【IAG】Script Single Sign-On (SSO) Configuration Guide_V13.0.80
Scenario
A customer uses a Microsoft AD server to manage intranet users who are on Windows systems. The customer wants to control the intranet users’ online behavior and traffic information while also performing identity verification for these users. Among the various ways of combining Microsoft AD domain authentication, the script SSO has the highest success rate.
Configuration Steps
The configuration steps are as shown in the figure below. It should be noted that to make everyone familiar with the AD domain faster, we added the AD domain configuration method, which is the part marked as not necessary. You may focus on configuring IAG if the AD domain has been deployed.
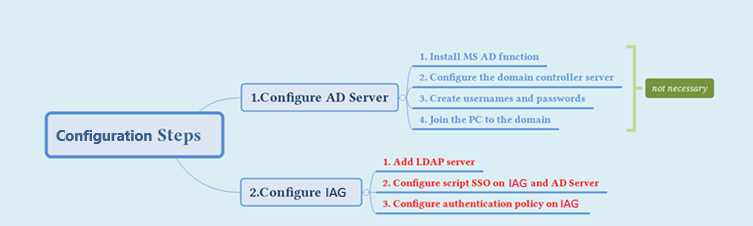
Configure Active Directory Server
Install MS AD Function
- Open Server Manager in Windows Server 2019.
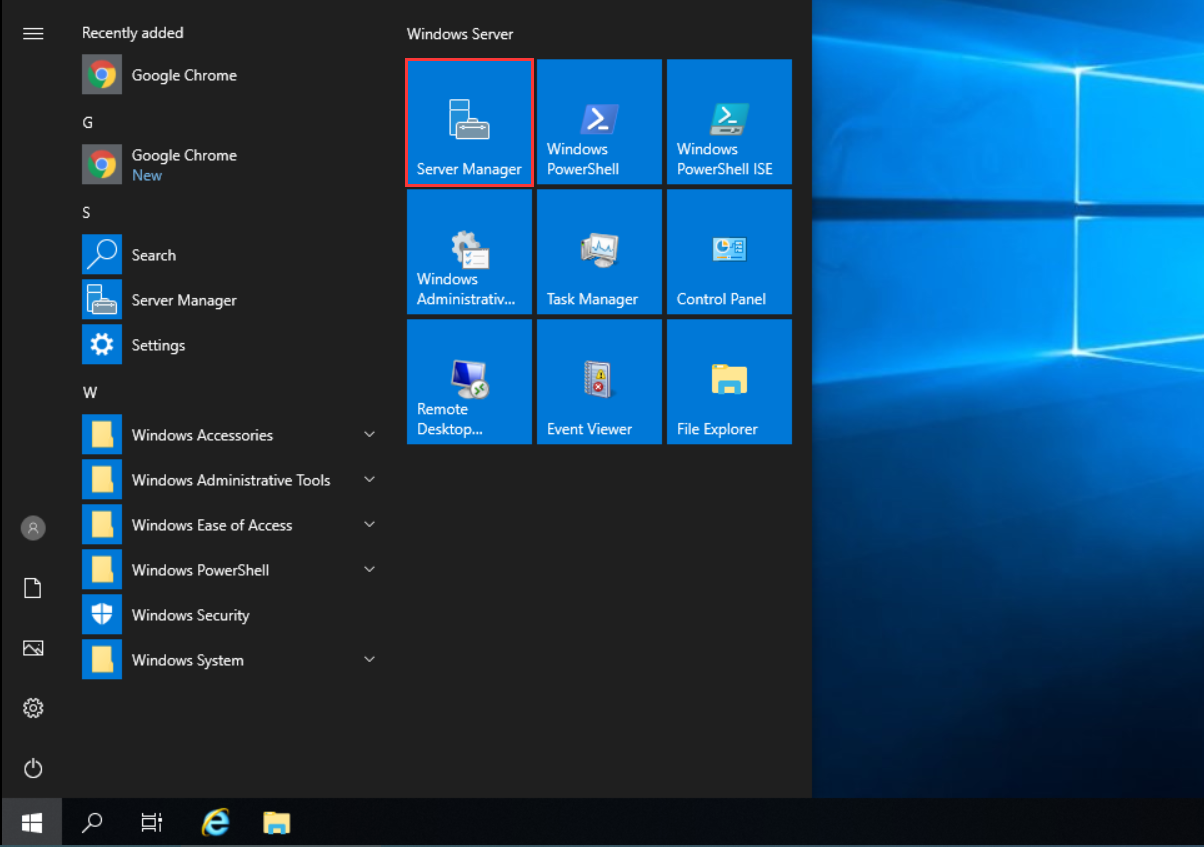
- On the Dashboard, click Add roles and features to open the Add Roles and Features Wizard.
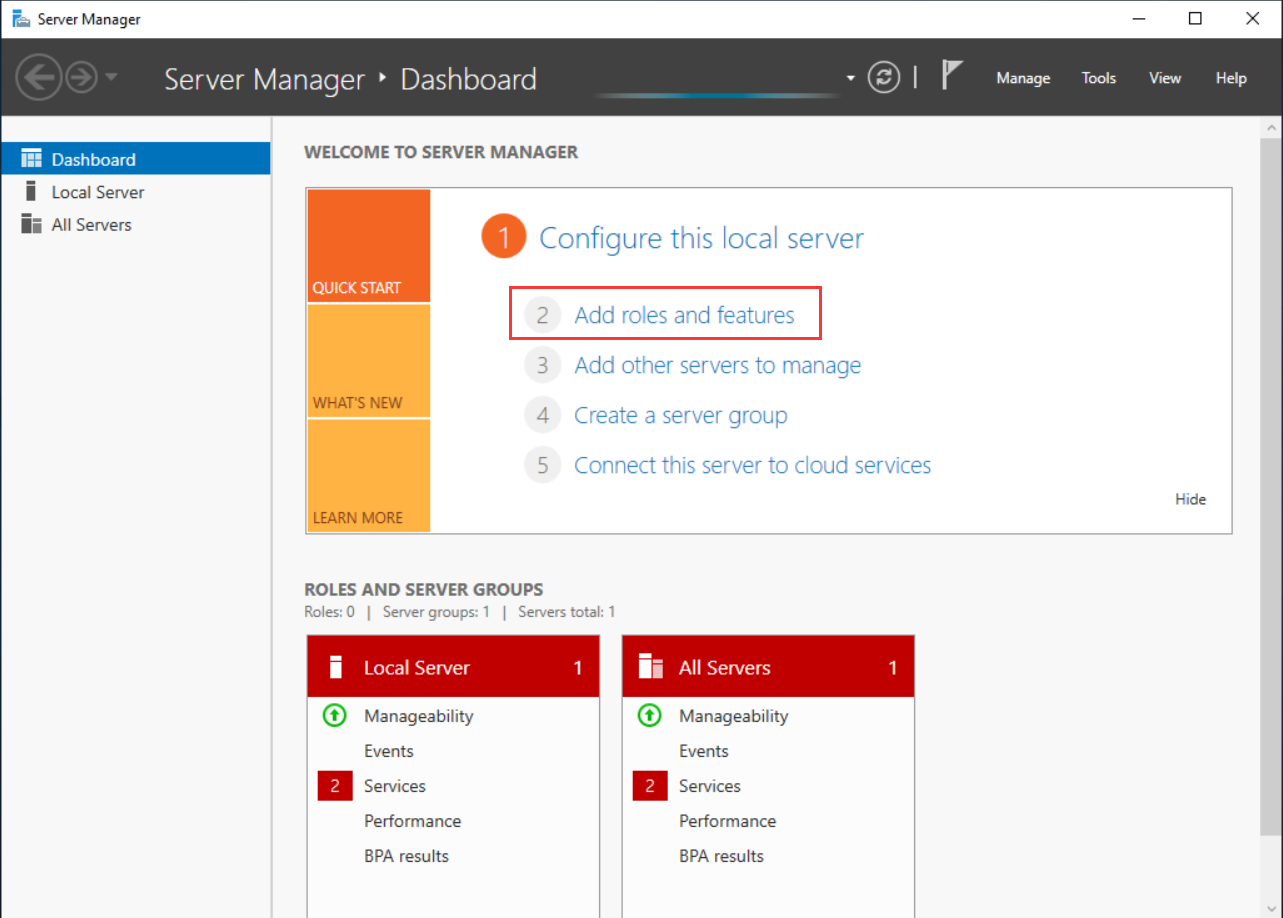
- On the Before You Begin tab, click Next.
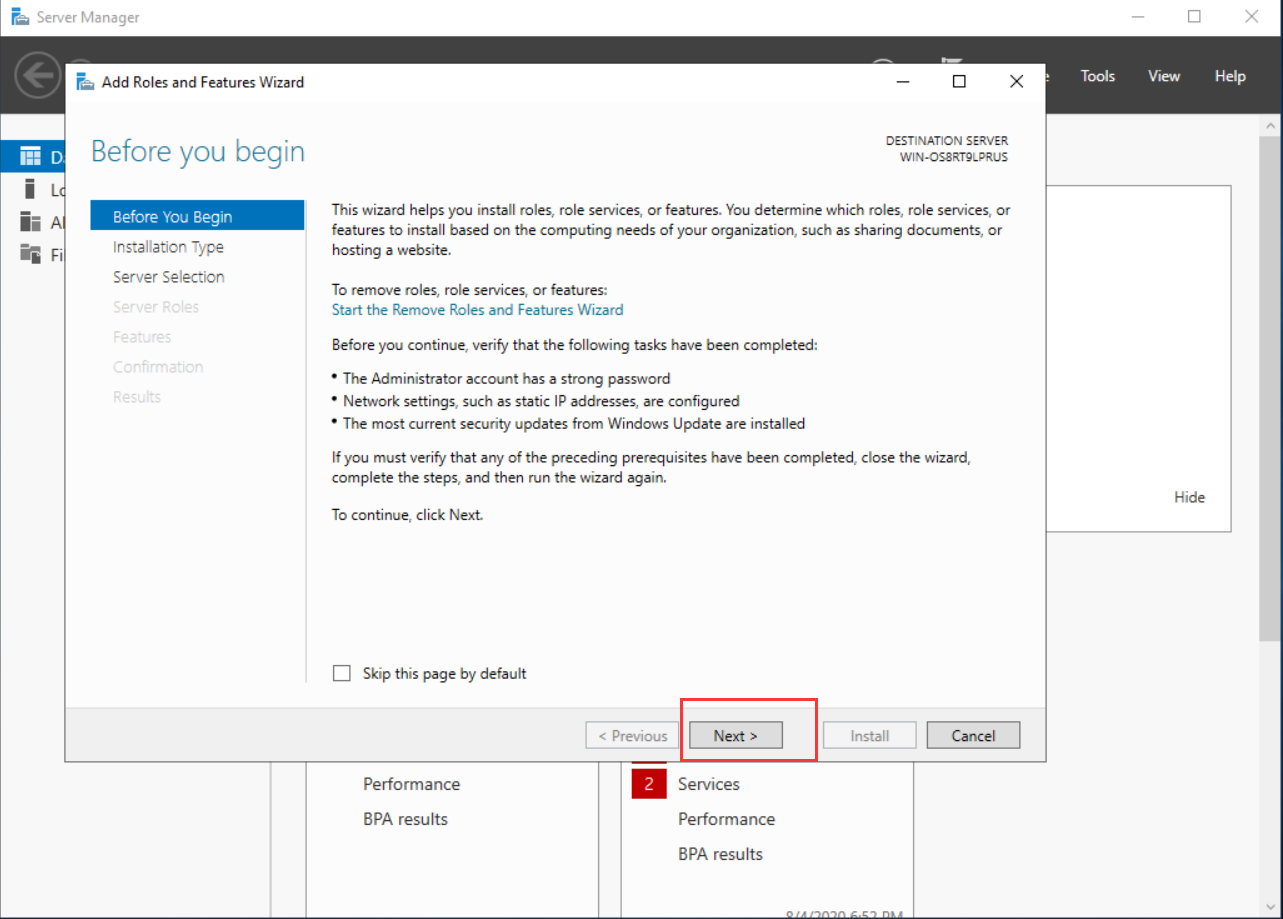
- On the Installation Type tab, select Role-based or feature-based installation. Then click Next.
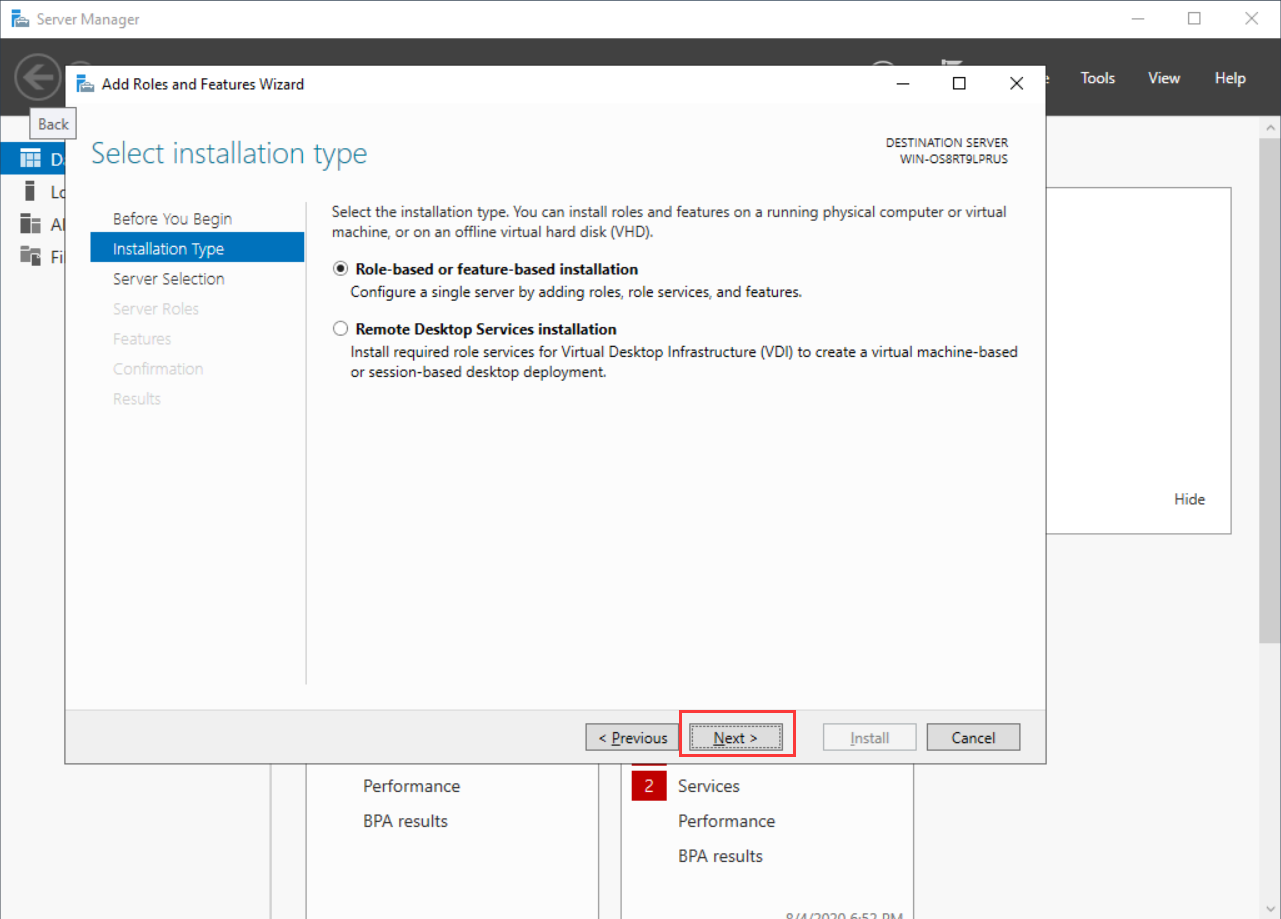
- On the Server Selection tab, choose Select a server from the server pool, and then click Next.
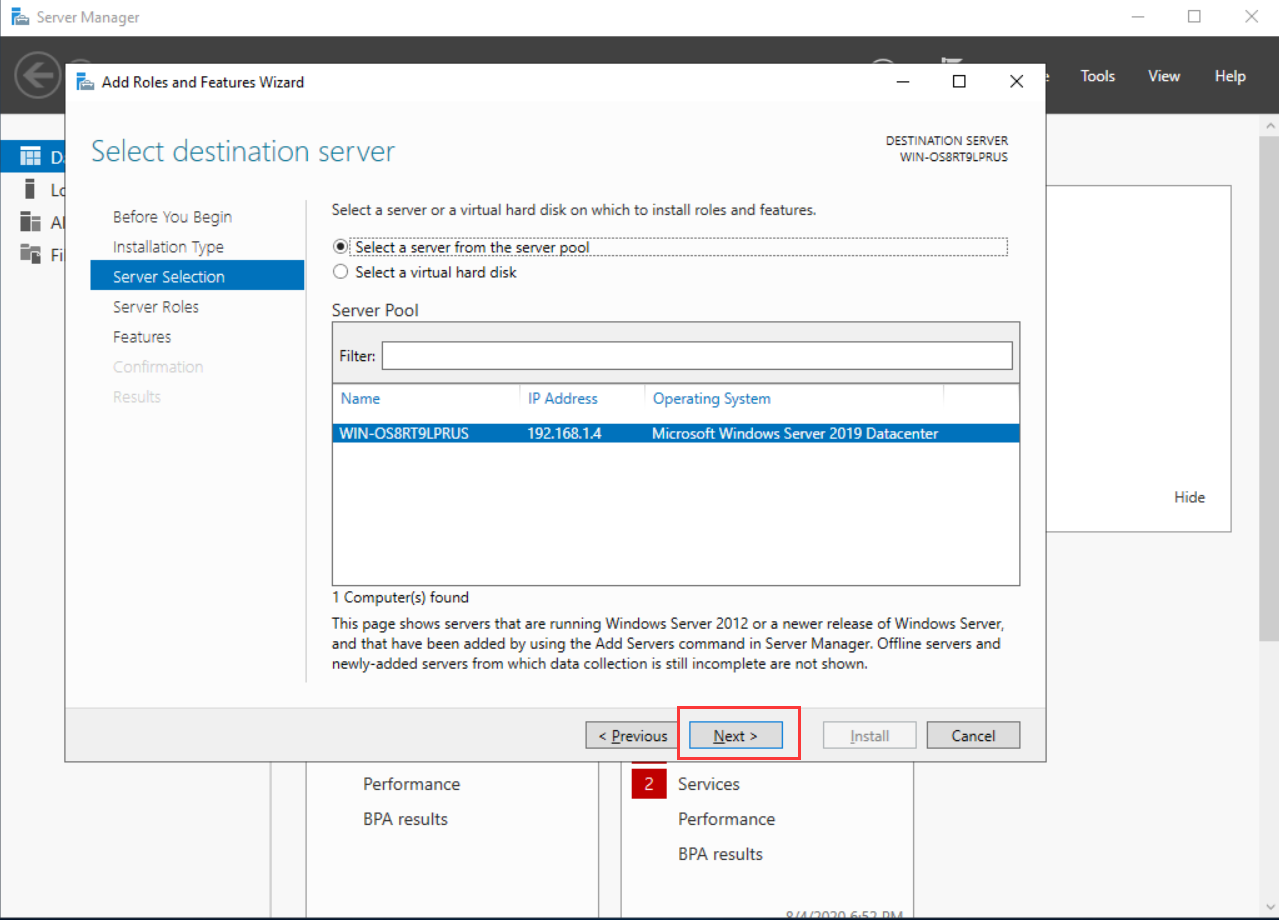
- On the Server Roles tab, select the functions that need to be installed, such as Active Directory Domain Services and DNS Server, then click Next.
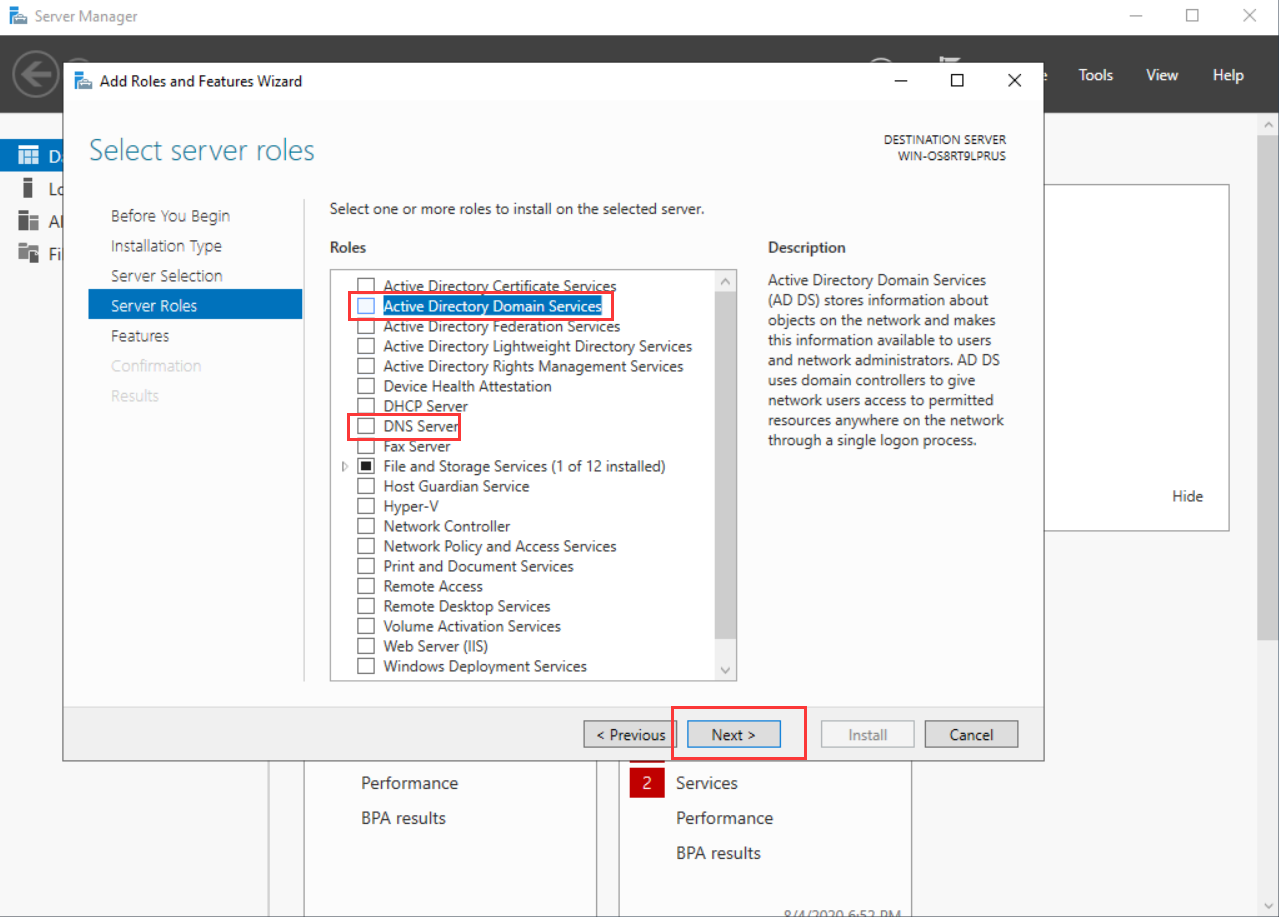
- On the Features tab, select Group Policy Management, and click Next.
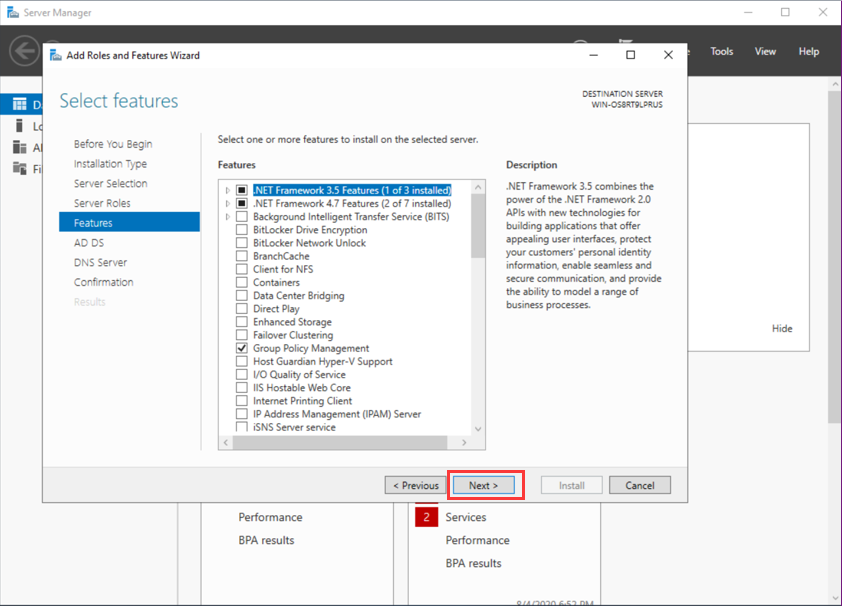
- On the AD DS tab, click Next to proceed.
- On the DNS Server tab, click Next to continue.
- On the Confirmation tab, check the Restart the destination server automatically if required checkbox. Then, click Install.
- Wait for the installation to be completed. You can view the installation progress on the Results tab.
- Click Close after the installation is completed.
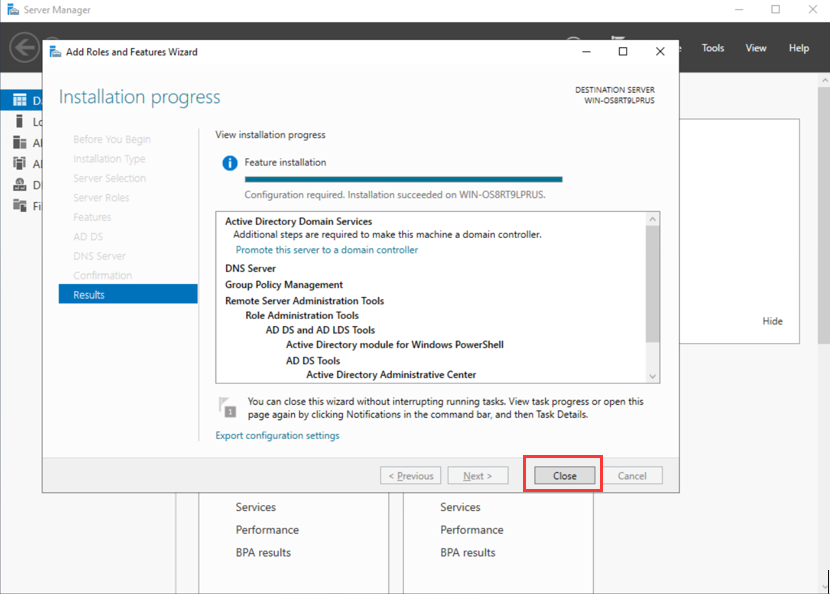
Configure the Domain Controller
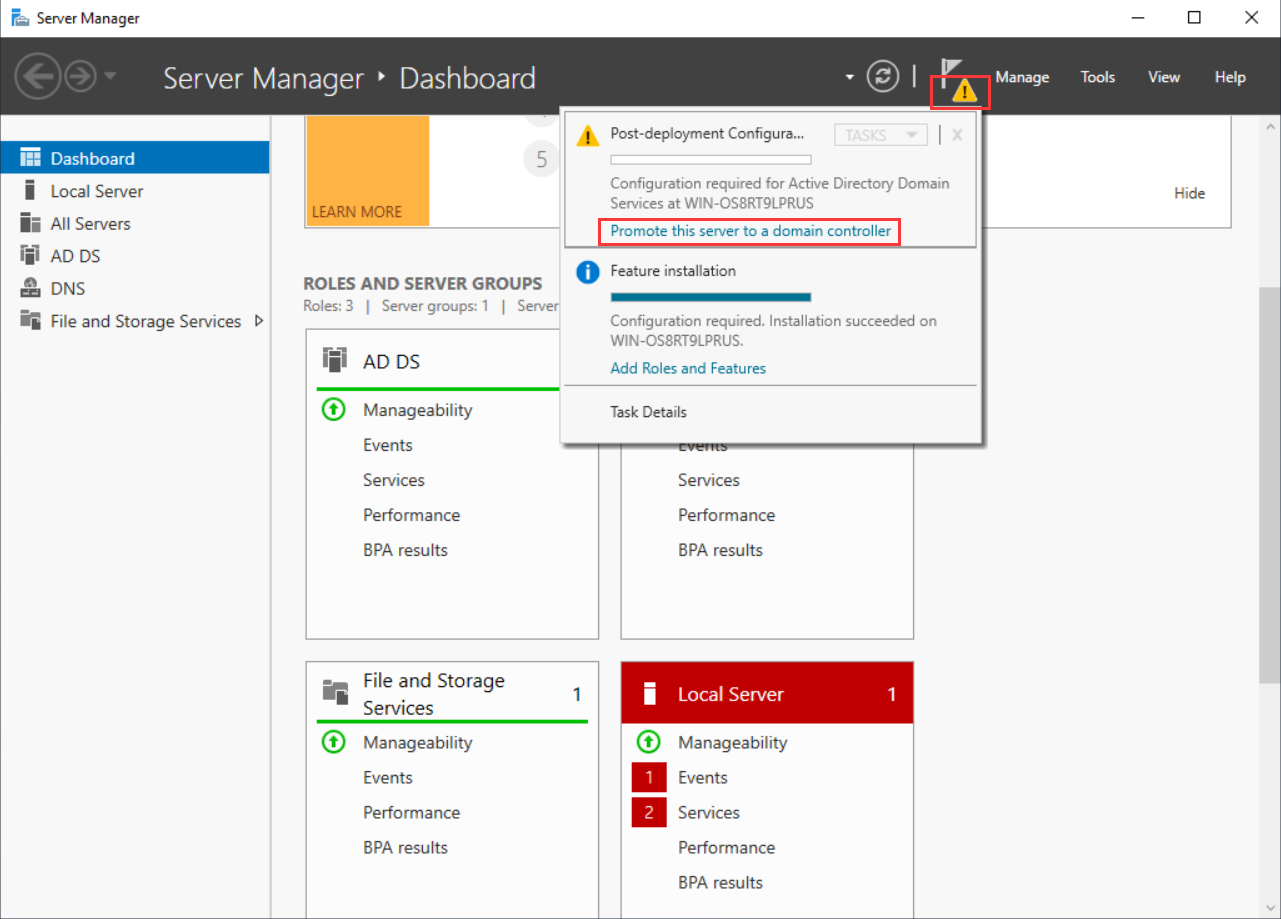
- Open Server Manager. On the Dashboard, click Promote this server to a domain controller.
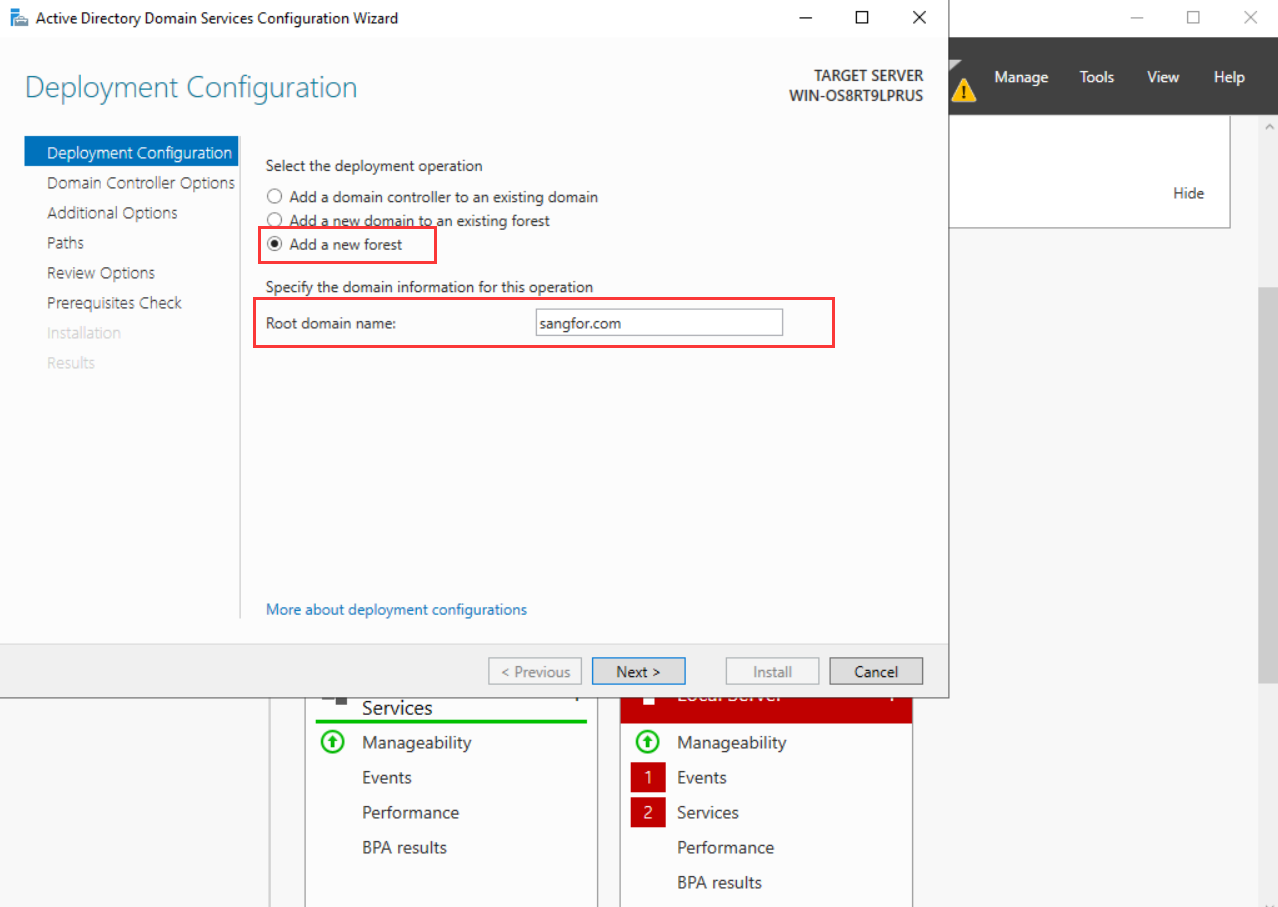
- After entering the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard, on the Deployment Configuration tab, select Add a new forest and specify the Root domain name for the AD domain, such as sangfor.com.
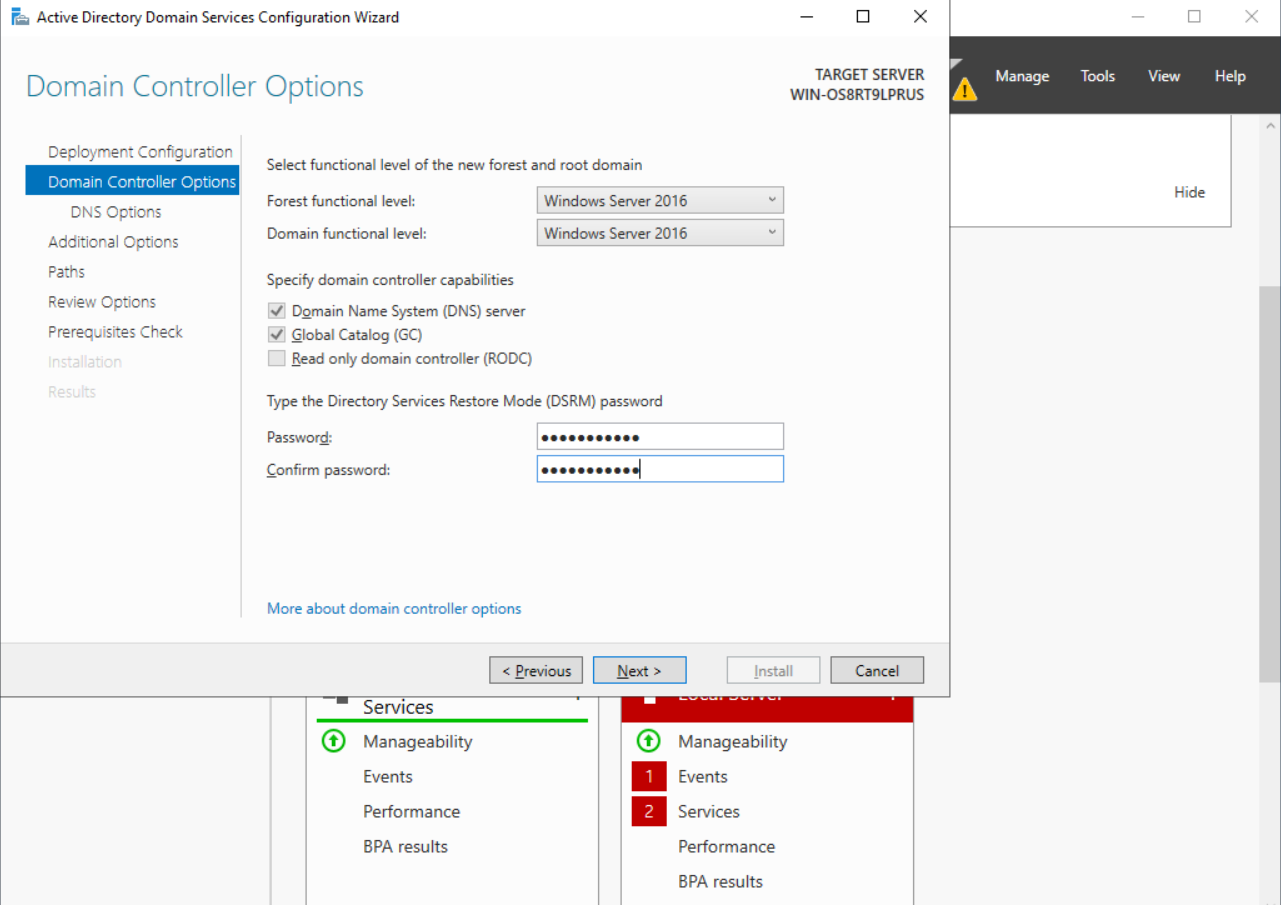
- On the Domain Controller Options tab, set a password, for example, @sangfortest.
- On the DNS Options tab, click Next to proceed.
- On the Additional Options tab, set The NetBIOS domain name. You can use the default NetBIOS name SANGFOR.
- On the Paths tab, click Next to continue.
- On the Prerequisites Check tab, click Install to begin the installation.
-
Wait for the equipment to install and deploy related functions.
-
After the installation is complete, the Windows Server will automatically restart.
-
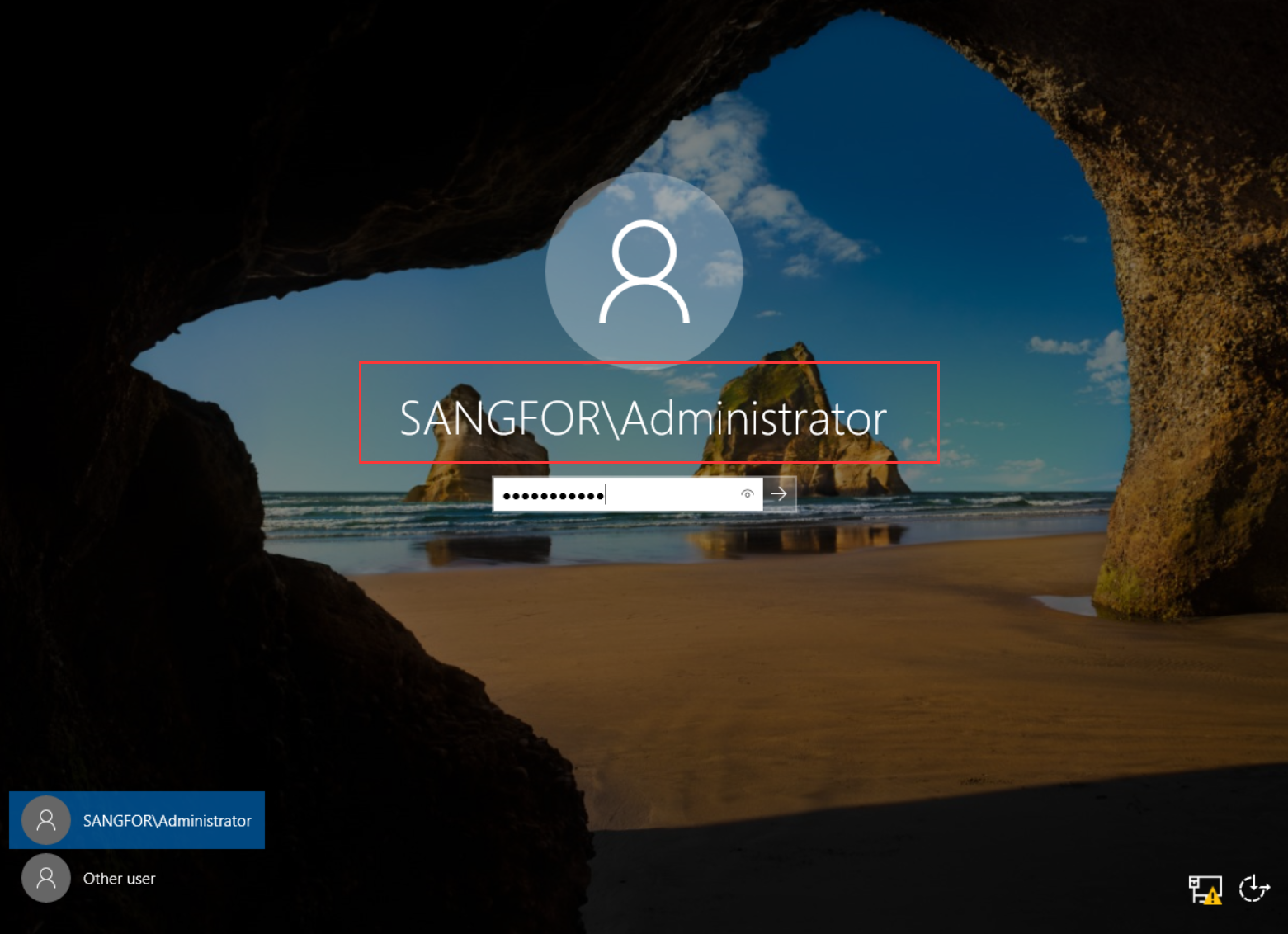
After the Windows Server restarts, you can see on the login page that the default local administrator, who logs in to the operating system, has become the administrator in the domain, and the login password is the same as the password of the local administrator account.
Create Usernames and Passwords for Other Users on the Domain
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
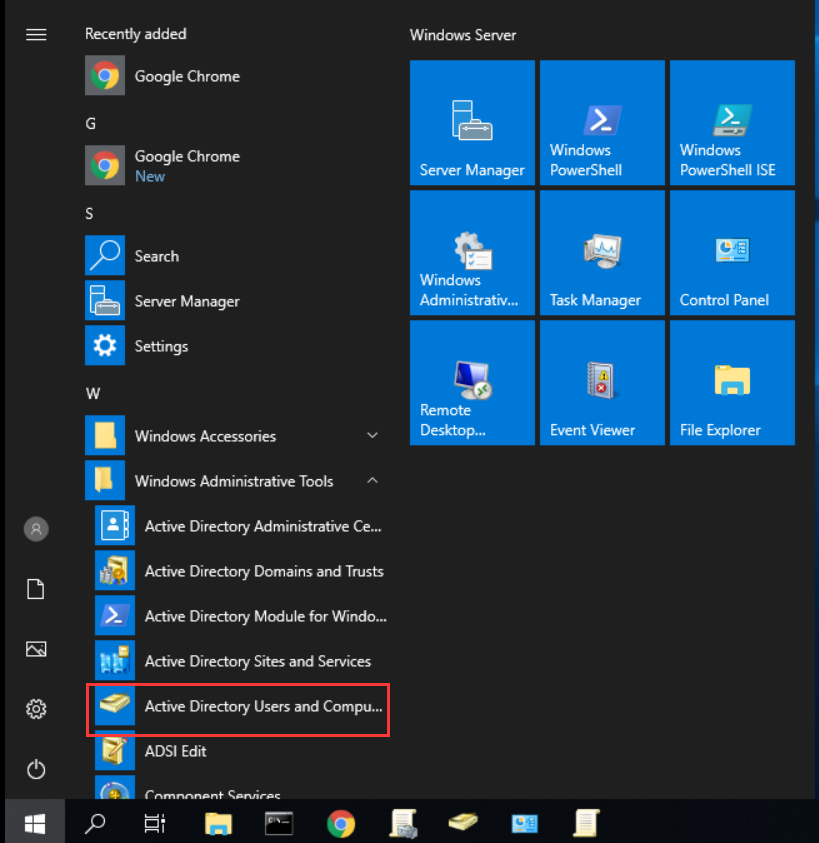
- To facilitate the management of users according to the company’s organizational structure, navigate to the domain name sangfor.com and expand it. Right-click and select New > Organizational Unit to create a logical container to represent a department. For example, create a department named Sangfor Tech.
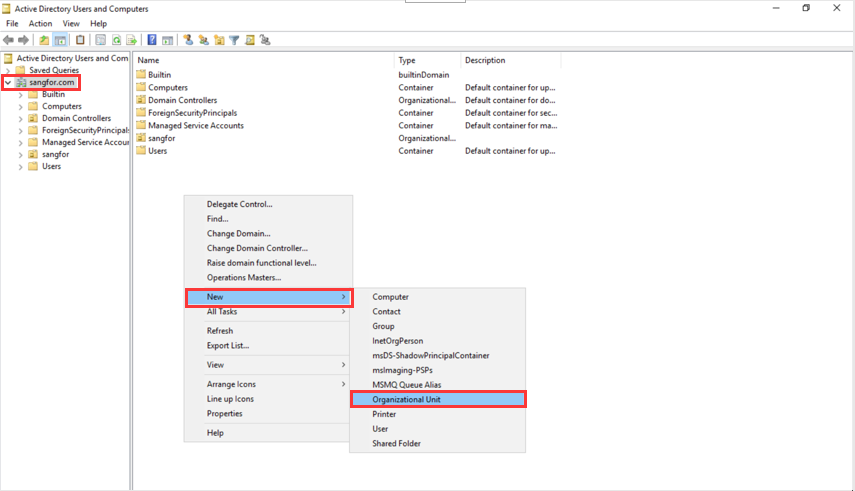
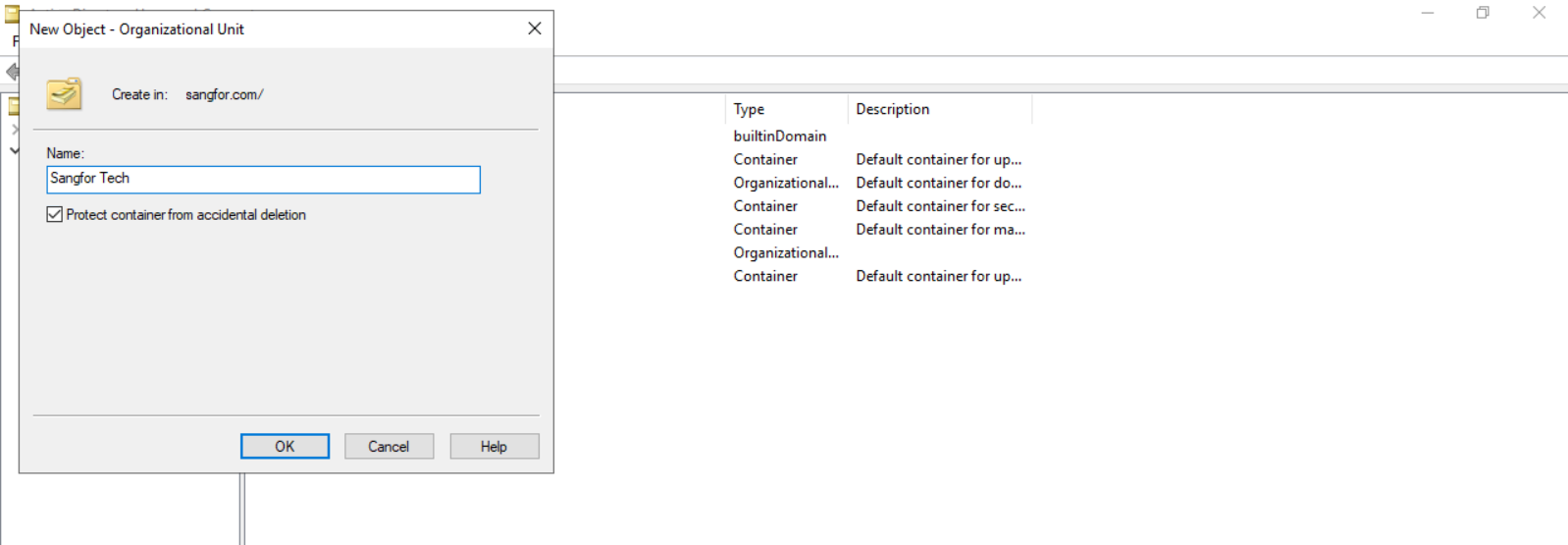
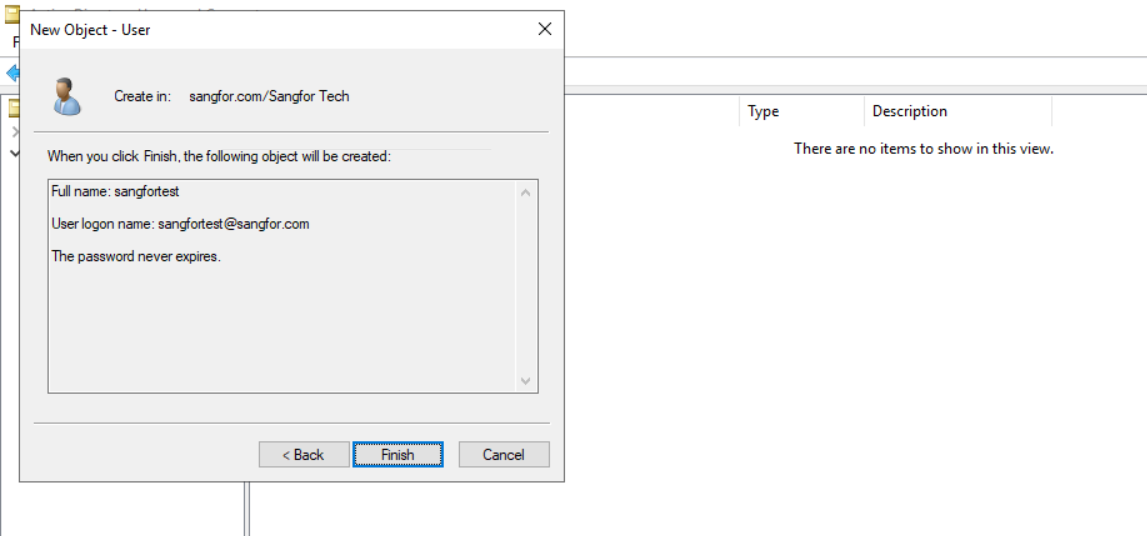
- Right-click the container, and select New > User to create a user in the container, for example, sangfortest.
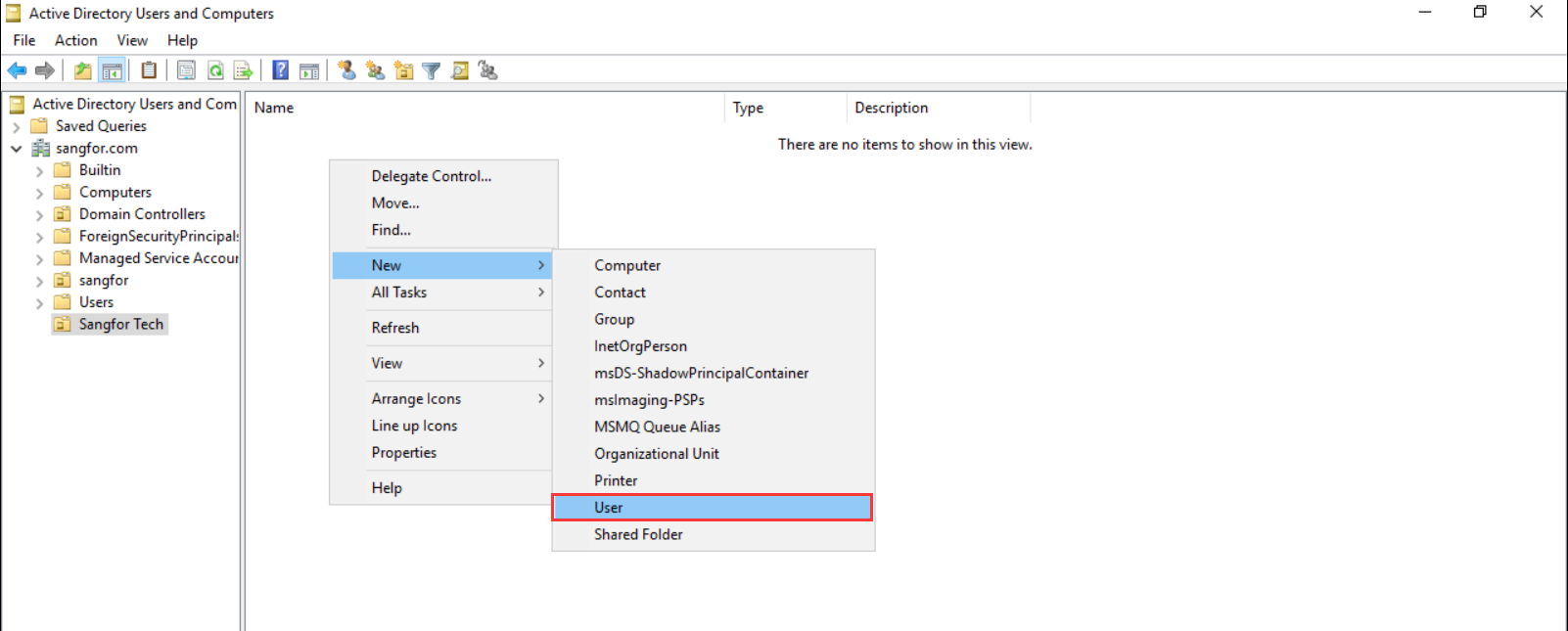
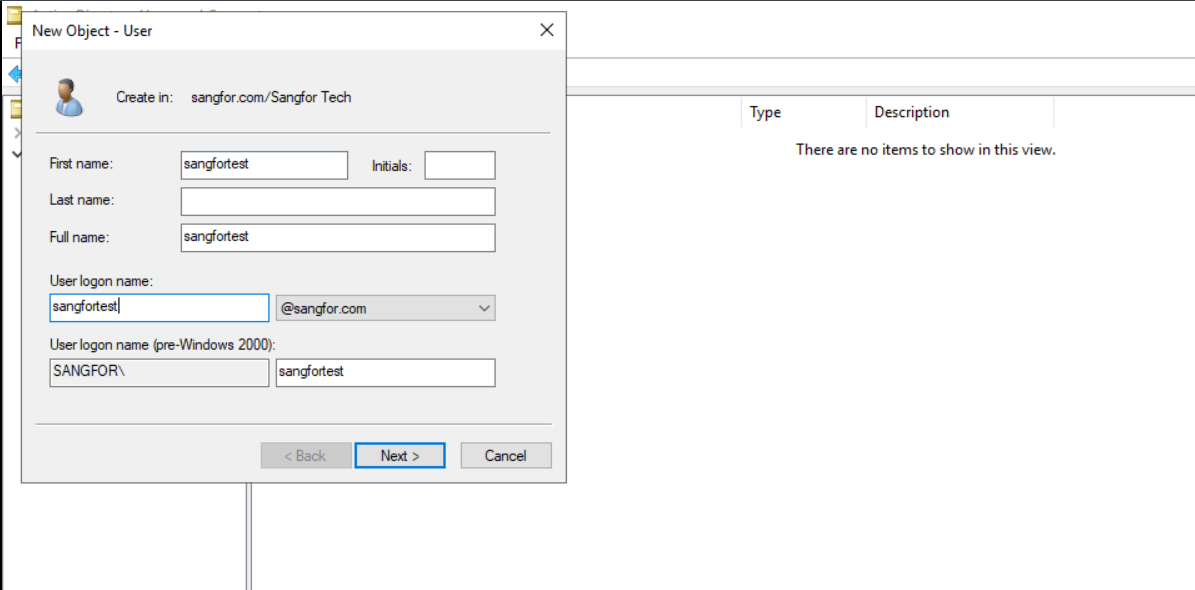
-
Set a login password for this user.
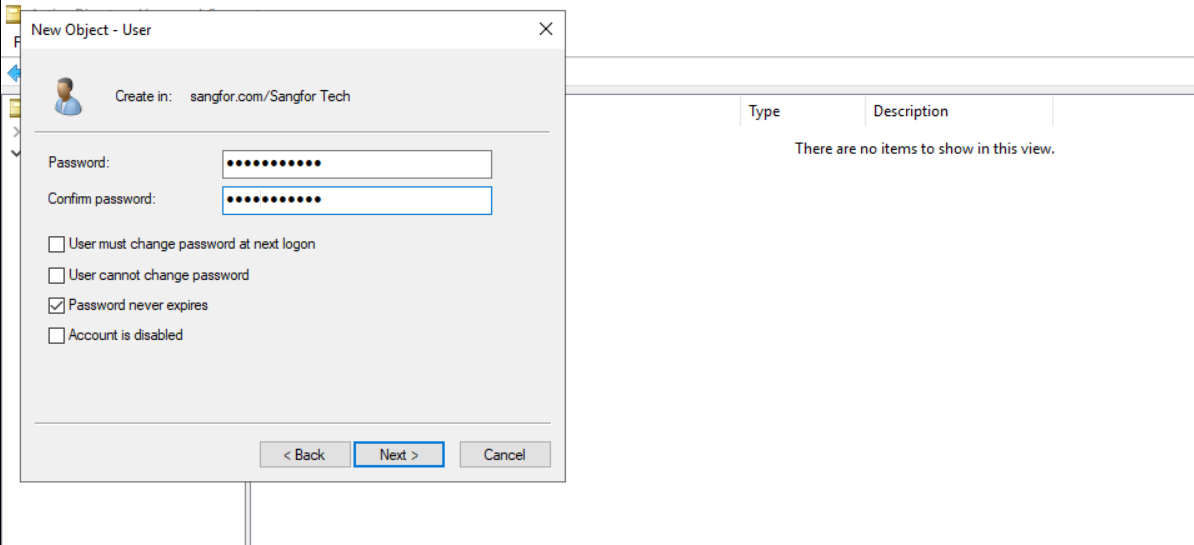
-
Click Finish to complete the settings for creating the user.
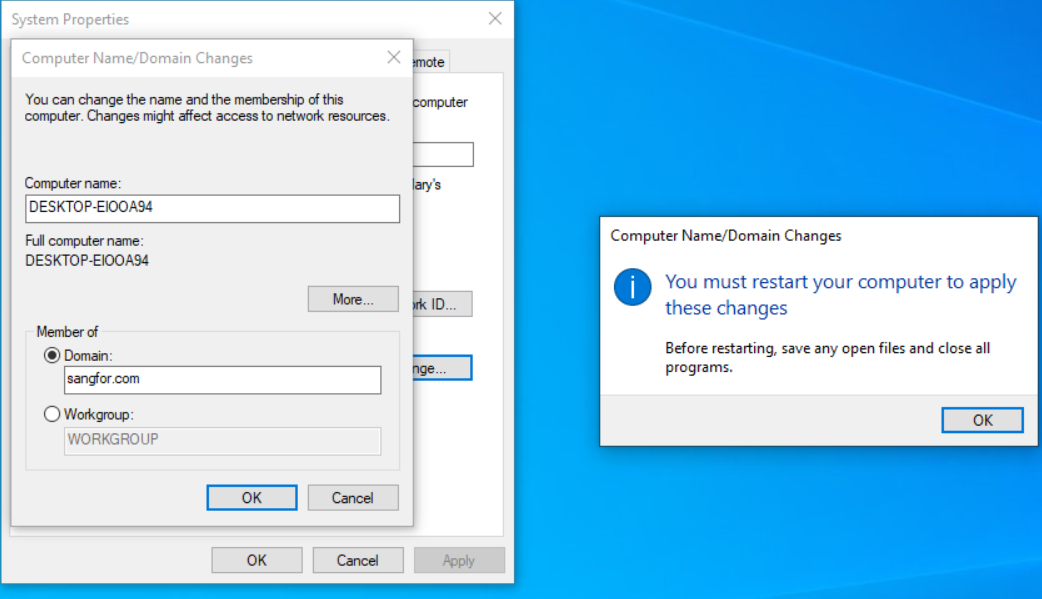
Join the PC to the Domain
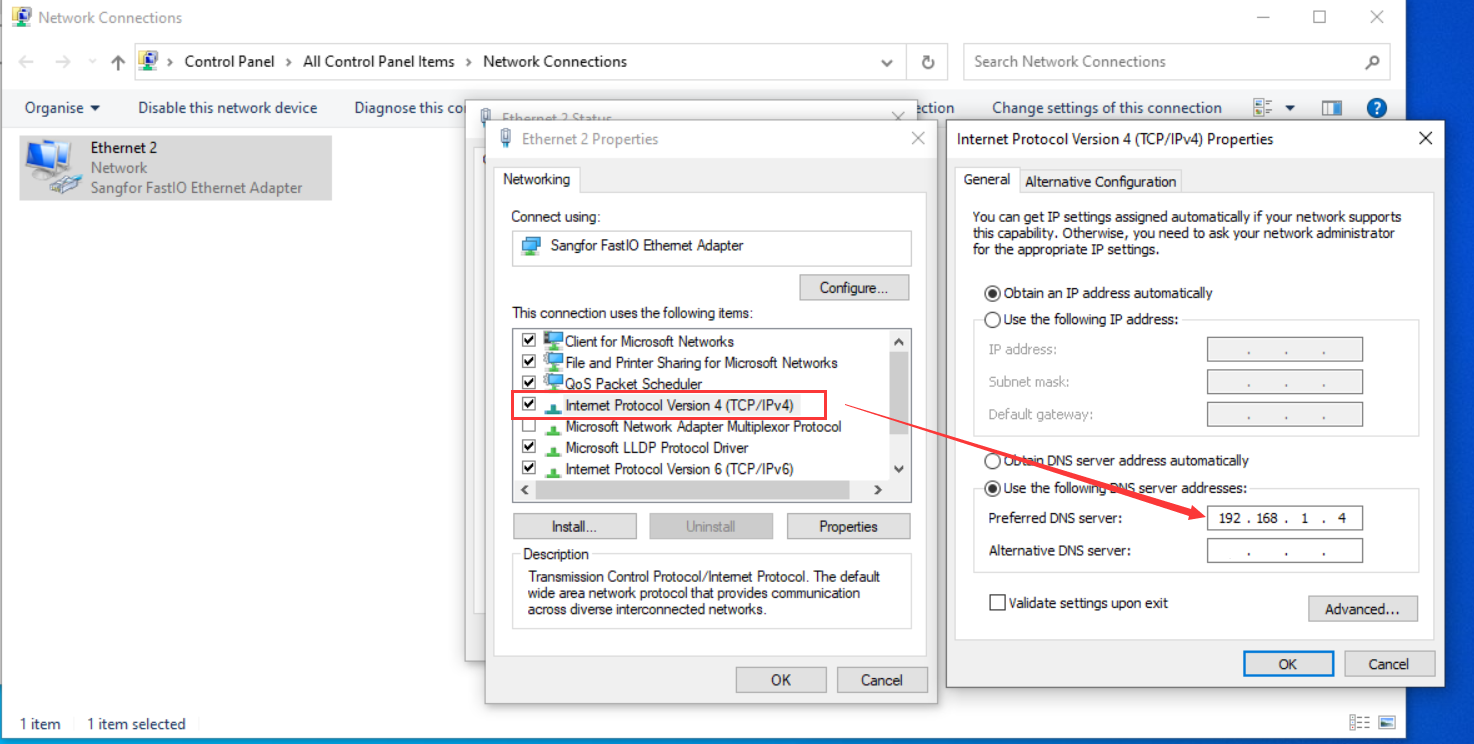
- Configure the PC’s network card, and set the DNS to the IP address of the domain control server: 192.168.1.4.
- Join the PC to the domain.
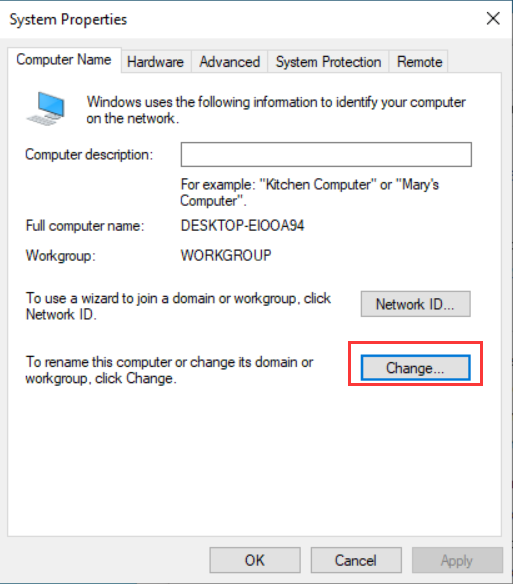
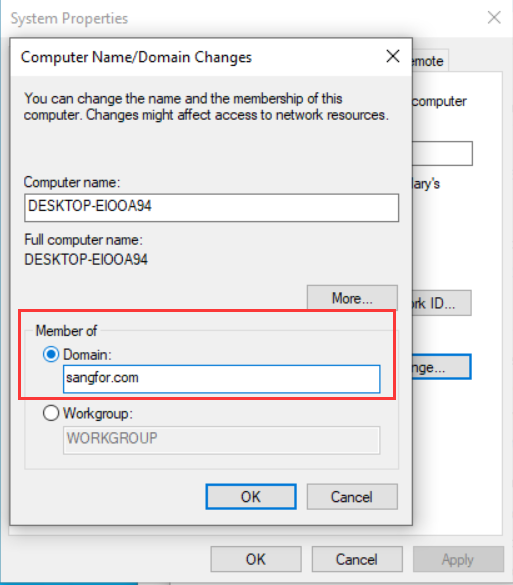
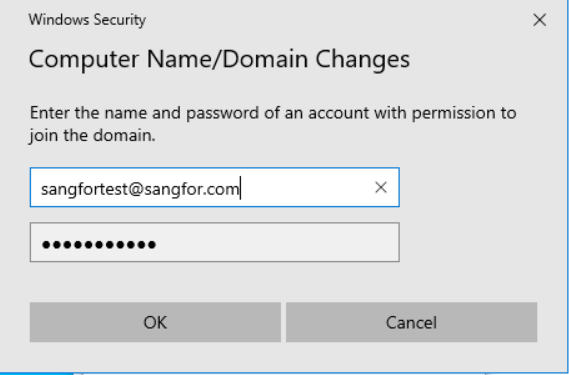
- In the process of joining the domain, you need to verify your identity. Use the user sangfortest created on the AD domain controller 192.168.1.4 for testing.
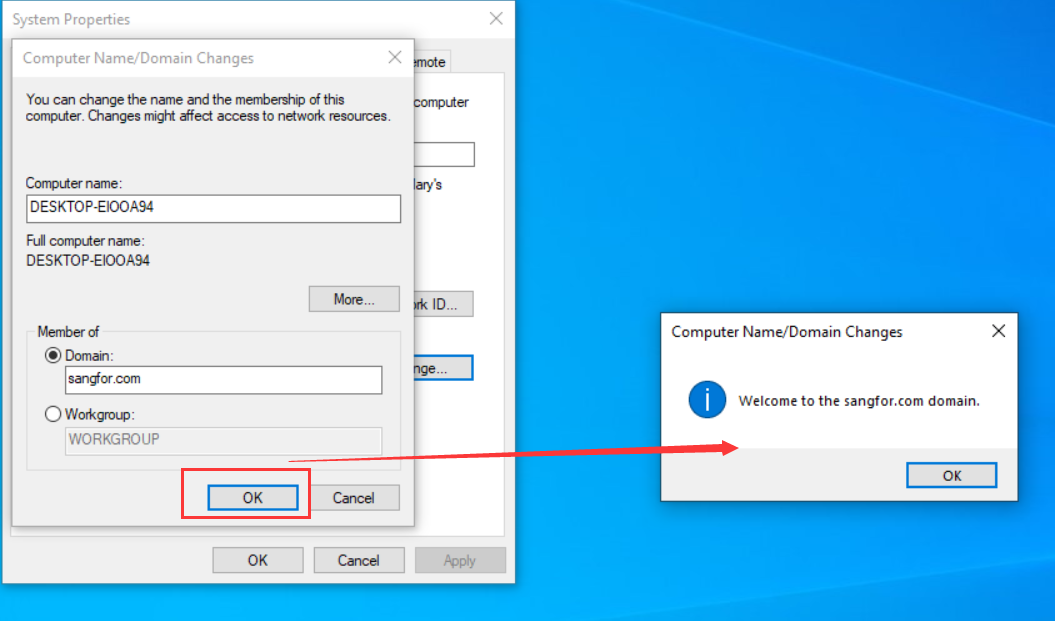
- After successfully joining the domain, you need to restart the PC.
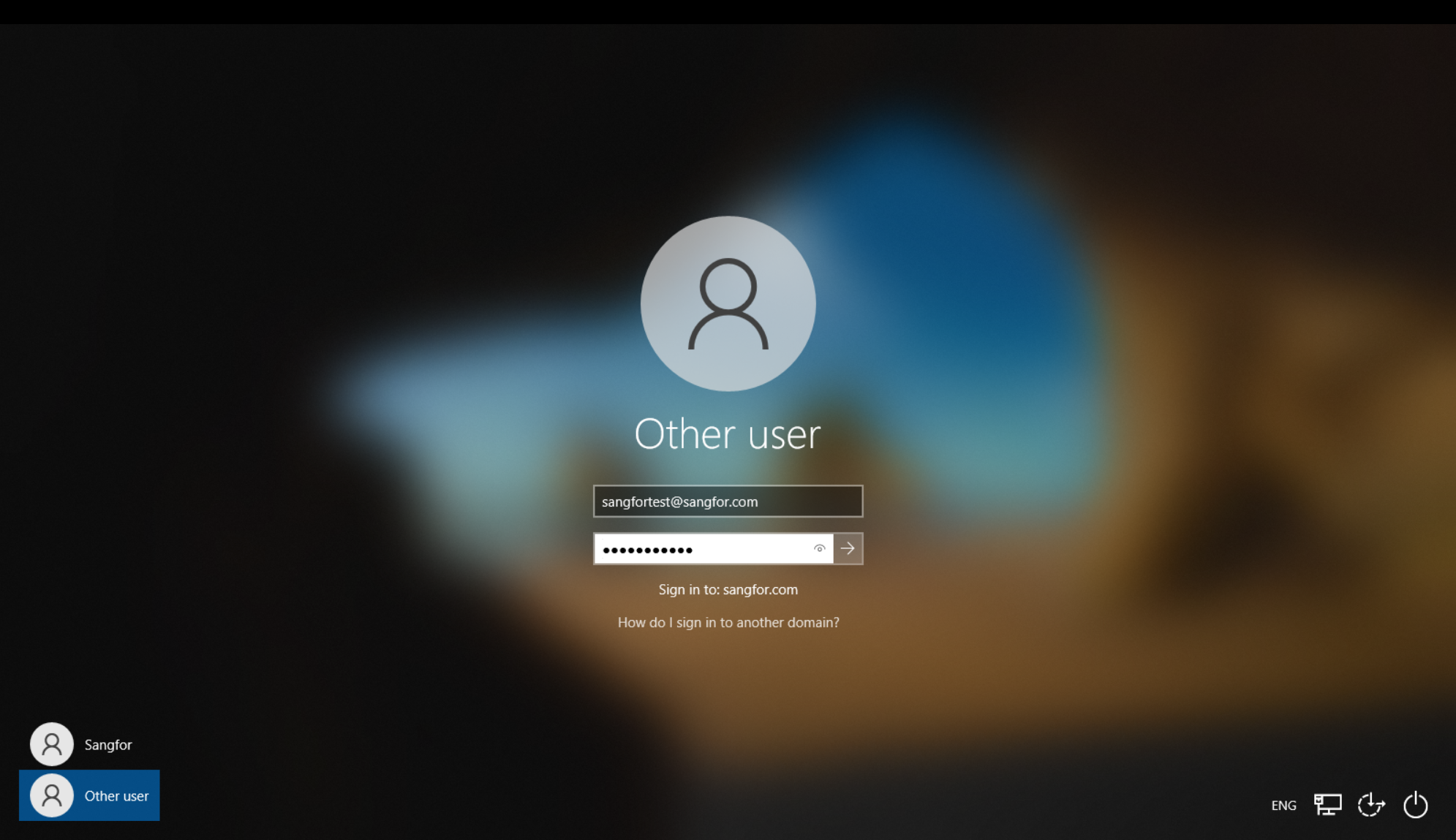
- After restarting, you will see the login page of the PC. Choose to use the domain account sangfortest to log in.
Configuration in IAG
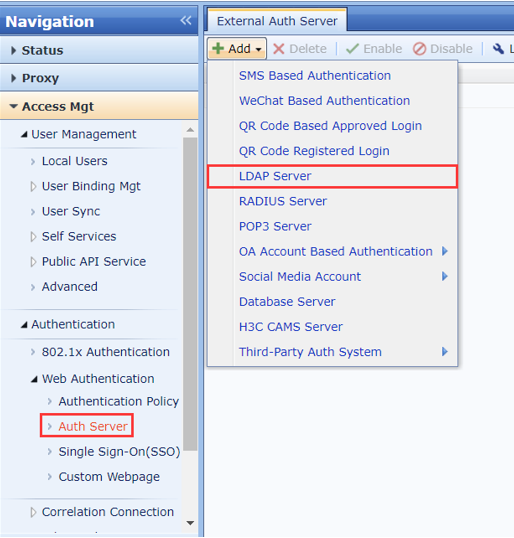
Add LDAP Server
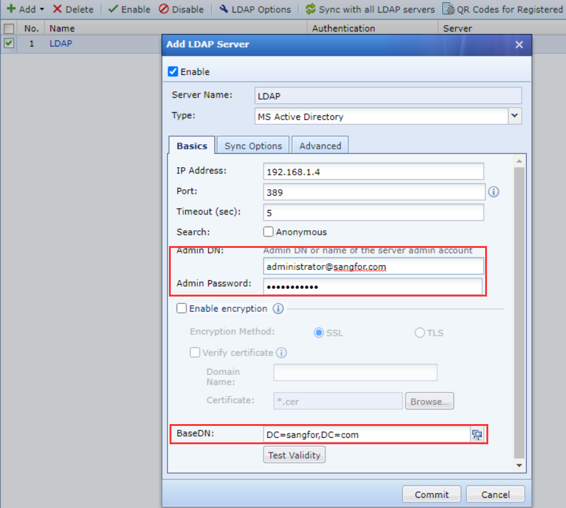
- On the IAG web console, navigate to Access Mgt > Authentication > Web Authentication > Auth Server. Click Add > LDAP Server to add a Microsoft AD server on IAG.
- Pay attention to entering the username with the complete domain name in the Admin DN field. You can use the newly created sangfortest@sangfor.com, but it is usually recommended to use the administrator account to avoid the lack of permissions that cause IAG to fail to interact with the Microsoft AD server. You can choose sangfor for the BaseDN.
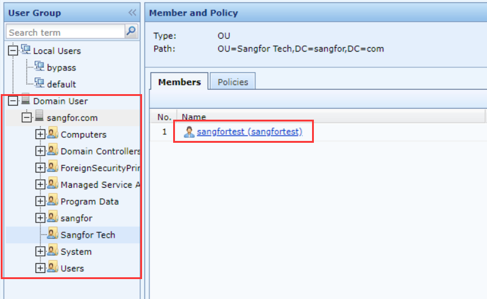
- If IAG and AD server can interact normally, navigate to Access Mgt > User Management > Local Users. You can see that IAG has obtained the domain user information of the AD server, including the user sangfortest we created earlier.
Configure Script SSO on IAG and AD Server
- On the IAG web console, navigate to Access Mgt > Authentication > Web Authentication > Single Sign-On(SSO) > MS AD Domain. Select Enable Domain SSO and Obtain login profile by executing logon script through domain to turn on script SSO. Here you need to configure a secret Shared Key for authentication, for example, 123456.
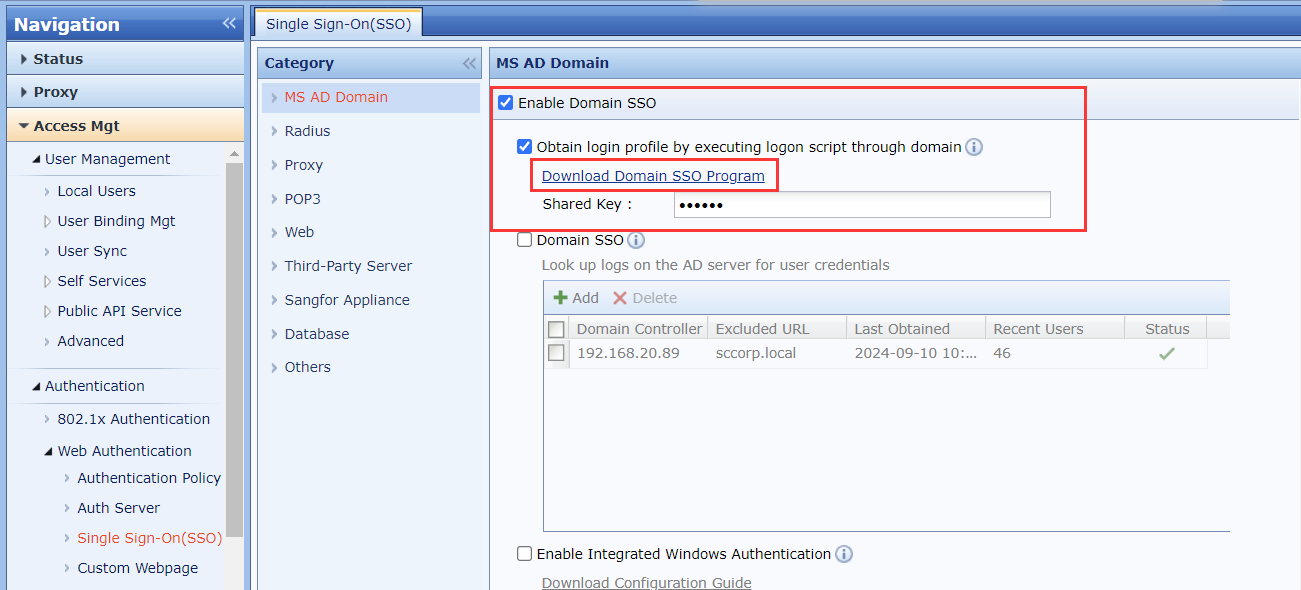
- Click Download Domain SSO Program to download the program from the page, including the logon script and logoff script.
Configure the Logon and Logoff Scripts on the AD Server
- Open Run, type gpmc.msc in the Run dialog box to open the Group Policy Management console.
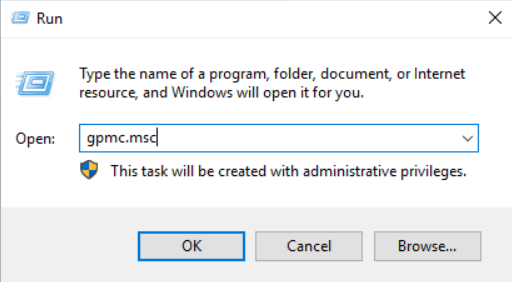
- Right-click the newly created Sangfor Tech container, select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here… to create a Group Policy Object (GPO).
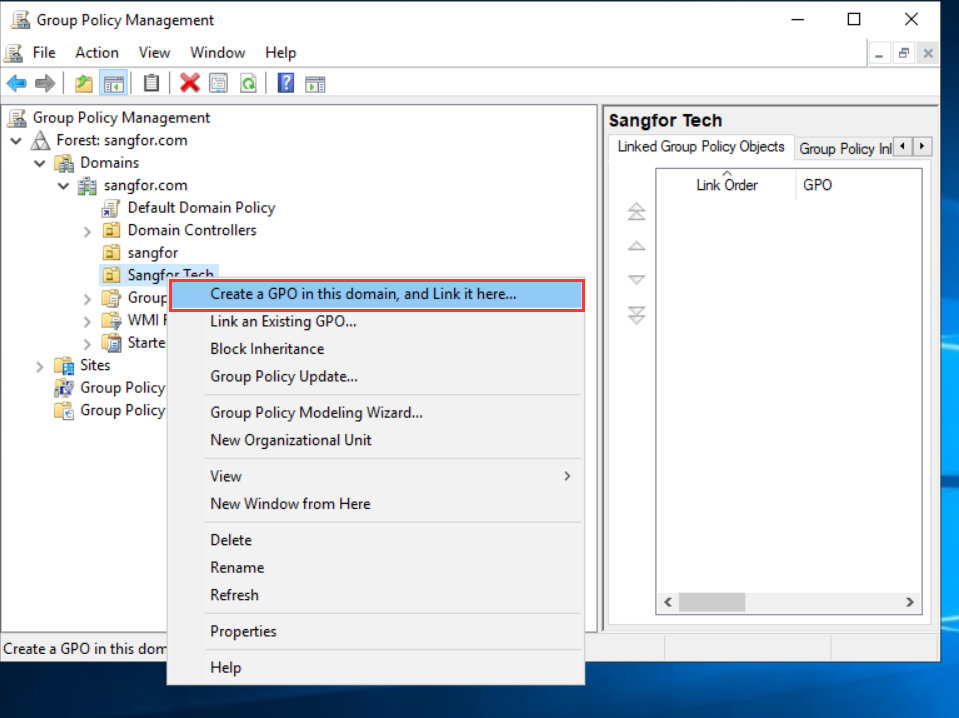
-
Create a name for the GPO.
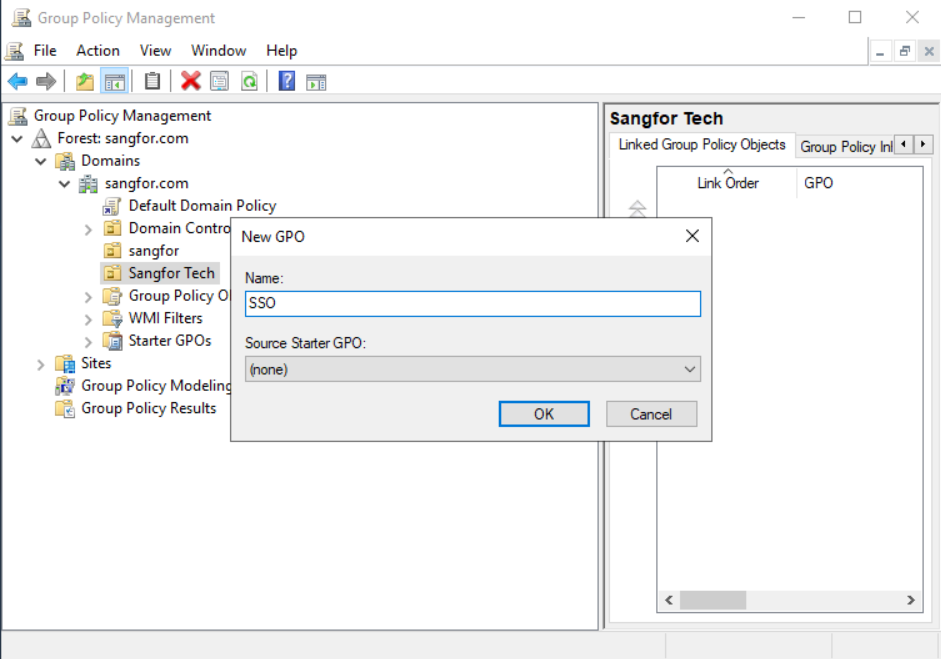
-
Right-click the new GPO, and select Edit… to edit it.
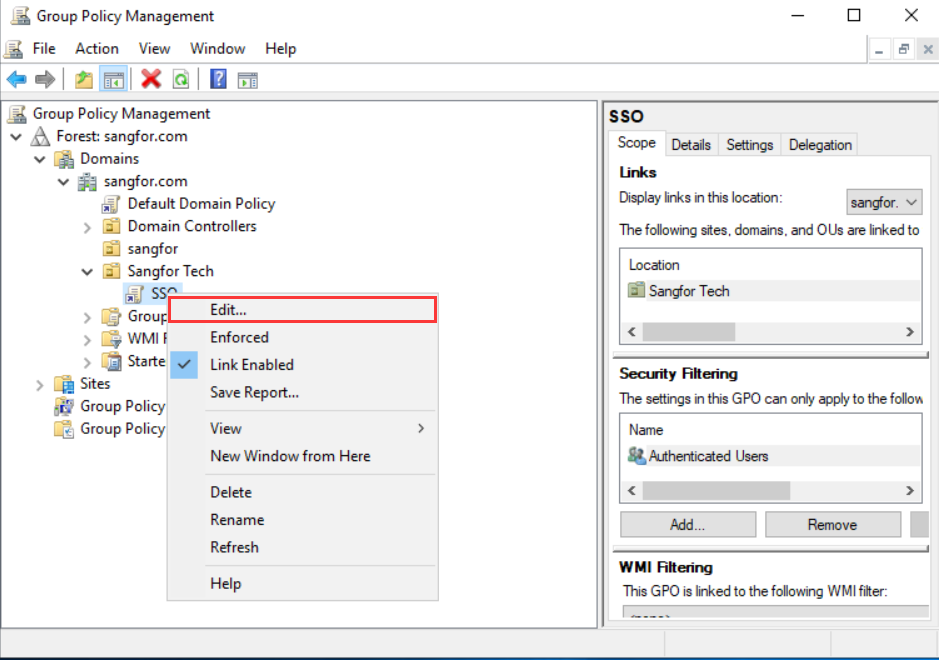
- On the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to User Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Scripts (Logon/Logoff), and select the Logon script.
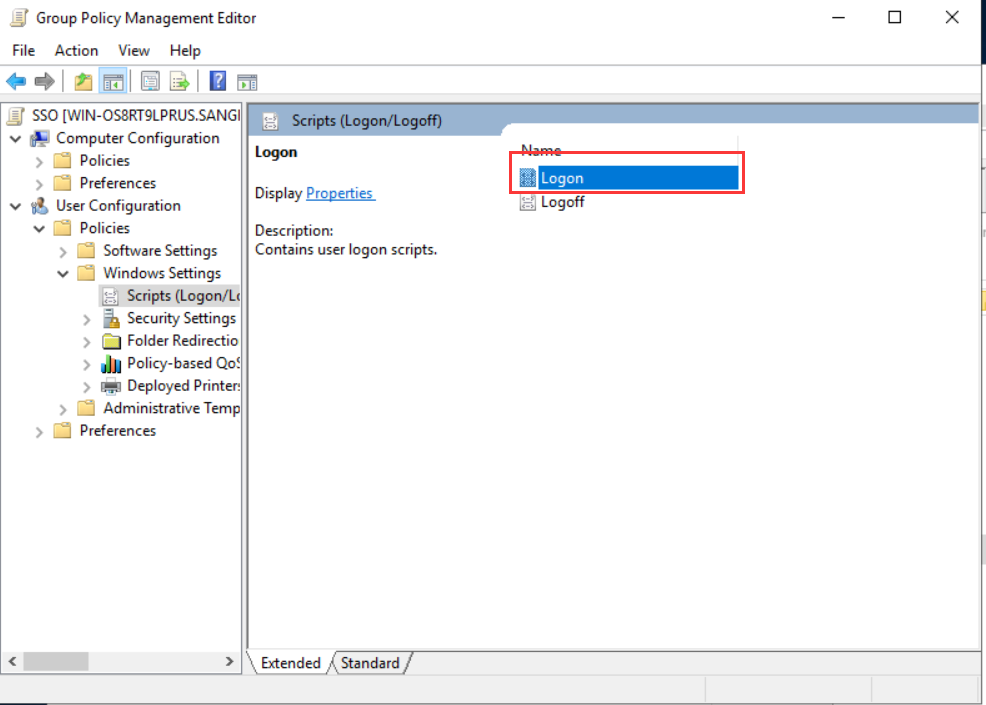
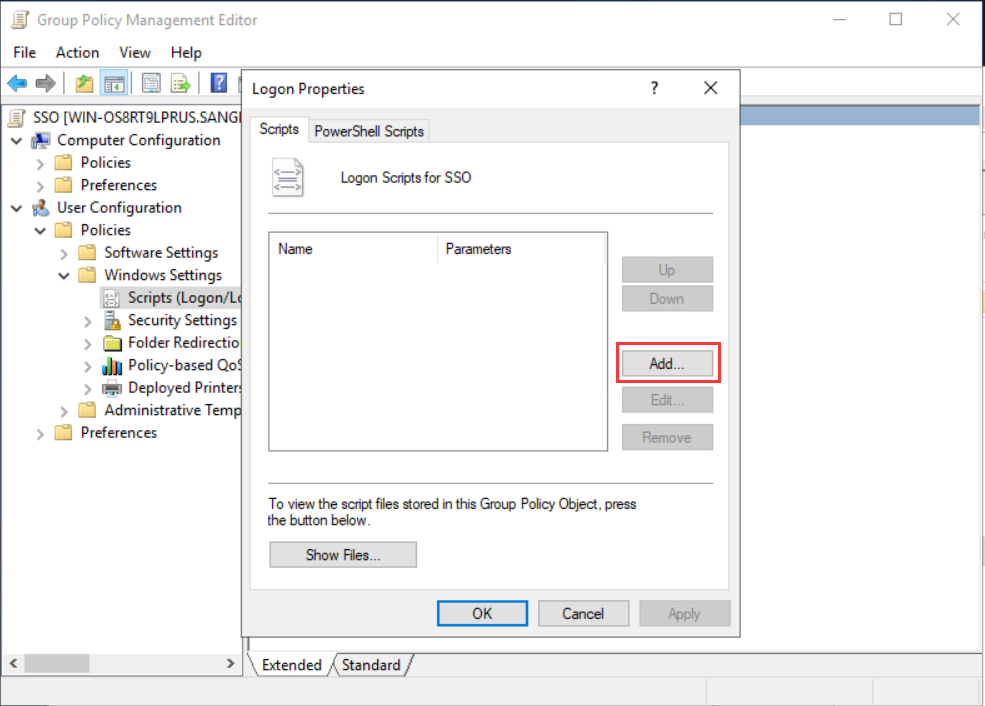
- In the Logon Properties dialog box, click Add, and then select Browse to copy the Logon script downloaded from the IAG web console to the designated path.
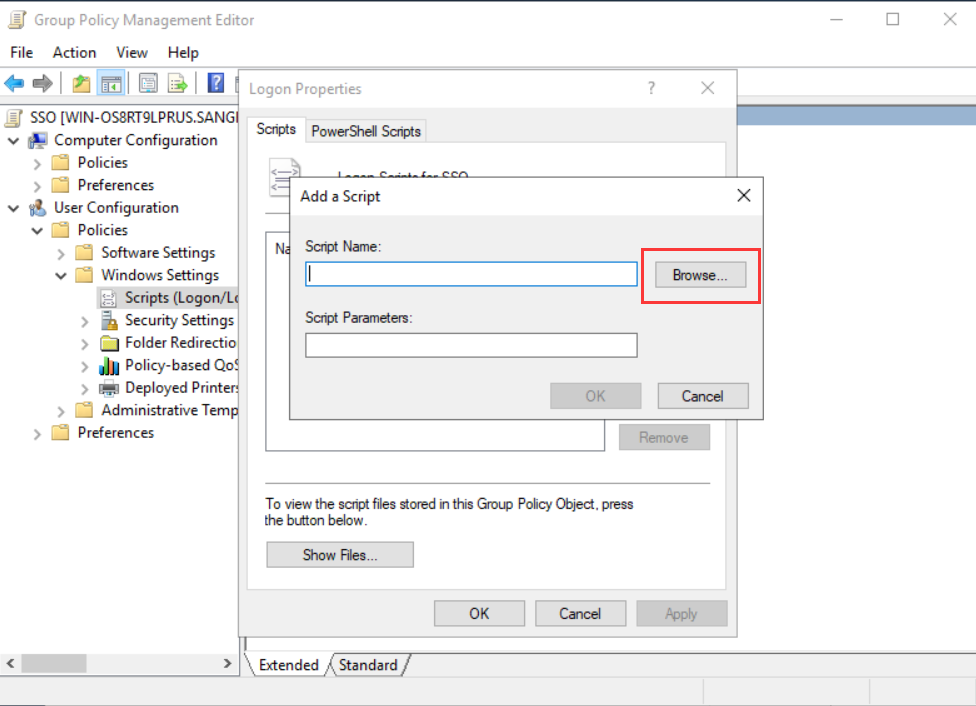
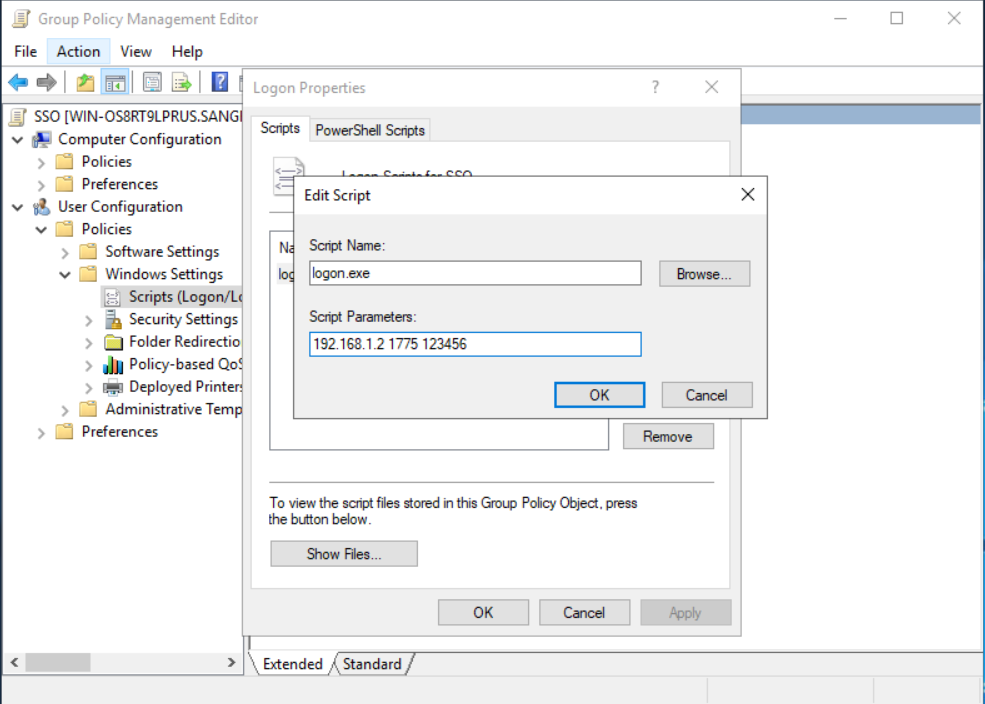
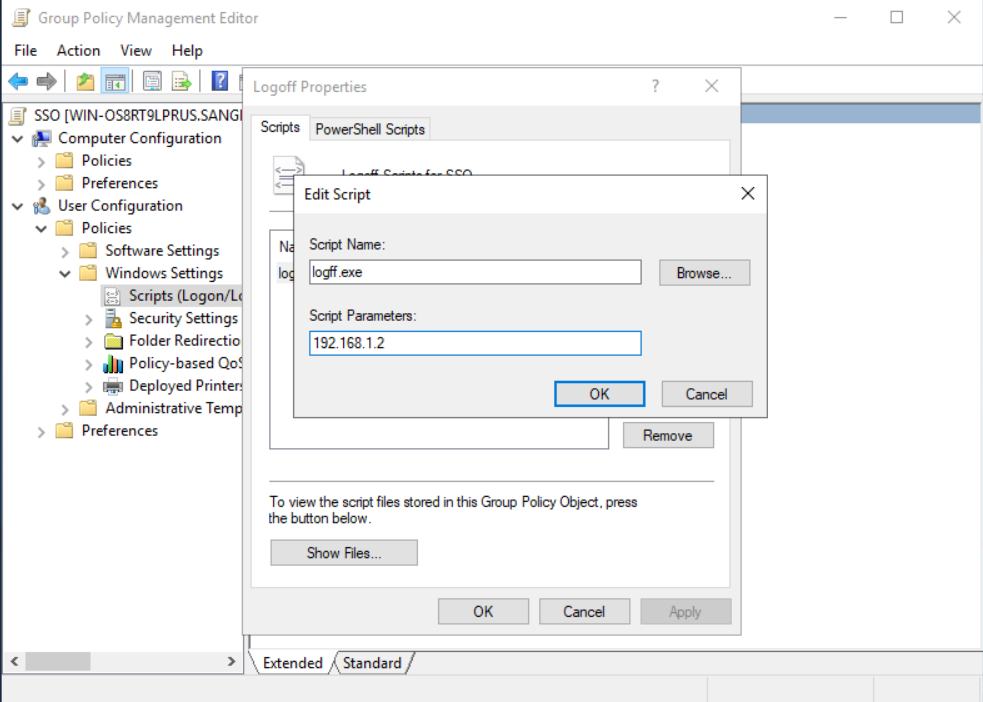
- In the Edit Script dialog box, set the Script SSO parameters. Specify the IAG IP address 192.168.1.2 and the UDP port number 1775, which is used to accept the authentication information actively transmitted by the PC. Then, fill in the secret shared key 123456 that we configured on the IAG web console.
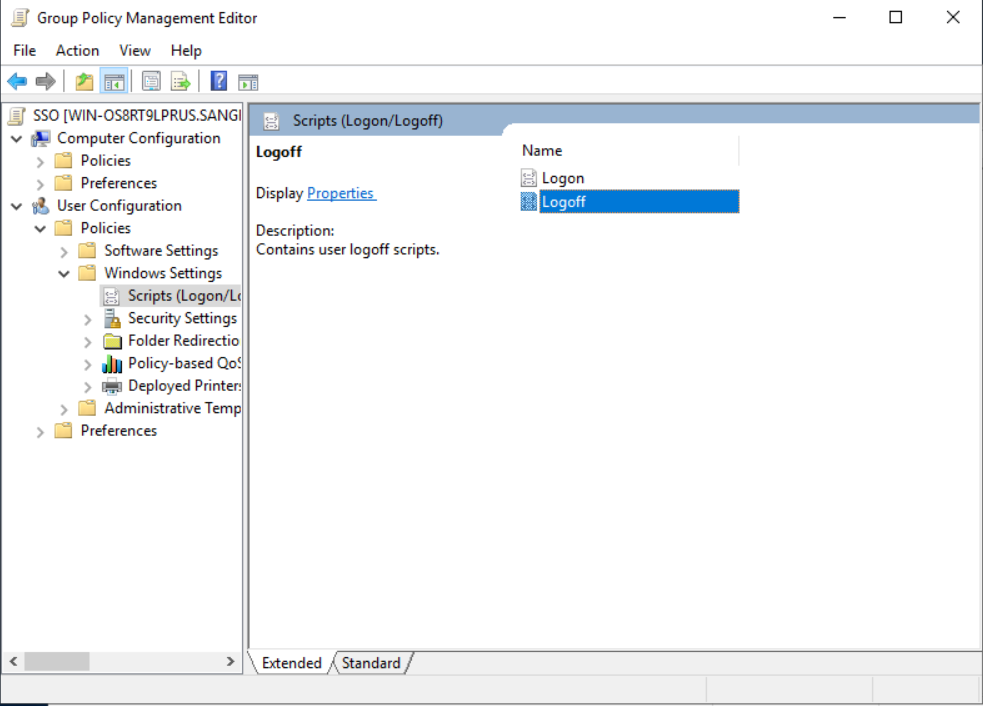
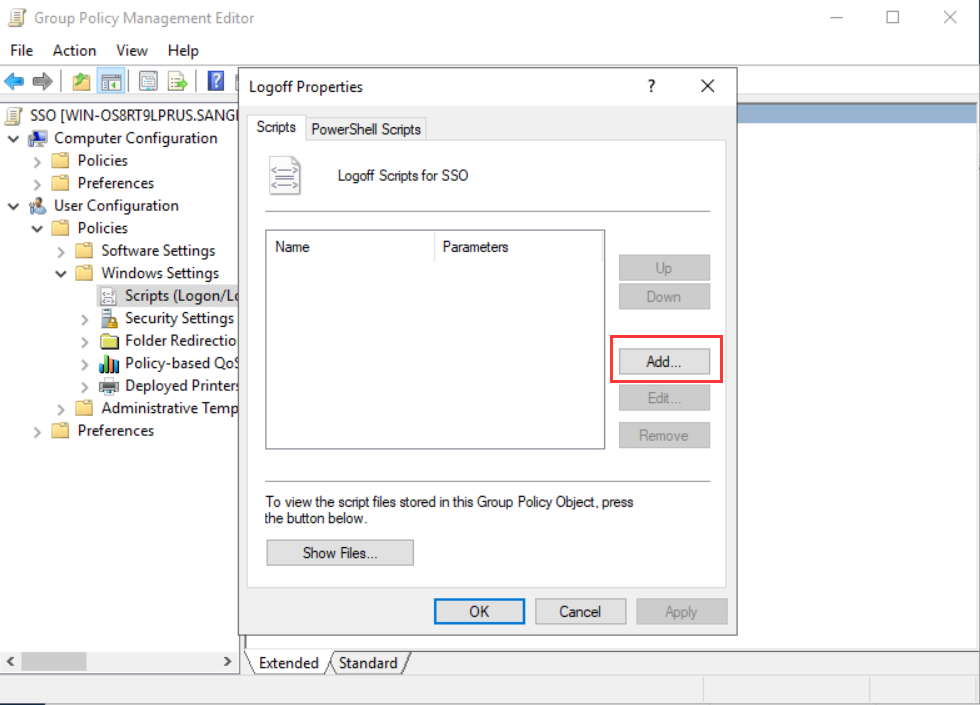
- For the Logoff script, copy the one downloaded from the IAG web console to the designated path, and fill in the Script Parameter as the IAG’s IP address 192.168.1.2.
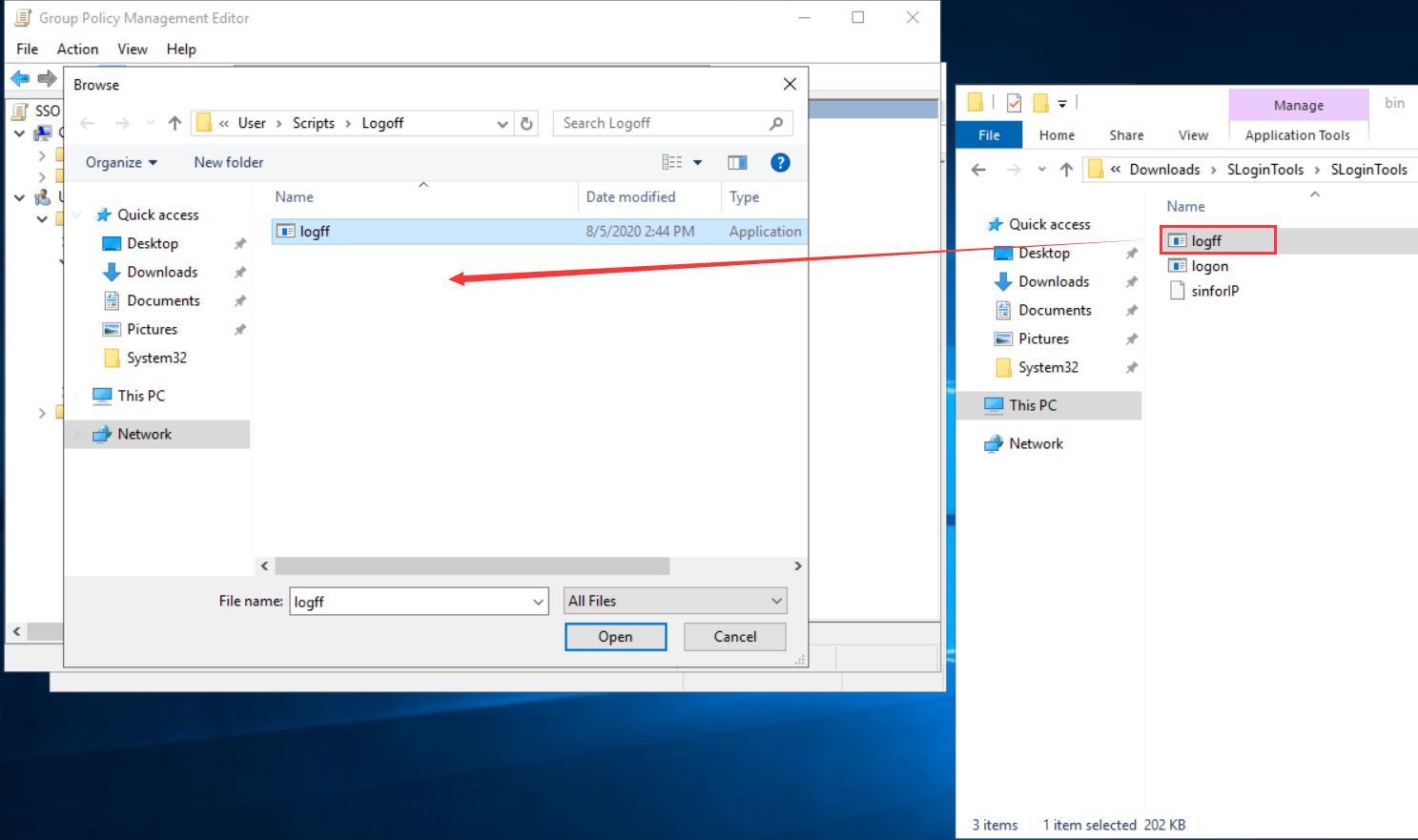
- After modifying the AD domain server, run the gpupdate/force command in CMD to forcibly refresh all group policies.

Configure Authentication Policy on IAG
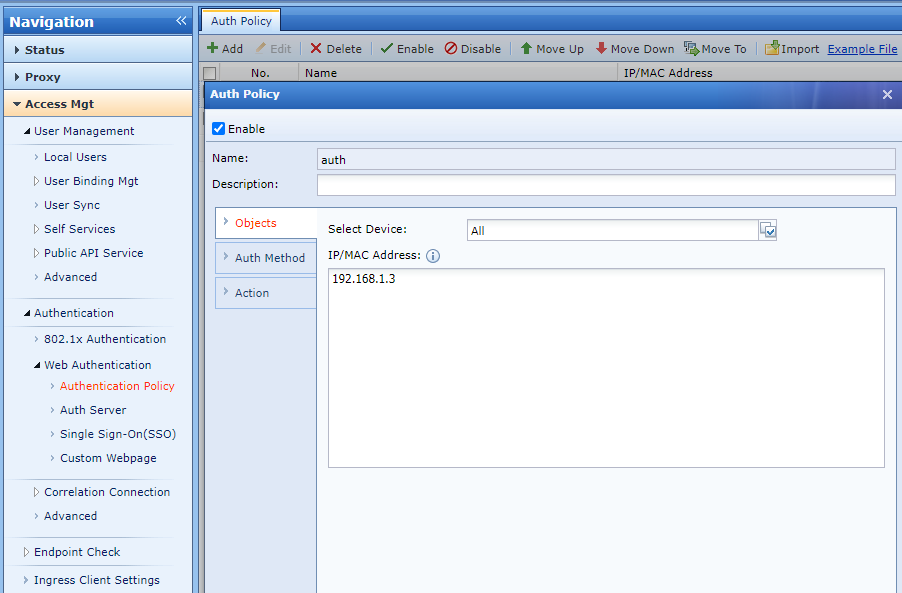
- Navigate to Access Mgt > Authentication > Web Authentication > Authentication Policy. Click Add to enter the Auth Policy dialog box. On the Objects tab, set the scope of the authentication policy in the IP/MAC Address field, meaning which IP address should match the authentication policy.
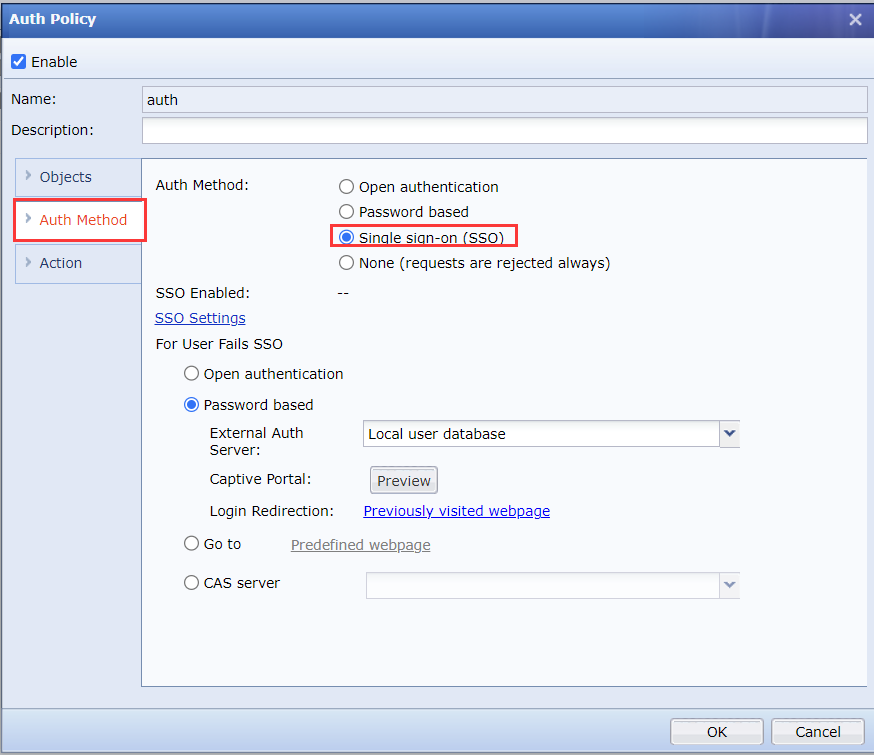
- On the Auth Method tab, select Single sign-on (SSO) for the Auth Method.
- Restart the user’s PC and log in to the PC with a domain account. You can see that the user is online in IAG and the authentication method is SSO on the Status > Users > Online Users list.

Precautions
- The strict security mechanisms or firewall of Windows Server may prevent other devices from obtaining relevant data from the AD Server. Adjust the security policy if necessary.
- UDP port 1775 is required for script SSO. Ensure that the PC can reach the IAG on port 1775.