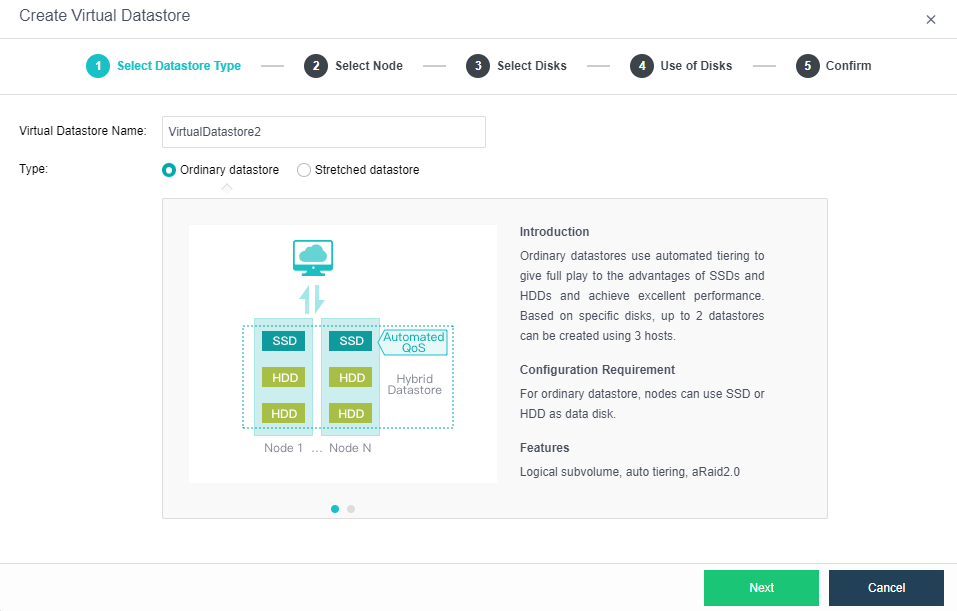
Create Ordinary Datastore
- Go to Storage > Virtual Storage > New and select the volume type as Ordinary Datastore.
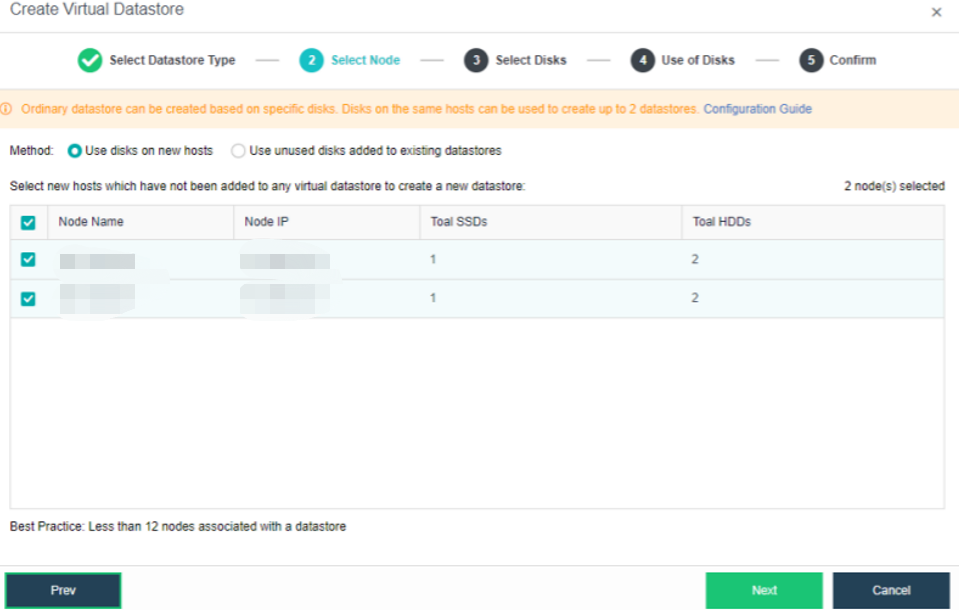
- Select the corresponding method and nodes to create a virtual datastore. Since we are creating the first virtual datastore, choose the Use disks on new hosts.
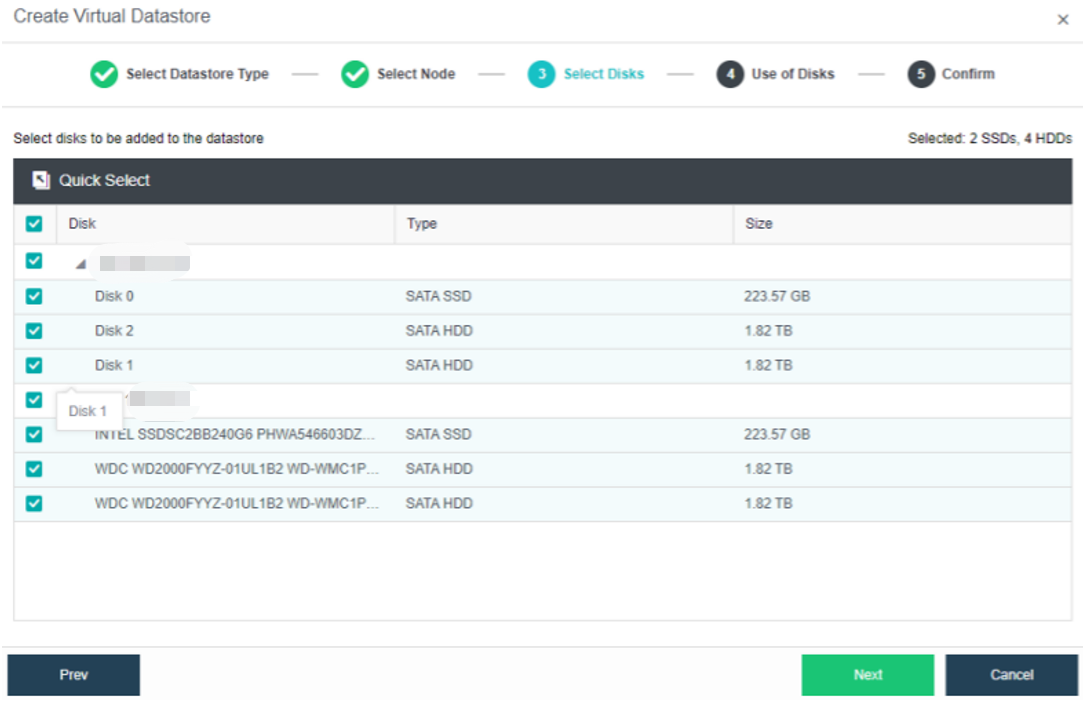
-
Select the hard disk to be added to the node. Configure hard disks and hard disk groups, then make a detailed usage plan for each node’s disk. The system will automatically detect the disks of all nodes in the cluster. By default, mechanical disks are selected as data disks and solid-state disks as cache disks. Using the default configuration is recommended. If you need to deploy multiple databases, you need to plan to reserve the disks of the second database group.
Select the disks that will be used to create a virtual datastore.
A hybrid datastore requires at least one SSD as a cache disk.
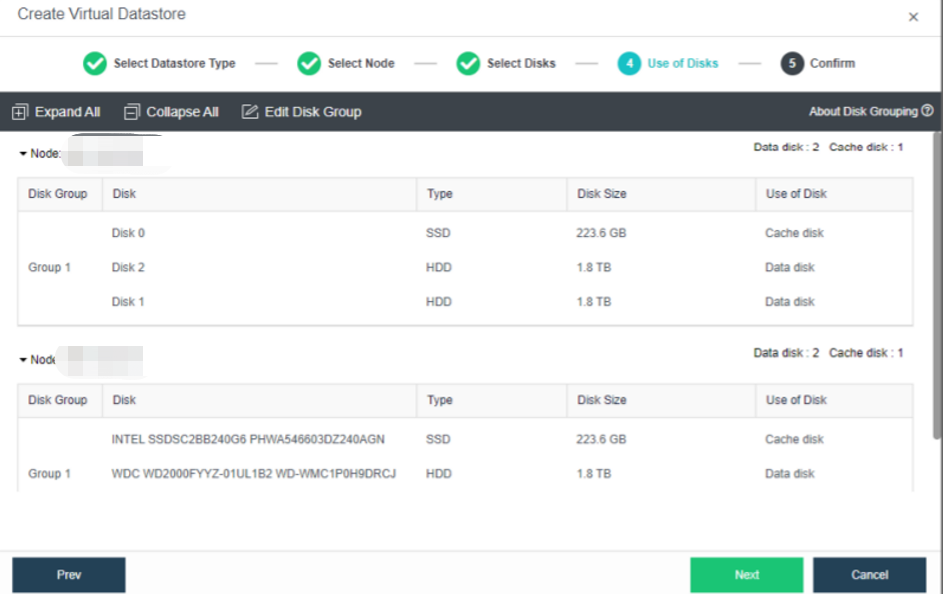
- Confirm the details and proceed.
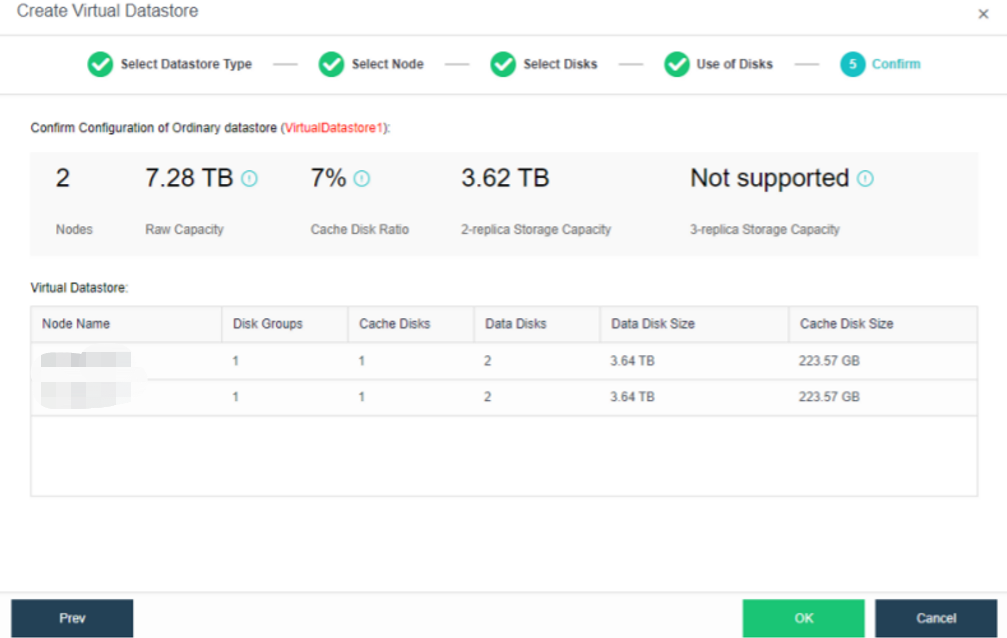
- The following page displays virtual storage configurations, including available disk space, the number of data copies, and the total number of disks. After confirming configurations, click OK. Then, input the administrator account password: admin. Then, click Finish to begin initializing virtual storage.
Create Stretched Datastore
- Configure the storage datastore type. Navigate to Storage > Virtual Storage and click New. Then, select the datastore type as Stretched datastore.
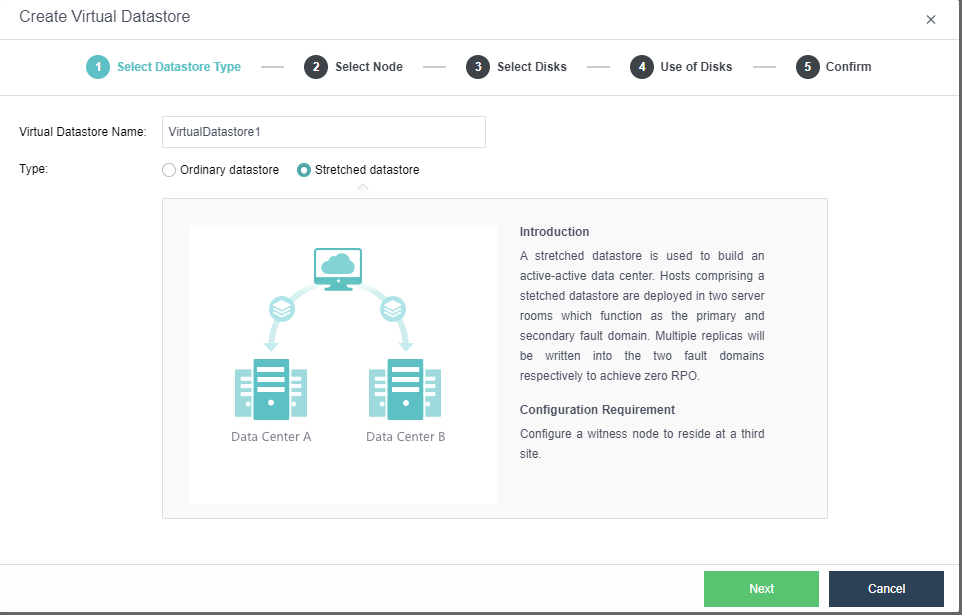
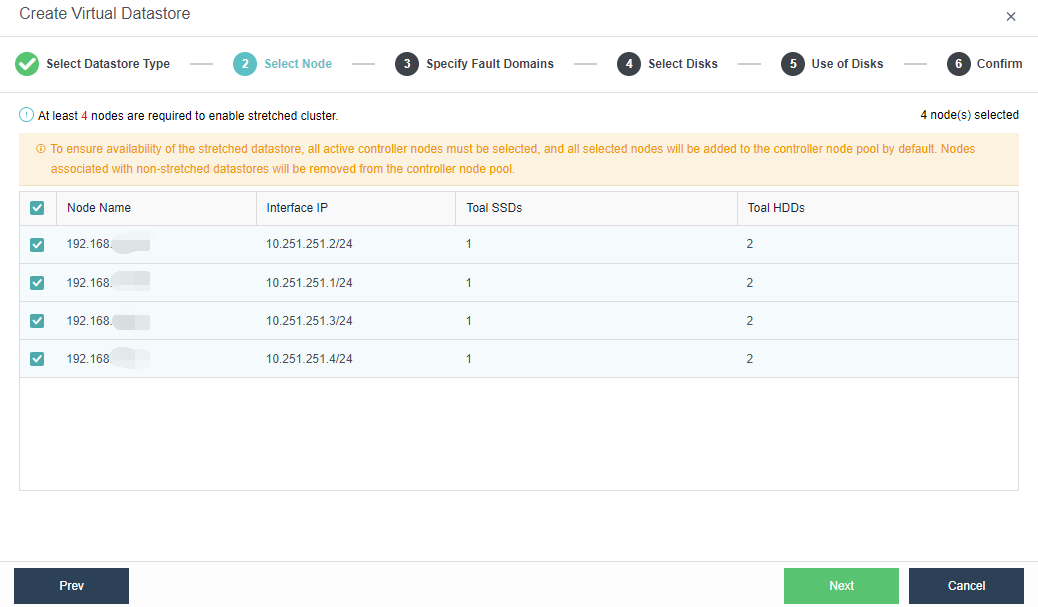
- Select the nodes to be added to the stretched datastore. The stretched cluster requires at least 4 nodes.
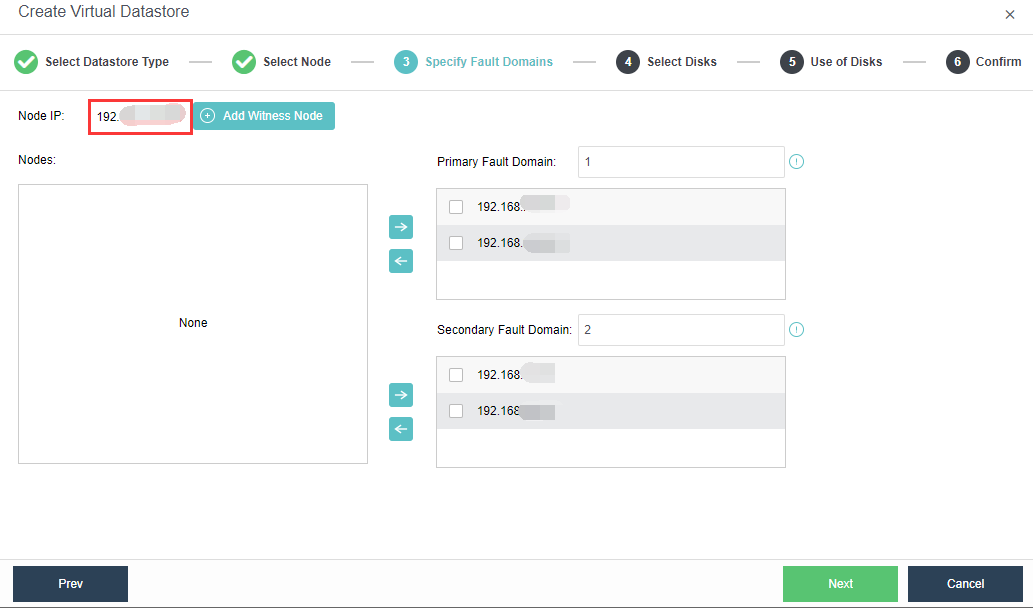
- Specify fault domains. Add the required nodes to the corresponding fault domains. There are four nodes in this example, so two nodes are added to the Primary Fault Domain, while another two are added to the Secondary Fault Domain.
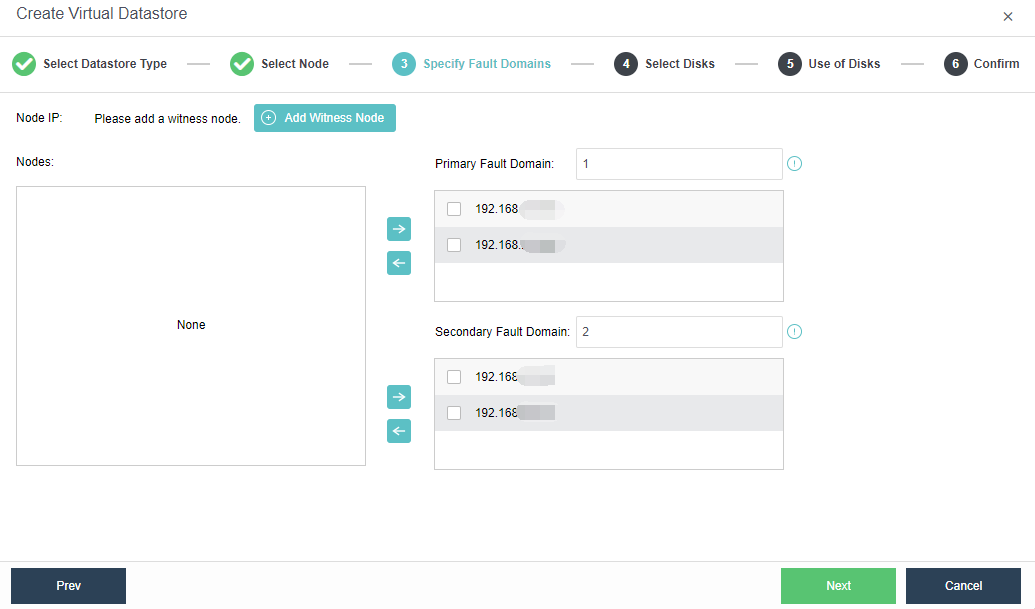
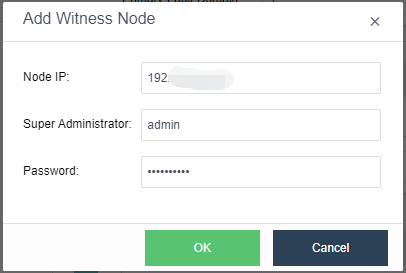
- Add Witness Node: Configure the witness node IP according to the pre-installed witness node after naming the Primary Fault Domain and the Secondary Fault Domain. Follow the wizard to enter the password to confirm the configuration of the witness node.
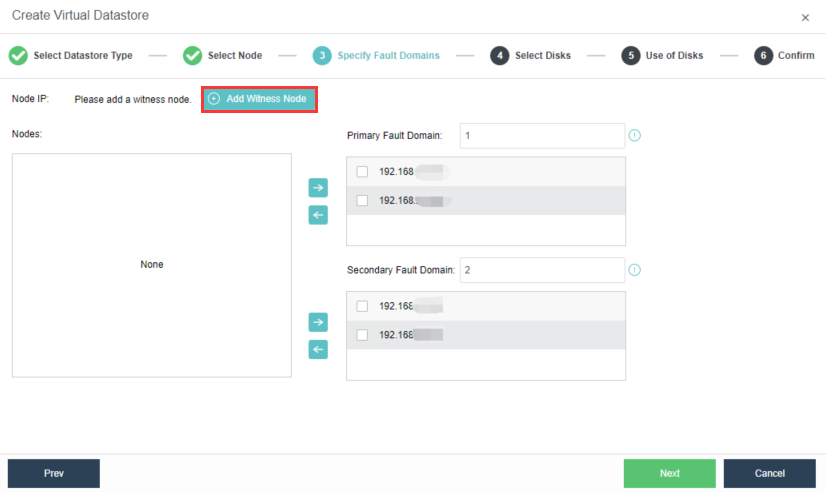
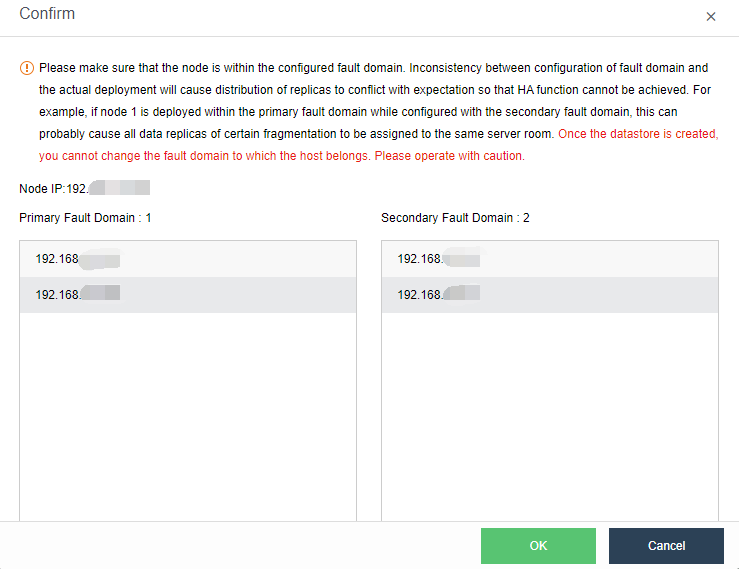
- Confirm the configuration: Confirm the configuration of the fault domain. Modifying the fault domain where the node is located after the datastore is created is not supported.
- Configure the Use of Disks. Next, you need to plan the use of disks, including data disk, cache disk, and spare disk. Generally, SSD is used as a cache disk to improve the IO performance of virtual storage. The system automatically recommends the type of hard disk according to the configuration. You can follow the default recommendations of the system.
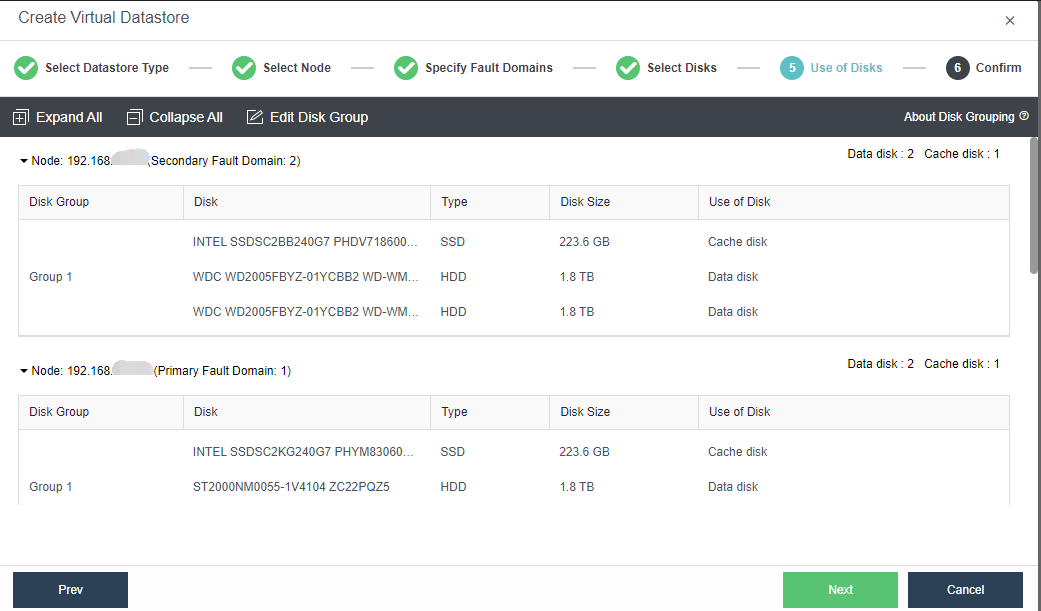
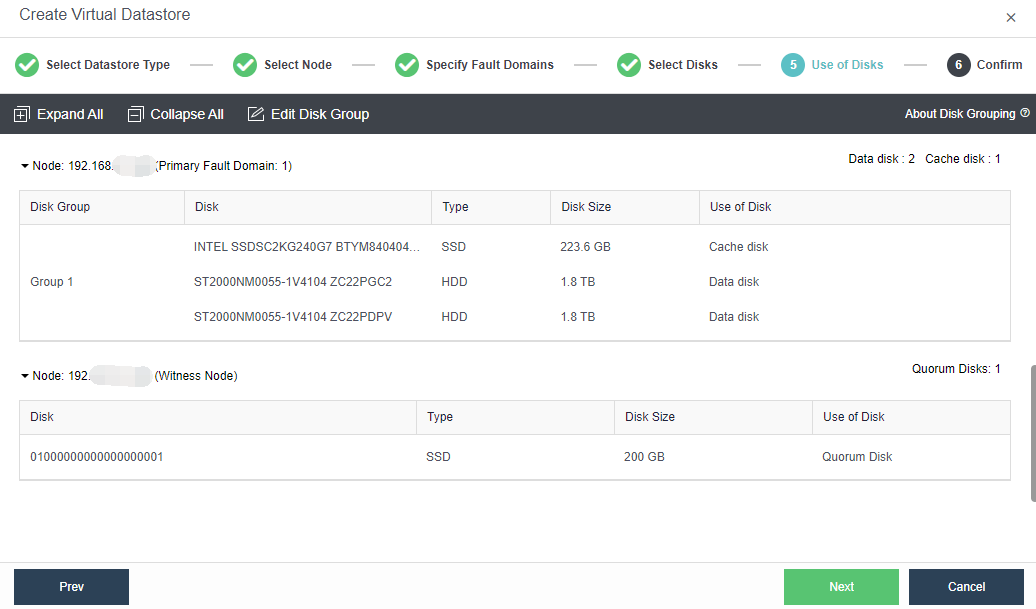
- Confirm the configuration. Finally, the page displays the configuration result information of the virtual datastore, including the final storage capacity, the number of copies, and the number of disks. After confirming that the configuration is correct, enter the administrator password and click OK to start initializing the virtual datastore.
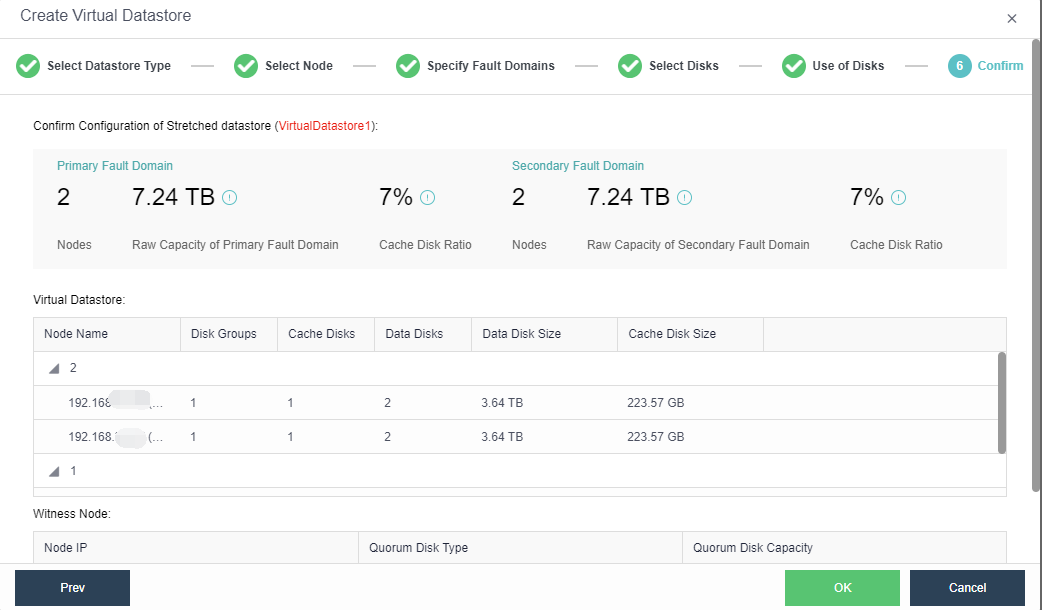
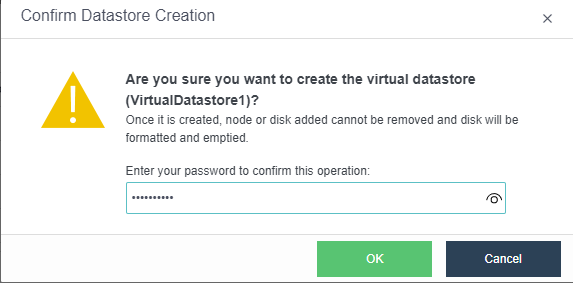
Precautions
- If the HCI host is an aServer hardware, it must use a hard disk/SSD purchased from a Sangfor representative. It is not allowed to add third-party disks to form virtual storage.
- The volume of the cache disk cannot be lower than the 5% ratio of the total volume data disk in a disk group.