[AF] Destination address mapping is unavailable, but bidirectional address mapping is normal: Layer 3 conflict causes
Problem Description
Layer 3 AF routing mode is deployed at the egress, and services are released to the outside through telecommunications lines.
One day, it was suddenly discovered that users of the mobile 4G Network could not access the services released to the public, while other Network were normal.
Process——
-
First check the fault phenomenon. Internet users can access the service normally through China Telecom fixed lines, China Unicom lines, and China Telecom 4G Network. Only China Mobile 4G Network cannot access the service. It is preliminarily determined that the service access of China Mobile 4G network is abnormal.

2.png (14.07 KB) -
Testing with a computer on a 4G Network revealed that the business public network address could be pinged, but the telnet business public network address port was blocked.
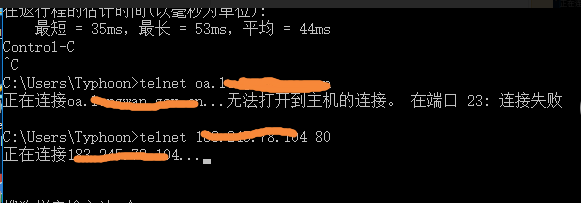
1.png (10.7 KB) -
Compare the routes of normal access and abnormal access through tracert, and find that when abnormal access occurs, Layer 3 to the AF internal network port and cannot be accessed.
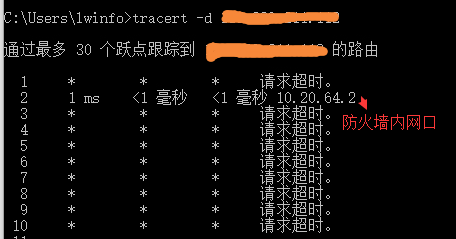
5.png (13.43 KB)
Suspecting that there is an internal abnormality, turn off [IPS Policies], [content security Policies], and [Web App Firewall Policies] and start direct test on the device.
Or not.
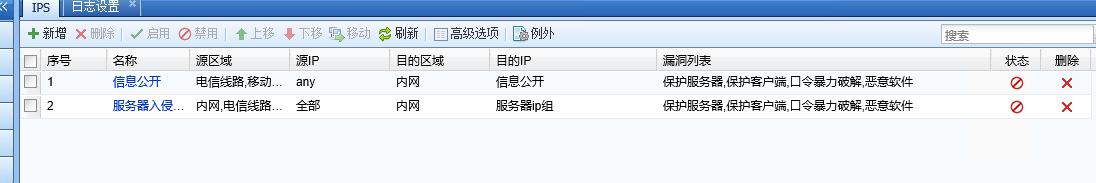
7.png (23.54 KB)
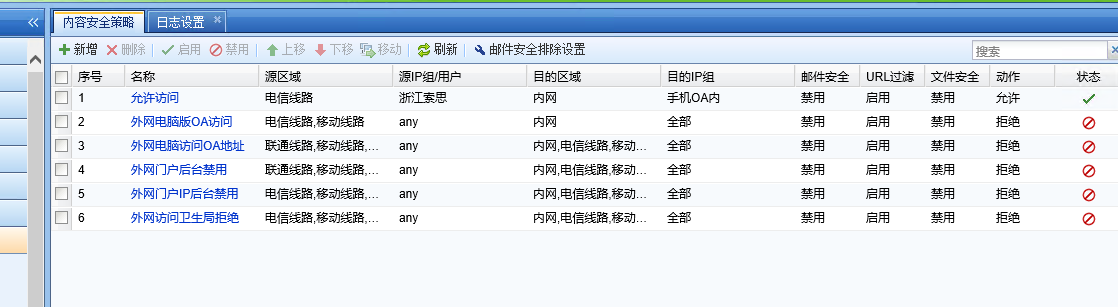
6.png (54.52 KB)
6.png (63.5 KB)
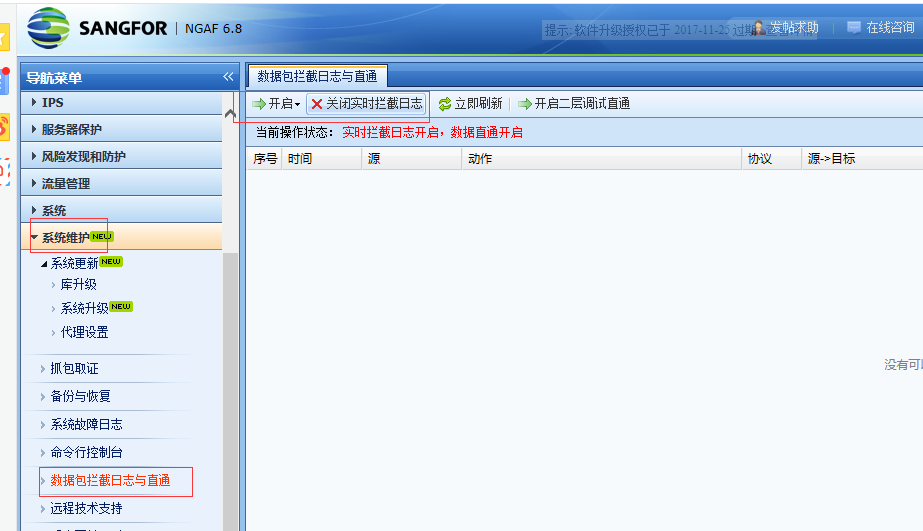
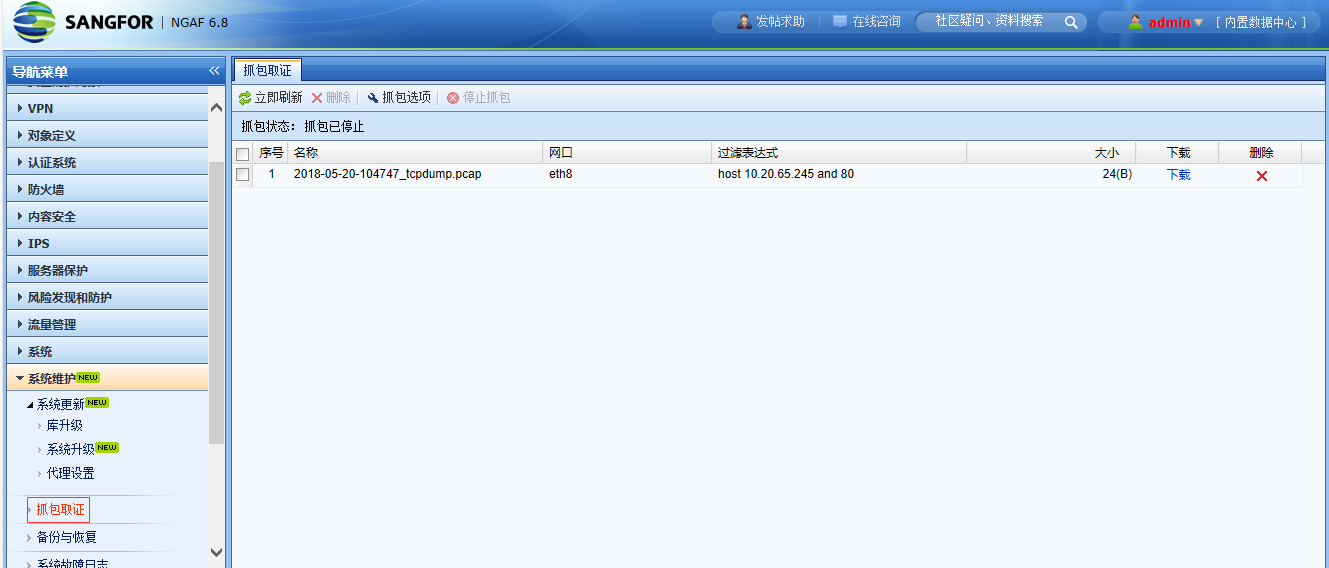
4. Set up the intranet port to capture packets in the console [Maintenance] – [Packet Capture and Forensics]. After capturing, analyze it through Wireshark and find that the device has sent request packets but has not received response packets.
8.png (75.76 KB)
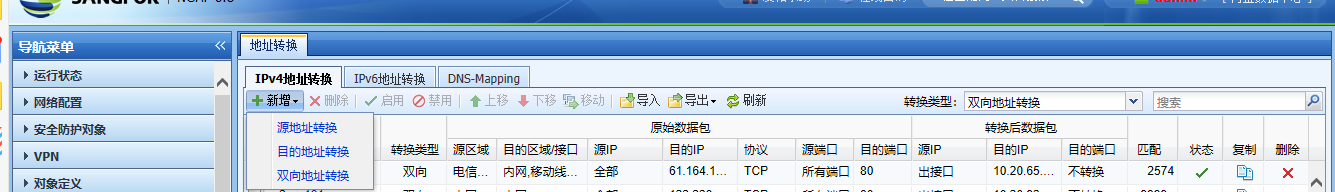
5. [Local] – [NAT] Change the Destination NAT to Bidirectional NAT. Access through mobile 4G is normal; it is suspected that the Layer 3 abnormal.
9.png (61.22 KB)
6. Check AF Layer 3 [Network Configuration] – [Routing] – [All Routes] and find that the public Network Segment starting with 113 is learned at the intranet port, and the public network address of the mobile 4G Network is the segment starting with 113, resulting in a Layer 3 conflict; the 113 public Network Segment in the AF intranet direction is learned through dynamic Layer 3 BGP. Check the intranet BGP Layer 3 and find that the intranet mistakenly publishes the 113 public Network Segment. After the intranet deletes the address segment, Network returns to normal.
Root cause
The internal Network publishes the public network address as a private network Layer 3, resulting in Layer 3 conflicts and abnormal packet returns.
solution
Change the destination address mapping on the AF device to bidirectional address mapping; or adjust Layer 3 to resolve Layer 3 conflict.
**Principle: The source IP of the destination Destination NAT is accessed using the public network IP. The Bidirectional NAT will convert the source NAT into the intranet port address of af to access the intranet server. **
Suggestions and Conclusion
Although this failure is not caused by the AF device, it allows us to have a clearer understanding of Destination NAT and Bidirectional NAT.
**If the Destination NAT port does not work, but the bidirectional NAT is successful, it is usually due to limitations of the intranet intermediate device or the server itself, or an intranet Layer 3 problem. **
Original Link
https://support.sangfor.com.cn/cases/list?product_id=13&type=1&category_id=347&isOpen=true